One Of The Most Abindant Elements In The Ocean Is
listenit
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
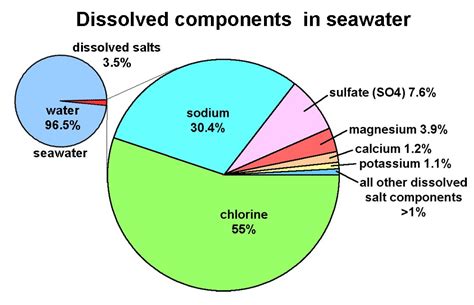
Table of Contents
One of the Most Abundant Elements in the Ocean Is: Unveiling the Secrets of Chloride
The ocean, a vast and mysterious realm covering over 70% of our planet, holds within its depths a treasure trove of elements and compounds. While the shimmering blue surface might suggest a simple composition, the reality is far more complex and fascinating. Among the myriad components dissolved and suspended within the saline waters, one element reigns supreme in terms of abundance: chloride. This article delves deep into the world of chloride in the ocean, exploring its sources, its impact on marine life and ecosystems, and its broader significance in the Earth's geochemical cycles.
Understanding Chloride's Oceanic Dominance
Chloride (Cl⁻), an anion of the element chlorine, is not just abundant in the ocean; it's the most abundant anion by far. It constitutes approximately 55% of the total dissolved solids in seawater, dwarfing the concentrations of other major ions like sodium, sulfate, magnesium, and calcium. This overwhelming dominance shapes the ocean's physical and chemical properties in profound ways. But how did chloride accumulate to such staggering levels?
The Sources of Oceanic Chloride
The story of oceanic chloride is intricately linked to the Earth's geological history. Several key processes contributed to its accumulation over billions of years:
-
Volcanic Activity: Volcanic eruptions release significant amounts of chlorine gas (HCl) into the atmosphere. This gas dissolves in rainwater, forming hydrochloric acid, which subsequently washes into rivers and eventually flows into the ocean. This process, ongoing for eons, has delivered a massive quantity of chloride ions to the marine environment.
-
Hydrothermal Vents: Deep-sea hydrothermal vents, located along mid-ocean ridges, release hot, mineral-rich fluids into the ocean. These fluids are often rich in chloride ions, further contributing to the ocean's chloride reservoir. These vents play a crucial role in the global geochemical cycling of various elements, including chloride.
-
Weathering of Rocks: The weathering of rocks on land, particularly those containing chloride-bearing minerals, also contributes to the chloride influx into the ocean. Rainwater interacts with these minerals, dissolving chloride ions that are then transported via rivers and runoff.
-
Sea Spray: The constant action of waves generates sea spray, which carries microscopic droplets of seawater into the atmosphere. Some of this seawater evaporates, leaving behind chloride salts that eventually return to the ocean via precipitation. This process helps to maintain the overall chloride balance.
Chloride's Influence on Marine Ecosystems
Chloride's high concentration in seawater is not merely a chemical curiosity; it plays a pivotal role in shaping the physical and biological aspects of marine ecosystems.
Salinity and Osmosis: A Delicate Balance
The high salinity of seawater, largely attributable to chloride, profoundly affects the osmotic balance of marine organisms. Osmosis is the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration. Marine organisms have evolved diverse mechanisms to cope with the hypertonic environment (higher solute concentration outside their cells) created by the high chloride concentration. Some organisms have adapted by maintaining a similar internal solute concentration to seawater, while others actively regulate their internal salt balance. This constant osmotic adjustment is crucial for their survival.
Ion Interactions and Chemical Reactions
Chloride ions interact extensively with other ions and molecules in seawater, influencing various chemical reactions. These interactions affect the availability of essential nutrients, the formation of mineral precipitates, and the overall chemical composition of the ocean. For example, chloride interacts with other ions to form complexes, which can affect the solubility and bioavailability of certain metals.
Impact on Marine Life
The abundance of chloride, while crucial for maintaining osmotic balance, also has implications for the specific physiology of individual species. Different organisms exhibit varied levels of tolerance to salinity changes. Changes in chloride concentrations, even within the natural range of variation, can stress marine organisms and potentially impact their reproductive success and growth. Pollution events that cause significant shifts in salinity, such as industrial discharge or agricultural runoff, can have severe consequences for marine ecosystems.
Chloride's Role in Global Geochemical Cycles
Chloride's journey through the ocean is not confined to the marine environment; it participates in broader global geochemical cycles that impact the entire planet.
Chloride and the Hydrologic Cycle
The ocean acts as a massive reservoir of chloride, exchanging it with the atmosphere and land through the hydrologic cycle. Evaporation, precipitation, river runoff, and sea spray all contribute to the dynamic interplay between oceanic chloride and the terrestrial and atmospheric environments. Understanding these exchanges is crucial for predicting and managing global water resources.
Chloride in Sedimentary Rocks
Over geological time, chloride ions are incorporated into sedimentary rocks, becoming part of the long-term geological record. The composition of ancient sedimentary rocks can provide valuable insights into past oceanic conditions and the evolution of chloride concentrations throughout Earth's history. Analyzing chloride isotopes in these rocks can reveal information about past climate change and tectonic activity.
Chloride and Climate Change
The ocean plays a crucial role in regulating global climate, and chloride's influence on ocean chemistry is implicated in these climate-regulating processes. For example, changes in oceanic salinity due to melting glaciers and altered precipitation patterns can affect ocean circulation and heat distribution, potentially influencing global weather patterns. Furthermore, the interaction of chloride with other elements, such as carbon, can impact the ocean's ability to absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide, a significant greenhouse gas.
Exploring Further: Research and Future Directions
While we have a solid understanding of chloride's abundance and its role in the ocean, there are still many unanswered questions that require further investigation.
Chloride Isotopes and Tracing Sources
Analyzing the isotopic composition of chloride can help scientists trace its sources and pathways through the environment. This is particularly useful in studying pollution events, understanding the impact of human activities on the ocean's chemistry, and deciphering the long-term evolution of oceanic chloride concentrations.
Chloride's Impact on Marine Microorganisms
The role of chloride in the physiology and ecology of marine microorganisms, particularly bacteria and archaea, is an area ripe for further research. These microscopic organisms play crucial roles in nutrient cycling and other biogeochemical processes, and understanding their response to chloride concentrations is essential for comprehending the health of marine ecosystems.
Chloride and Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification, driven by increased atmospheric carbon dioxide absorption, is a major concern for marine ecosystems. Further research is needed to understand how the interaction between chloride and other ions is altered by ocean acidification and how this affects the viability of various marine species.
Predictive Modeling of Chloride Dynamics
Developing accurate predictive models of chloride dynamics in the ocean is crucial for managing ocean resources and mitigating the impacts of climate change. These models need to incorporate diverse factors, including climate variability, human activities, and the complex interplay between chloride and other oceanic components.
Conclusion
Chloride stands as a testament to the ocean's immense complexity and its influence on the Earth's overall chemical balance. Its overwhelming abundance shapes the ocean's properties, influences marine ecosystems, and participates in vital geochemical cycles. While our understanding of chloride's role is extensive, continued research is essential to unveil the remaining mysteries of this ubiquitous element and its crucial role in maintaining the health of our planet. Through ongoing exploration and a deeper understanding of chloride's influence, we can better protect and manage our precious oceans for generations to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 9
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is The Lowest Common Multiple Of 2 And 5
Mar 13, 2025
-
Is Burning Paper A Chemical Change
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Many 1 3 Cups In A Cup
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Did The Policy Of Fordism Affect Workers
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about One Of The Most Abindant Elements In The Ocean Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
