Simplify The Square Root Of 150
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 4 min read
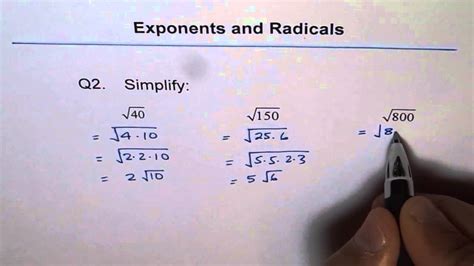
Table of Contents
Simplifying the Square Root of 150: A Comprehensive Guide
Simplifying square roots is a fundamental concept in mathematics, crucial for various applications from algebra to calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of simplifying the square root of 150, explaining the underlying principles and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll explore different methods, address common mistakes, and even touch on the historical context of square roots. By the end, you'll not only know how to simplify √150 but also possess the skills to tackle similar problems with confidence.
Understanding Square Roots and Prime Factorization
Before we jump into simplifying √150, let's establish a firm foundation. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. However, not all numbers have perfect square roots (i.e., whole numbers). This is where simplification comes in.
Prime factorization is the cornerstone of simplifying square roots. It involves breaking down a number into its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). This process is essential because it allows us to identify perfect square factors within the original number.
Let's illustrate this with a simpler example: simplifying √36.
-
Find the prime factorization of 36: 36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
-
Identify perfect square factors: We have 2² and 3², both perfect squares.
-
Simplify: √36 = √(2² x 3²) = √2² x √3² = 2 x 3 = 6
Therefore, √36 simplifies to 6.
Simplifying √150: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's apply the same principles to simplify √150.
-
Find the prime factorization of 150:
We can start by dividing 150 by the smallest prime number, 2: 150 ÷ 2 = 75. 75 is not divisible by 2, but it is divisible by 3: 75 ÷ 3 = 25. 25 is divisible by 5: 25 ÷ 5 = 5. 5 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 150 is 2 x 3 x 5 x 5 = 2 x 3 x 5².
-
Identify perfect square factors: We have 5², which is a perfect square.
-
Simplify:
√150 = √(2 x 3 x 5²) = √(2 x 3) x √5² = √6 x 5 = 5√6
Therefore, the simplified form of √150 is 5√6.
Alternative Methods for Simplification
While the prime factorization method is the most reliable, there are other approaches you can use, especially when dealing with larger numbers. However, these methods often require a good understanding of perfect squares.
Method 2: Identifying Perfect Square Factors Directly:
You might notice that 150 is divisible by 25 (a perfect square): 150 ÷ 25 = 6.
Therefore, √150 = √(25 x 6) = √25 x √6 = 5√6. This method can be quicker if you recognize the perfect square factor easily.
Method 3: Using a Factor Tree (Visual Approach):
A factor tree visually represents the prime factorization process. It's particularly helpful for larger numbers.
150
/ \
2 75
/ \
3 25
/ \
5 5
From the factor tree, we again see that 150 = 2 x 3 x 5², leading to the simplified form 5√6.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can hinder the simplification process:
-
Incomplete Factorization: Ensure you completely factor the number into its prime factors. Missing a factor can lead to an incorrect simplified form.
-
Incorrect Square Root Application: Remember that √(a x b) = √a x √b, but √(a + b) ≠ √a + √b. This is a crucial distinction.
-
Leaving Perfect Squares Inside the Radical: The goal is to extract all perfect square factors from under the square root symbol.
Advanced Applications and Further Exploration
Understanding square root simplification is crucial for various mathematical concepts:
-
Algebra: Solving quadratic equations often involves simplifying square roots.
-
Geometry: Calculating lengths and areas of geometric figures frequently requires simplifying square roots.
-
Trigonometry: Many trigonometric identities and calculations involve square roots.
-
Calculus: Derivatives and integrals may involve simplifying square roots to reach a final solution.
Furthermore, exploring the concept of irrational numbers provides a deeper understanding of square roots. Numbers like √6, which cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, are classified as irrational numbers. Simplifying square roots helps us represent these numbers in a more manageable form.
Conclusion: Mastering Square Root Simplification
Simplifying square roots, such as √150, is a fundamental skill with broad applications across various mathematical disciplines. By understanding prime factorization and applying the steps outlined above, you can confidently tackle this type of problem. Remember to practice regularly and avoid common mistakes to build your proficiency. The ability to efficiently simplify square roots will greatly enhance your mathematical understanding and problem-solving capabilities. The more you practice, the easier and faster it will become, ultimately boosting your confidence and making more complex mathematical tasks more accessible. Now, go forth and simplify those square roots!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Derivative Of 4 Square Root Of X
Mar 22, 2025
-
5 4 On A Number Line
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Fraction For 0 9
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Far Is Earth From Pluto In Light Years
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is 3 4 Equal To 6 8
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Simplify The Square Root Of 150 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
