Is Supports Combustion A Physical Or Chemical Property
listenit
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
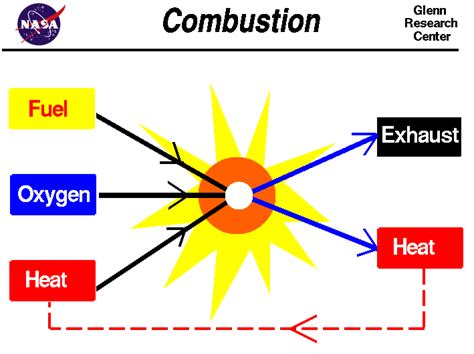
Table of Contents
Is "Supports Combustion" a Physical or Chemical Property? A Deep Dive
The question of whether "supports combustion" is a physical or chemical property is a deceptively complex one. It touches upon fundamental concepts in chemistry and physics, requiring a nuanced understanding of both property types and the combustion process itself. While a quick answer might seem straightforward, a thorough exploration reveals a more intricate reality. This article will delve into the intricacies of this question, clarifying the definitions, exploring the combustion process, and ultimately arriving at a well-supported conclusion.
Understanding Physical and Chemical Properties
Before we tackle the central question, let's establish a clear understanding of physical and chemical properties. These terms describe the inherent characteristics of a substance and how it behaves under different conditions.
Physical Properties
Physical properties are characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's chemical composition. These include:
- Appearance: Color, odor, texture, shape, etc.
- Density: Mass per unit volume.
- Melting point: Temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
- Boiling point: Temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
- Solubility: Ability to dissolve in a solvent.
- Conductivity: Ability to conduct electricity or heat.
- Hardness: Resistance to scratching or indentation.
- Malleability: Ability to be hammered into thin sheets.
- Ductility: Ability to be drawn into wires.
Crucially, observing these properties doesn't alter the substance's molecular structure. For example, melting ice into water is a physical change; the water molecules remain H₂O.
Chemical Properties
Chemical properties, on the other hand, describe a substance's ability to undergo a chemical change or reaction, resulting in the formation of a new substance with a different chemical composition. Examples include:
- Flammability: Ability to burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Reactivity with acids: How a substance reacts with acids.
- Reactivity with water: How a substance reacts with water.
- Toxicity: Ability to cause harm to living organisms.
- Stability: Resistance to decomposition or reaction.
These properties are observed only when a substance undergoes a chemical transformation, altering its molecular structure. Burning wood is a chemical change; the wood's cellulose molecules are broken down and transformed into ash, carbon dioxide, and water.
The Combustion Process: A Chemical Transformation
Combustion is a rapid chemical reaction between a substance (fuel) and an oxidant (usually oxygen), producing heat and light. This process fundamentally alters the chemical composition of the fuel. The original molecules are broken apart, and new molecules are formed as products.
Several key factors are crucial for combustion to occur:
- Fuel: The substance that undergoes oxidation. This can be a solid, liquid, or gas.
- Oxidant: Typically oxygen, but other oxidizing agents can support combustion.
- Ignition temperature: The minimum temperature required to initiate combustion.
- Heat: The energy released during combustion.
The chemical reaction involved in combustion is often exothermic, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat and light. The products of combustion are typically different from the reactants. For instance, burning methane (CH₄) in oxygen (O₂) produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O):
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
This clearly demonstrates that combustion is a chemical process, involving the breaking and forming of chemical bonds and the creation of new substances.
"Supports Combustion": A Chemical Property Descriptor
Now, let's return to the core question: Is "supports combustion" a physical or chemical property? The answer is that "supports combustion" is a chemical property.
The statement "substance X supports combustion" means that substance X can act as an oxidant in a combustion reaction. It facilitates the rapid oxidation of a fuel, resulting in a chemical change. This ability is intrinsically linked to the substance's chemical reactivity and its capacity to participate in redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions.
Consider oxygen (O₂), a quintessential supporter of combustion. Its ability to support combustion stems from its high electronegativity – its tendency to attract electrons. This allows it to readily accept electrons from other substances during oxidation, initiating the combustion process and forming new chemical compounds. This isn't a physical property; the oxygen molecule's structure isn't fundamentally altered when it merely supports the burning of another material. However, once the reaction begins, the oxygen is consumed as a reactant, participating directly in the chemical change.
Other substances like chlorine (Cl₂) or fluorine (F₂) can also support combustion, albeit often in more specialized contexts. Their ability to do so is tied directly to their chemical reactivity and the electron transfer involved in the reaction. Again, this supports the classification of "supports combustion" as a chemical property.
Differentiating Between Physical and Chemical Involvement in Combustion
It's important to distinguish between the physical process of mixing reactants and the chemical process of combustion itself. The physical act of bringing a fuel and an oxidant together does not constitute combustion. The crucial aspect is the chemical reaction that subsequently occurs, leading to the formation of new substances.
For example, physically mixing gasoline and oxygen in a container does not automatically cause combustion. You need an ignition source to overcome the activation energy and initiate the chemical reaction. The combustion itself is the chemical change, not the simple mixing of reactants. Therefore, the ability of a substance to support this chemical process is rightly categorized as a chemical property.
Practical Applications and Implications
Understanding whether "supports combustion" is a physical or chemical property is important for various applications:
- Fire safety: Recognizing materials that support combustion is vital for fire prevention and suppression.
- Material selection: Choosing appropriate materials for specific applications requires understanding their combustion properties.
- Chemical engineering: Designing and optimizing combustion processes requires a deep understanding of the chemical reactions involved.
- Environmental science: Understanding combustion helps analyze the environmental impact of burning fuels.
The classification of "supports combustion" as a chemical property underscores the importance of considering the chemical reactivity of substances, especially in safety-critical applications.
Conclusion: Supporting Combustion – A Definitive Chemical Property
After a thorough examination of the concepts of physical and chemical properties and a detailed look at the combustion process, the conclusion is clear: the ability of a substance to support combustion is a chemical property. This stems from the inherent chemical reactivity of the substance and its direct participation in the redox reactions that define combustion. While the physical mixing of reactants is necessary for combustion to occur, the ability of a substance to facilitate the chemical reaction is itself a chemically defined property. It is not simply an observational trait, but a reflection of a substance's fundamental chemical behavior. This understanding has far-reaching implications in various fields, highlighting the crucial role of chemical properties in diverse applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Benzene A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is 1 4 3 8 Reduced To The Lowest Terms
Mar 31, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 40
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Do You Find Change In Velocity
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Percent Is 5 Out Of 8
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Supports Combustion A Physical Or Chemical Property . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
