The Elbow Is Distal To The Shoulder
listenit
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
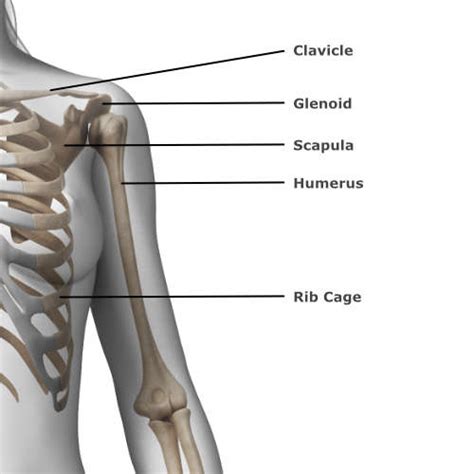
Table of Contents
The Elbow is Distal to the Shoulder: Understanding Anatomical Terminology and its Clinical Significance
Understanding anatomical terminology is fundamental to comprehending the human body's structure and function. One crucial concept is the relationship between body parts using directional terms. This article delves into the statement "the elbow is distal to the shoulder," exploring its meaning, significance in various medical fields, and its application in everyday life. We'll explore the anatomical planes, directional terms, and the clinical implications of understanding this simple yet crucial anatomical relationship.
Understanding Anatomical Position and Directional Terms
Before diving into the specifics of the elbow and shoulder relationship, it's crucial to establish a common reference point. Anatomical position refers to a standardized posture: body erect, feet together, palms facing forward, and thumbs pointing away from the body. Directional terms are used to describe the location of body parts relative to this standard position.
Key Directional Terms:
- Proximal: Closer to the point of attachment or origin (usually the trunk).
- Distal: Further from the point of attachment or origin.
- Superior (Cranial): Towards the head.
- Inferior (Caudal): Towards the feet.
- Anterior (Ventral): Towards the front.
- Posterior (Dorsal): Towards the back.
- Medial: Towards the midline of the body.
- Lateral: Away from the midline of the body.
These terms are essential for precise communication among healthcare professionals and for accurate understanding of anatomical descriptions.
The Elbow's Position Relative to the Shoulder: Distal
The statement "the elbow is distal to the shoulder" simply means that the elbow joint is farther away from the point of attachment of the limb (the shoulder) than the shoulder joint itself. The upper limb originates at the shoulder girdle, which connects the arm to the trunk. The elbow joint is located between the shoulder and the wrist. Therefore, following the established directional terminology, the elbow is unequivocally distal to the shoulder. This seemingly straightforward statement has far-reaching implications in medical diagnosis, treatment, and understanding of human movement.
Anatomical Planes and Axes of Movement
Understanding anatomical planes provides a three-dimensional perspective of the body's structure and movement. The three primary planes are:
- Sagittal Plane: Divides the body into left and right halves. Movement in this plane is flexion (bending) and extension (straightening). The elbow primarily flexes and extends within the sagittal plane.
- Frontal (Coronal) Plane: Divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) halves. Movement in this plane includes abduction (movement away from the midline) and adduction (movement towards the midline). The elbow joint has limited movement in the frontal plane.
- Transverse (Horizontal) Plane: Divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) halves. Movement in this plane includes rotation. The elbow joint has minimal rotation compared to other joints like the shoulder.
Each plane of movement is associated with a corresponding axis of rotation. For example, flexion and extension at the elbow occur around a transverse axis. Understanding these planes and axes is crucial for analyzing joint movement, assessing range of motion, and identifying potential pathologies.
Clinical Significance of Understanding Distal and Proximal Relationships
The understanding of distal and proximal relationships is crucial in various medical contexts:
1. Fracture Classification and Treatment:
Fractures of the upper limb are often described based on their location relative to other anatomical landmarks. For example, a fracture distal to the elbow would be closer to the wrist, while a fracture proximal to the elbow would be closer to the shoulder. This precise anatomical localization is essential for appropriate surgical planning and post-operative care. Accurate description of the fracture location – whether proximal or distal to specific anatomical landmarks – is critical for effective communication amongst the healthcare team.
2. Neurological Examination:
Assessing neurological function often involves evaluating sensation and reflexes in the extremities. Knowledge of proximal-distal relationships aids in systematically testing nerve function. For instance, a neurological deficit affecting the hand (distal) may suggest a problem in the nerves originating from the brachial plexus (proximal) in the neck and shoulder. The careful observation of proximal and distal neurological signs helps healthcare professionals to pinpoint the precise location of nerve injury or disease.
3. Vascular Assessment:
The blood supply to the upper limb follows a proximal-distal pattern. Assessing blood flow in the hand (distal) can provide clues about the patency of arteries originating from the subclavian artery (proximal). Distal pulses are palpated during routine physical examinations to detect potential vascular compromise. Weak or absent distal pulses necessitate further investigation to identify the source of impaired circulation. The understanding of blood flow patterns from proximal to distal sites assists medical practitioners in diagnosis and treatment planning.
4. Imaging Interpretation:
Medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs are crucial for visualizing the skeletal and soft tissues of the upper limb. Radiologists and other healthcare professionals use directional terms like proximal and distal to precisely describe the location of any abnormalities identified. For instance, a description stating a lesion is found 2cm distal to the elbow joint is more precise and useful than simply saying it's in the forearm. This precision in description improves diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
5. Musculoskeletal Injuries:
Many musculoskeletal injuries involve both proximal and distal structures. For example, a shoulder dislocation (proximal) can affect the function of the elbow (distal) due to pain, inflammation, and altered biomechanics. Understanding this interconnectedness is vital for effective injury management and rehabilitation. Precise localization of injury from proximal to distal sites allows for targeted treatments and effective rehabilitation strategies.
Everyday Applications of Understanding Anatomical Terminology
While the precise application of distal and proximal terminology is crucial in clinical settings, a basic understanding of these terms enhances our everyday lives. For example, a clearer understanding of injuries like sprains and strains can be gained with a basic grasp of anatomical terminology. Knowing the location of an injury – whether proximal or distal to a joint – can aid in understanding the severity of the injury and inform appropriate self-care. This improved understanding allows for making informed decisions about when to seek professional medical help.
This basic understanding of anatomical relationships can also be beneficial when following exercise instructions. Many fitness routines involve specific movements of proximal and distal limb segments. For example, a bicep curl specifically targets a distal muscle group of the arm, whilst a shoulder press involves a proximal muscle group. Understanding this can assist in correctly performing exercises for optimal results.
Conclusion: The Importance of Precision in Anatomical Language
The statement, "the elbow is distal to the shoulder," is a seemingly simple anatomical fact. However, its implications extend far beyond a basic understanding of body positioning. Precise anatomical terminology is essential for effective communication among healthcare professionals, accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, and a deeper understanding of the human body's intricate workings. By mastering these fundamental concepts, we can improve our understanding of human anatomy, clinical applications, and improve our overall comprehension of the human body. The use of precise language, including directional terminology, is fundamental to the advancement of healthcare and provides an improved quality of care for patients. The continued accurate usage of anatomical terminology, like distal and proximal, is vital for the progress of medicine and the wellbeing of individuals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Henry David Thoreau If One Advances Confidently
May 09, 2025
-
If G Is The Inverse Function Of F
May 09, 2025
-
Find The Square Root Of 196
May 09, 2025
-
Is Rubbing Alcohol A Pure Substance
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes Does A Fruit Fly Have
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Elbow Is Distal To The Shoulder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.