The Outermost Layer Of The Kidney
listenit
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
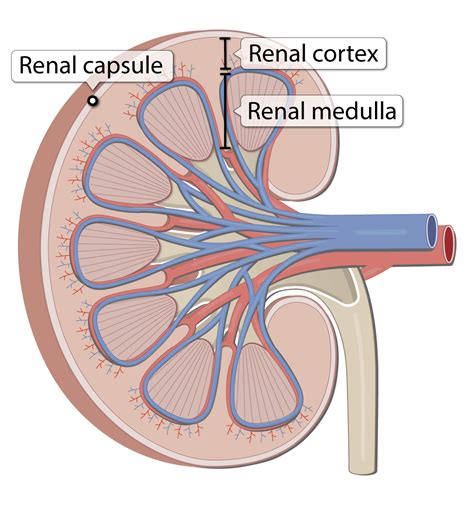
Table of Contents
The Renal Capsule: Unveiling the Outermost Layer of the Kidney
The kidney, a vital organ responsible for filtering blood and maintaining homeostasis, possesses a fascinatingly intricate structure. While the internal workings of the nephrons and their complex filtration processes often take center stage, the outermost layer, the renal capsule, plays a crucial, albeit often overlooked, role in protecting this essential organ. This article delves deep into the anatomy, histology, function, and clinical significance of the renal capsule, providing a comprehensive understanding of this vital protective covering.
Anatomy and Histology of the Renal Capsule
The renal capsule is a tough, fibrous membrane that completely encloses the kidney. Its smooth, glistening surface is directly adherent to the underlying renal parenchyma, the functional tissue of the kidney. This intimate contact ensures effective protection against external trauma and infection. Imagine it as a tightly fitted, protective jacket shielding the delicate machinery within.
Microscopic Structure: A Closer Look
Microscopically, the renal capsule is composed of two distinct layers:
-
Outer fibrous layer: This layer, predominantly composed of dense, irregular connective tissue, provides the capsule’s structural integrity and tensile strength. Collagen fibers, arranged in a complex interwoven pattern, contribute significantly to its resistance to stretching and tearing. Fibroblasts, the cells responsible for collagen production and maintenance, are scattered throughout this layer. The strength of this layer is crucial in preventing the kidney from being easily damaged by external forces.
-
Inner cellular layer: Beneath the fibrous layer lies a thinner, more cellular layer. This layer contains a mixture of fibroblasts and a specialized type of cell called renal capsule cells. These cells are believed to play a role in maintaining the integrity of the capsule and mediating its interaction with the underlying renal parenchyma. Their exact functions remain an area of ongoing research, with potential roles in tissue repair and immune response being investigated. This inner layer contributes to the capsule's adherence to the kidney.
The Renal Capsule's Functional Roles: More Than Just a Protective Barrier
While the protective function of the renal capsule is paramount, its role extends beyond simple physical shielding. The capsule performs several other crucial functions contributing to overall kidney health and function:
1. Physical Protection: A Shield Against Trauma
The primary function of the renal capsule is protection against physical trauma. Its tough, fibrous nature acts as a barrier against external impacts, blows, and accidental injuries, mitigating potential damage to the delicate renal parenchyma. This protective role is particularly important given the kidney's location, relatively vulnerable within the retroperitoneal space.
2. Maintaining Organ Shape and Integrity: Structural Support
The renal capsule contributes significantly to maintaining the kidney's characteristic shape and size. Its adherence to the kidney surface prevents distortion and maintains the organ's structural integrity. Without this supportive layer, the kidney's shape could be easily compromised, potentially affecting its vascular supply and overall function.
3. Barrier Against Infection: A First Line of Defense
The renal capsule acts as a barrier against bacterial invasion and infection. Its dense structure and relative impermeability to microorganisms help prevent pathogens from directly accessing the renal parenchyma. This protective function, in conjunction with the body's immune system, plays a vital role in preventing kidney infections like pyelonephritis. While not impenetrable, the capsule acts as a first line of defense, slowing the progression of infection.
4. Facilitating Renal Movement: Allowing for Flexibility
The renal capsule's flexibility allows the kidney to move slightly within the retroperitoneal space during respiration and changes in body posture. This adaptability prevents undue strain on the renal vasculature and ureters, ensuring the continuous flow of blood and urine. The capsule's elasticity helps accommodate these movements without compromising its protective function.
Clinical Significance: When the Renal Capsule is Compromised
While normally a silent guardian, the renal capsule’s integrity can become clinically relevant in several scenarios:
1. Renal Infections: The Capsule's Response
In cases of severe kidney infections (pyelonephritis), the inflammatory process can involve the renal capsule. Inflammation causes the capsule to become thickened and edematous, contributing to the pain and tenderness characteristic of these infections. The capsule's response to infection highlights its role in immune defense.
2. Renal Trauma: The Capsule's Limits
Severe blunt trauma to the abdomen or flank can result in injury to the kidney. The renal capsule may be torn or ruptured, leading to bleeding and potential damage to the underlying renal parenchyma. The severity of the injury depends on the force of the trauma and the extent of capsule disruption.
3. Renal Tumors: A Potential Indicator
The renal capsule can be involved in the growth and spread of renal tumors. Tumors may invade the capsule, increasing the risk of local spread and metastasis. The presence of capsule involvement is an important prognostic factor in renal cancer. The capsule's integrity becomes a crucial factor in staging and treatment planning.
4. Renal Abscesses: Localized Infections
A renal abscess is a localized collection of pus within the kidney. The capsule may become stretched and thinned due to the pressure exerted by the abscess. The capsule's response to this localized infection can cause severe pain and may necessitate surgical drainage.
5. Nephroptosis (Floating Kidney): An Unusual Condition
In rare cases, the renal capsule may be abnormally lax, leading to nephroptosis, or a "floating kidney." This condition causes the kidney to move abnormally within the retroperitoneal space, potentially causing pain, intermittent obstruction of the ureter, and other complications. This highlights the importance of the capsule in maintaining proper kidney positioning.
Research and Future Directions: Unveiling the Capsule's Secrets
While much is understood about the renal capsule's anatomy and basic functions, ongoing research continues to explore its intricacies. Areas of current investigation include:
-
The role of renal capsule cells in tissue repair and immune response: A deeper understanding of these cells' functions may reveal new therapeutic targets for kidney diseases.
-
The capsule's contribution to kidney fibrosis: Research is exploring the capsule's role in the development of kidney scarring and its potential as a therapeutic target.
-
The development of novel imaging techniques: Advanced imaging modalities may improve the visualization of the renal capsule and help diagnose subtle abnormalities.
-
The use of the renal capsule in regenerative medicine: The capsule's properties may be harnessed to support the regeneration of damaged kidney tissue.
The renal capsule, often a silent protector, plays a crucial role in maintaining kidney health and function. Its protective, structural, and immunological roles underscore its importance in preserving the integrity of this vital organ. Continued research promises to further illuminate its complexities and unlock its full potential in the fight against kidney disease. By understanding this often-overlooked layer, we can gain a more complete appreciation for the intricate workings of the kidney and its remarkable ability to maintain homeostasis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Inverse Of A Quadratic Function
Apr 01, 2025
-
Oz In A Fifth Of Alcohol
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is To The 1 2 Power
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is Water Evaporating A Chemical Or Physical Change
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Two Elements Make Up Water
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Outermost Layer Of The Kidney . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
