Part Of The Sun Or Moon Is Visible
listenit
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
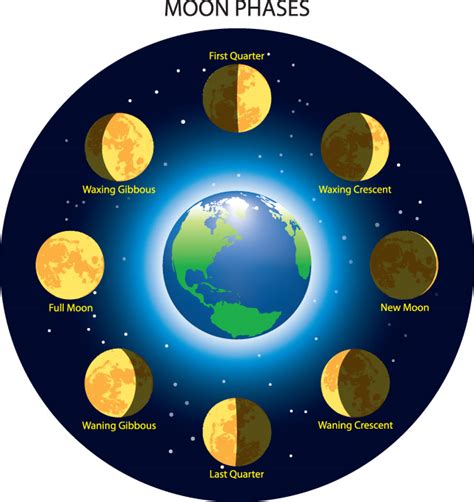
Table of Contents
Part of the Sun or Moon is Visible: Understanding Partial Eclipses and Other Phenomena
Have you ever looked up at the sky and seen only a sliver of the sun or moon? This fascinating phenomenon, where only a portion of the celestial body is visible, is more common than you might think and encompasses a range of astronomical events. Understanding why this happens requires delving into the mechanics of celestial orbits, shadows, and the relative positions of the Earth, sun, and moon. This article will explore the various reasons why we might only see part of the sun or moon, focusing on partial eclipses, phases of the moon, and other atmospheric effects.
Partial Solar Eclipses: When the Moon Partially Obscures the Sun
One of the most dramatic reasons for seeing only a part of the sun is a partial solar eclipse. This occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the earth, but not directly in line. Instead of completely blocking the sun's light (a total solar eclipse), the moon casts only a partial shadow on the earth. The extent to which the sun is obscured varies depending on your location on Earth and the precise alignment of the sun, moon, and earth.
Understanding the Umbra and Penumbra
The key to understanding partial solar eclipses lies in understanding the umbra and penumbra. The umbra is the darkest part of the moon's shadow, where the sun is completely blocked. Only observers within the umbra experience a total solar eclipse. Surrounding the umbra is the penumbra, a region of partial shadow where the sun is only partially obscured. Observers in the penumbra witness a partial solar eclipse. The further you are from the central path of the umbra, the smaller the portion of the sun that appears to be covered.
Safety Precautions During a Partial Solar Eclipse
Crucially, it is extremely dangerous to look directly at the sun during a partial solar eclipse without proper eye protection. Even with a portion of the sun obscured, the remaining light is still intense enough to cause serious and permanent eye damage. Never look at the sun through binoculars, telescopes, or cameras without specialized solar filters designed for this purpose. Improper eye protection can lead to solar retinopathy, a condition that can result in blurred vision, blind spots, and even complete blindness. Safe viewing options include using certified solar viewing glasses, pinhole projectors, or attending a public viewing event hosted by an astronomy club or observatory.
Phases of the Moon: A Cyclical Partial Visibility
The moon’s changing appearance throughout the month is due to its orbit around the Earth and the relative positions of the sun, Earth, and moon. This is commonly known as the phases of the moon. These phases are the result of changing amounts of sunlight reflected off the moon's surface as seen from Earth. While not technically a partial visibility of the entire moon itself, it demonstrates how we only see parts of the moon's illuminated surface during certain times of the month.
From New Moon to Full Moon and Back
The new moon phase is when the moon is positioned between the Earth and the sun. From Earth, we cannot see the moon because the sunlit side faces away from us. As the moon orbits the Earth, a progressively larger portion of the sunlit side becomes visible, leading to the waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, and finally the full moon phases. After the full moon, the process reverses, going through the waning gibbous, third quarter, and waning crescent phases before returning to the new moon. During all phases except the full moon, we only see a portion of the moon illuminated.
Atmospheric Effects: Clouds, Haze, and Other Obstructions
Sometimes, only part of the sun or moon is visible not because of the relative positions of celestial bodies, but due to atmospheric conditions. Clouds, haze, smog, and dust can obscure our view of the sun or moon, causing them to appear partially hidden or dimmed. This isn't a celestial event per se, but a very common experience that affects our ability to see celestial bodies fully.
The Impact of Weather on Visibility
Heavy cloud cover can completely block our view of the sun or moon, while thinner clouds or haze can create a diffused, softened appearance, reducing brightness and potentially making it seem like a portion is obscured. Atmospheric refraction, the bending of light as it passes through different layers of the atmosphere, can also cause distortions in the appearance of the sun or moon near the horizon, leading to a distorted or partially obscured image.
Other Phenomena Affecting Partial Visibility
Beyond partial eclipses and atmospheric conditions, other phenomena can occasionally affect the visibility of the sun or moon. These are less common but worth mentioning:
Lunar Occultations
A lunar occultation occurs when the moon passes in front of a star or planet, temporarily blocking it from view. Depending on the size and position of the moon, only a portion of the star or planet might be hidden, creating the impression of partial visibility.
Solar Transists
Similarly, a solar transit happens when a planet (like Mercury or Venus) passes between the Earth and the sun. This can appear as a small, dark spot traversing the sun's surface, again affecting the partial visibility of the sun. These are infrequent events.
Observing and Photographing Partial Celestial Events
Observing partial celestial events can be a rewarding experience, offering glimpses into the intricate movements and interactions within our solar system. Remember always to prioritize safety when observing the sun. For the moon, a good pair of binoculars or a telescope can enhance the viewing experience, allowing you to see greater detail in the lunar surface.
Photographing these events requires a bit more preparation and equipment. For solar events, specialized solar filters are absolutely essential to protect your camera's sensor. For lunar events, a tripod is recommended to maintain stability during long exposures. Experimenting with different camera settings and compositions can lead to stunning images of these celestial wonders.
Conclusion: The Intrigue of Partial Visibility
Whether it's a partial solar eclipse, a waxing crescent moon, or atmospheric interference, the partial visibility of the sun or moon offers a fascinating insight into the dynamic interplay of celestial mechanics and terrestrial phenomena. By understanding the underlying causes, we can appreciate the beauty and wonder of these events, while always prioritizing safety and responsible observation practices. The next time you see only a sliver of the sun or moon, take a moment to consider the fascinating processes at play, and perhaps even try to capture the moment with your camera or just enjoy the spectacle with your own eyes (safely!). Remember to check online resources and astronomical calendars for predictions of upcoming eclipses and other celestial events in your area.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Part Of The Sun Or Moon Is Visible . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
