Look At The Figure. Find The Value Of X.
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
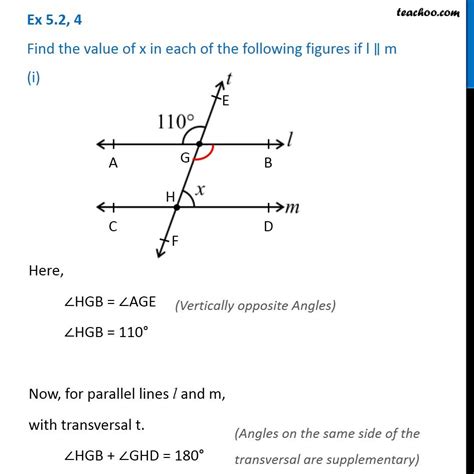
Table of Contents
Look at the Figure: Finding the Value of x – A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the value of 'x' in geometric figures is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from basic geometry to advanced calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve into various methods and strategies for solving for 'x' in different geometric figures, equipping you with the knowledge to tackle a wide range of problems. We'll explore different types of figures, from simple triangles and quadrilaterals to more complex shapes, focusing on the underlying principles and problem-solving techniques. We'll also touch upon the importance of understanding geometric theorems and properties in successfully determining the value of 'x'.
Understanding Geometric Principles: The Foundation for Solving for 'x'
Before we jump into specific examples, it's crucial to establish a strong foundation in fundamental geometric principles. Understanding these principles is the key to accurately and efficiently solving for 'x' in any given figure. Some essential concepts include:
-
Angles: The basic building blocks of geometry. Understanding angle types (acute, obtuse, right, straight, reflex), angle relationships (complementary, supplementary, vertically opposite), and angle properties within specific shapes is paramount.
-
Lines: Understanding parallel and perpendicular lines, transversals, and their resulting angle relationships (alternate interior angles, corresponding angles, consecutive interior angles) is essential for solving problems involving lines intersecting other lines or shapes.
-
Triangles: Knowing the properties of different triangles (equilateral, isosceles, scalene, right-angled) including their angle sum (180°), side relationships, and area calculations is vital. Pythagorean theorem is particularly crucial for right-angled triangles.
-
Quadrilaterals: Understanding the properties of various quadrilaterals like squares, rectangles, parallelograms, rhombuses, trapezoids, and kites, including their angle sums, side relationships, and diagonals, will be critical.
-
Circles: Knowledge of circle theorems, including angles subtended by arcs, tangents, chords, and secants, is crucial for solving problems involving circles.
-
Similar and Congruent Figures: Recognizing similar and congruent figures helps establish relationships between corresponding angles and sides, enabling the calculation of unknown values.
Solving for 'x' in Different Geometric Figures
Let's delve into various examples, showcasing different techniques for finding the value of 'x' in different geometric figures. Remember to always clearly state the geometric principles being applied.
Example 1: Finding 'x' in a Triangle
Figure: [Imagine a simple triangle with angles labeled A, B, and C. Angle A is labeled as 70°, angle B as x°, and angle C as 50°.]
Solution: The sum of angles in a triangle is always 180°. Therefore:
70° + x° + 50° = 180°
120° + x° = 180°
x° = 180° - 120°
x = 60°
Example 2: Finding 'x' in a Right-Angled Triangle using Pythagorean Theorem
Figure: [Imagine a right-angled triangle with sides a, b, and hypotenuse c. Side a is labeled as 3, side b as x, and hypotenuse c as 5.]
Solution: The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (a² + b² = c²). Therefore:
3² + x² = 5²
9 + x² = 25
x² = 25 - 9
x² = 16
x = 4 (We take the positive square root since length cannot be negative.)
Example 3: Finding 'x' in a Parallelogram
Figure: [Imagine a parallelogram with consecutive angles labeled as x and 110°.]
Solution: Consecutive angles in a parallelogram are supplementary (add up to 180°). Therefore:
x + 110° = 180°
x = 70°
Example 4: Finding 'x' using Similar Triangles
Figure: [Imagine two similar triangles. The larger triangle has sides 6, 8, and 10. The smaller triangle has sides x, 4, and 5.]
Solution: In similar triangles, the ratio of corresponding sides is constant. Therefore:
6/x = 8/4 = 10/5
We can use any of these ratios to solve for x:
6/x = 2
x = 3
Example 5: Finding 'x' in a Circle using Circle Theorems
Figure: [Imagine a circle with a chord and a tangent intersecting at a point outside the circle. The angles formed are labeled. One angle is labeled as x, and the other angles are given numerical values that allow for the application of relevant circle theorems (e.g., the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment).]
Solution: Applying the relevant circle theorem (the specific theorem will depend on the angles given in the figure), you can form an equation to solve for x. The exact solution will depend on the specific arrangement of angles in the figure. The solution will often involve solving an equation involving x and the given angles.
Advanced Techniques and Problem-Solving Strategies
As you progress, you'll encounter more complex problems requiring advanced techniques. Here are a few strategies:
-
Break down complex shapes: Divide complex figures into simpler shapes (triangles, quadrilaterals, etc.) to make the problem easier to manage.
-
Utilize auxiliary lines: Drawing additional lines (e.g., altitudes, medians, perpendicular bisectors) can help reveal hidden relationships and simplify the problem.
-
Systematic approach: Follow a systematic approach, clearly identifying given information, applying relevant theorems, and meticulously working through the steps.
-
Algebraic manipulation: Be comfortable with algebraic manipulation to solve equations involving x.
-
Visualisation: Develop strong visualization skills to help you understand the relationships between angles and sides in different figures.
Practicing and Mastering the Skill
Consistent practice is key to mastering the skill of finding 'x' in geometric figures. Work through numerous problems of varying difficulty, focusing on understanding the underlying principles and applying appropriate techniques. Start with simpler problems and gradually progress to more challenging ones. Use online resources, textbooks, and workbooks to find a wide range of problems to practice with.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Geometry
Finding the value of 'x' in geometric figures is more than just a mathematical exercise; it’s a crucial skill that underpins a deeper understanding of geometry and its applications. By mastering the fundamental principles and applying the problem-solving strategies discussed in this comprehensive guide, you'll gain confidence and proficiency in tackling a diverse range of geometric problems. Remember, consistent practice and a systematic approach are the keys to success. So, grab your pencil, dive into some practice problems, and unlock the power of geometry!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Temperature Of The Earth With Depth
May 09, 2025
-
When The Net Force Of The Object Is Zero
May 09, 2025
-
2 In The Power Of 3
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 02 As A Percent
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Length Of Side B
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Look At The Figure. Find The Value Of X. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.