Limit Tanx As X Approaches 0
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
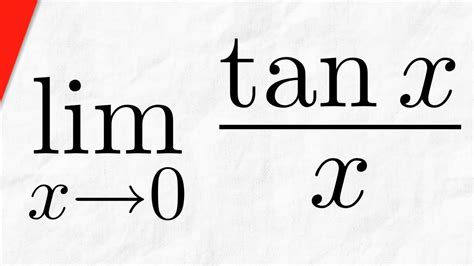
Table of Contents
Limit of tan x as x approaches 0: A Comprehensive Exploration
The limit of tan x as x approaches 0 is a fundamental concept in calculus with significant applications in various fields. Understanding this limit is crucial for grasping more advanced concepts and solving real-world problems. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of this limit, examining its derivation using different approaches, exploring its significance, and illustrating its applications.
Understanding the Limit
Before delving into the intricacies of the limit, let's establish a clear understanding of what it represents. In calculus, a limit describes the value a function approaches as its input approaches a particular value. In this case, we're interested in the behavior of the tangent function (tan x) as x gets arbitrarily close to 0. We express this mathematically as:
lim (x→0) tan x
This notation reads as "the limit of tan x as x approaches 0". The question is: what value does tan x approach as x gets closer and closer to 0?
Deriving the Limit Using Different Approaches
Several methods can be employed to determine the limit of tan x as x approaches 0. We'll explore three common approaches:
1. Using the Definition of the Tangent Function
The tangent function is defined as the ratio of the sine function to the cosine function:
tan x = sin x / cos x
Therefore, the limit we're interested in can be rewritten as:
lim (x→0) tan x = lim (x→0) (sin x / cos x)
We know that:
- lim (x→0) sin x = 0
- lim (x→0) cos x = 1
Applying the limit properties for quotients, we get:
lim (x→0) (sin x / cos x) = (lim (x→0) sin x) / (lim (x→0) cos x) = 0 / 1 = 0
Therefore, the limit of tan x as x approaches 0 is 0.
2. Using L'Hôpital's Rule
L'Hôpital's Rule is a powerful tool for evaluating limits of indeterminate forms (such as 0/0 or ∞/∞). As x approaches 0, tan x approaches 0/1 which is 0, this isn't an indeterminate form, so we don't need L'Hopital's rule. However for the sake of completeness, let's consider a related limit that does require it:
lim (x→0) (sin x / x). This is an indeterminate form 0/0. Applying L'Hôpital's rule by differentiating the numerator and denominator:
lim (x→0) (cos x / 1) = cos 0 = 1
While this doesn't directly solve our initial problem, it highlights a crucial relationship between sin x and x near 0. Knowing that lim (x→0) sin x / x = 1, and using the fact that lim (x→0) cos x = 1, we can indirectly derive our original limit:
Since tan x = sin x / cos x, and knowing the individual limits of sin x and cos x as x approaches 0, we can deduce that the limit of tan x approaches 0.
3. Using the Unit Circle and Geometric Interpretation
Consider a unit circle (a circle with a radius of 1). As the angle x approaches 0, the length of the arc subtended by x also approaches 0. The tangent of x is the length of the line segment tangent to the circle at (1,0) extending to where the line at angle x intersects. As x approaches 0, this length also approaches 0. Therefore, the limit of tan x as x approaches 0 is 0.
Significance of the Limit
The limit of tan x as x approaches 0 holds profound significance in various mathematical and scientific fields:
- Calculus: It's a foundational limit used in deriving derivatives and integrals of trigonometric functions. Many derivative formulas rely on this limit.
- Trigonometry: It clarifies the behavior of trigonometric functions near the origin, providing a better understanding of their oscillatory nature.
- Physics and Engineering: This limit is frequently used in approximating trigonometric functions in various physical models and engineering calculations where small angles are involved. For instance, in projectile motion, for small angles of launch, the tangent of the angle is approximately equal to the angle itself (in radians).
- Numerical Analysis: This limit is crucial in developing numerical methods for approximating solutions to differential equations and other complex mathematical problems.
Applications of the Limit
The limit's applications span various disciplines:
- Small Angle Approximations: In physics and engineering, when dealing with small angles (measured in radians), we can approximate tan x ≈ x. This simplification greatly simplifies many calculations. For example, in simple pendulum motion, this approximation allows for easier solutions to the equations of motion for small angular displacements.
- Linearization: The limit helps in linearizing nonlinear functions around a point. The tangent line at x=0 to the graph of tan(x) serves as a linear approximation of tan(x) for values of x close to 0.
- Taylor Series Expansion: The Taylor series expansion of tan x around 0 is directly related to this limit. The first term of the Taylor series is 0, reflecting the limit we've explored.
- Differential Equations: Many differential equations involving trigonometric functions can be simplified or solved using this limit as a crucial step in analysis.
Advanced Considerations and Related Limits
While we've focused on the limit as x approaches 0, it's important to acknowledge that the tangent function is not continuous for all x values. It has vertical asymptotes at odd multiples of π/2 (π/2, 3π/2, 5π/2, etc.). This discontinuity highlights the importance of considering the specific interval around which the limit is evaluated.
The limit of tan x as x approaches 0 is just one piece of a larger puzzle. Exploring related limits, such as:
- lim (x→0) sin x / x = 1
- lim (x→0) (1 - cos x) / x = 0
helps build a comprehensive understanding of the behavior of trigonometric functions around 0. These limits are often used together in various applications, emphasizing their interconnectedness.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Further Exploration
The limit of tan x as x approaches 0, while seemingly simple at first glance, holds significant weight in mathematics, science, and engineering. Its derivation using different methods enhances our understanding of fundamental calculus principles and its applications provide a glimpse into the power of mathematical analysis in solving real-world problems. A solid grasp of this limit forms a crucial foundation for more advanced studies in calculus and its applications. This article provided a comprehensive exploration, aiming to solidify your understanding and provide a solid base for further learning. Remember to practice solving problems involving this limit to fully integrate this important concept into your mathematical toolkit.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Difference Between A Coefficient And A Subscript
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Factor Of 9 And 15
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Correct Equation For Cellular Respiration
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Is 1 2 Kg
Mar 14, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple For 3 4 5
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Limit Tanx As X Approaches 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
