Number Of Valence Electrons In Br
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
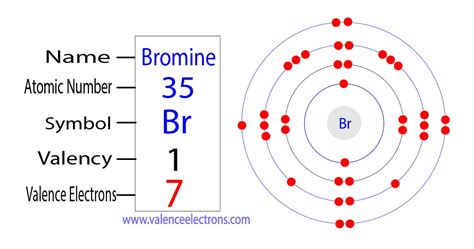
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Mysteries of Valence Electrons: A Deep Dive into Bromine (Br)
Bromine (Br), a fascinating halogen element, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Understanding its properties, particularly its valence electrons, is crucial for comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This comprehensive article explores the number of valence electrons in bromine, delving into the intricacies of its electronic configuration, its impact on bonding, and its implications in various applications.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we delve into the specifics of bromine, let's establish a fundamental understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are the primary players in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. The number of valence electrons dictates how many bonds an atom can potentially create, influencing its chemical properties and the compounds it can form.
The Significance of Valence Electrons
The significance of valence electrons cannot be overstated. They determine:
- Reactivity: Elements with nearly full or nearly empty valence shells are highly reactive, readily gaining or losing electrons to achieve a stable configuration.
- Bonding: Valence electrons participate directly in the formation of chemical bonds, including covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds.
- Oxidation States: The number of valence electrons influences an element's oxidation states, reflecting its ability to gain or lose electrons in chemical reactions.
- Chemical Properties: The overall chemical behavior of an element is largely governed by its valence electron configuration.
Determining Bromine's Valence Electrons
Bromine's atomic number is 35, meaning it possesses 35 protons and 35 electrons in a neutral atom. To determine the number of valence electrons, we need to examine its electron configuration. Electron configurations represent the arrangement of electrons within an atom's energy levels and subshells.
Bromine's Electron Configuration
Bromine's electron configuration is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁵.
This configuration tells us the distribution of electrons across different energy levels and subshells. Let's break it down:
- 1s², 2s², 2p⁶, 3s², 3p⁶: These inner shells are filled, representing core electrons that are tightly bound to the nucleus and do not typically participate in chemical bonding.
- 4s²3d¹⁰4p⁵: This is where the action is! These are the outermost electrons – the valence electrons.
Therefore, bromine has a total of seven valence electrons (4s² + 4p⁵ = 7).
The Octet Rule and Bromine
The octet rule, a crucial concept in chemistry, states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable configuration of eight valence electrons, similar to the noble gases. Bromine, with seven valence electrons, is one electron short of a stable octet. This explains its high reactivity and its tendency to form one covalent bond or gain one electron to form an anion (Br⁻).
Bromine's Chemical Behavior and Valence Electrons
Bromine's seven valence electrons profoundly influence its chemical behavior. It readily forms compounds with various elements, exhibiting diverse oxidation states.
Covalent Bonding in Bromine
Because bromine needs one more electron to achieve a stable octet, it often forms single covalent bonds with other atoms. In a covalent bond, atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This is exemplified in bromine's diatomic nature (Br₂), where two bromine atoms share one pair of electrons to complete their octets.
Ionic Bonding and Bromine
Bromine also participates in ionic bonding, gaining an electron to form the bromide anion (Br⁻). This negatively charged ion has a stable octet and readily forms ionic compounds with electropositive metals, like sodium bromide (NaBr).
Oxidation States of Bromine
Due to its seven valence electrons, bromine can exhibit various oxidation states, including -1, +1, +3, +5, and +7. The specific oxidation state adopted by bromine depends on the nature of the bonding partner and the reaction conditions.
Applications of Bromine and its Compounds
The unique properties of bromine, stemming directly from its seven valence electrons, lead to numerous applications across various industries.
Flame Retardants
Brominated flame retardants are widely used to prevent fires. These compounds contain bromine atoms, which interrupt the combustion process, hindering the spread of flames.
Water Treatment
Bromine compounds are used in water treatment as disinfectants, analogous to chlorine. They effectively kill bacteria and other harmful microorganisms, ensuring safe drinking water.
Pharmaceuticals
Bromine-containing compounds find application in the pharmaceutical industry, playing a role in the synthesis of various drugs and medications.
Dyes and Pigments
Certain bromine compounds are used as dyes and pigments, contributing vibrant colors to textiles and other materials.
Conclusion: The Importance of Valence Electrons in Bromine
The number of valence electrons in bromine – seven – is the key to understanding its chemical behavior and diverse applications. Its tendency to form one covalent bond or gain one electron to achieve a stable octet drives its reactivity and its ability to form a wide array of compounds. From flame retardants to pharmaceuticals, bromine's contribution to various industries underscores the significance of its electronic configuration and the pivotal role played by its seven valence electrons. Further research into bromine's chemistry continues to reveal new applications and deepen our understanding of this fascinating halogen.
Further Exploration: Beyond the Basics
This article provides a comprehensive overview of bromine's valence electrons and their implications. For those seeking a deeper understanding, further exploration can include:
- Advanced bonding theories: Delving into molecular orbital theory provides a more sophisticated understanding of bromine's bonding behavior.
- Spectroscopic techniques: Techniques like X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) can be used to experimentally confirm bromine's valence electron configuration.
- Computational chemistry: Quantum mechanical calculations can be employed to predict the reactivity and properties of bromine compounds.
- Organic Bromine Chemistry: Exploring the vast field of organobromine compounds and their synthetic applications.
Understanding the fundamental concept of valence electrons, specifically within the context of bromine's seven valence electrons, unlocks a deeper appreciation for its chemical behavior and its vital role in numerous applications. This knowledge forms the cornerstone for advanced studies in chemistry and related fields.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Number Of Valence Electrons In Br . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
