Is Naoh A Acid Or Base
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
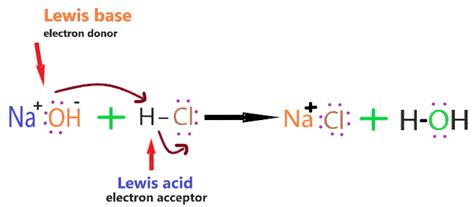
Table of Contents
Is NaOH an Acid or a Base? Understanding Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), also known as lye or caustic soda, is a ubiquitous chemical compound with a wide range of applications. However, a fundamental question often arises: is NaOH an acid or a base? The answer is clear and unambiguous: NaOH is a strong base. This article will delve deep into the properties of NaOH, explaining why it's classified as a base, its reactions, and its crucial role in various industries.
Understanding Acids and Bases
Before definitively labeling NaOH, let's establish a clear understanding of acids and bases. Several theories exist to define these fundamental chemical concepts, but two prominent ones are the Arrhenius theory and the Brønsted-Lowry theory.
Arrhenius Theory
The Arrhenius theory, proposed by Svante Arrhenius, defines acids as substances that produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water, while bases produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻). According to this theory, NaOH qualifies as a base because it dissociates in water to form sodium ions (Na⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻):
NaOH(s) → Na⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
Brønsted-Lowry Theory
The Brønsted-Lowry theory offers a broader definition. It defines acids as proton (H⁺) donors and bases as proton acceptors. NaOH fits this definition as well. While it doesn't directly donate protons, the hydroxide ion (OH⁻) readily accepts a proton, forming water:
OH⁻(aq) + H⁺(aq) → H₂O(l)
This proton-accepting ability solidifies NaOH's classification as a base, even under the more encompassing Brønsted-Lowry framework.
The Strong Base Nature of NaOH
NaOH isn't just any base; it's a strong base. This means that it almost completely dissociates into its ions (Na⁺ and OH⁻) when dissolved in water. This complete dissociation results in a high concentration of hydroxide ions, leading to a highly alkaline solution. The strength of a base is directly related to the extent of its dissociation. Weak bases, in contrast, only partially dissociate, resulting in a lower concentration of hydroxide ions.
The high concentration of OH⁻ ions makes NaOH solutions highly corrosive. Direct contact can cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Therefore, handling NaOH requires stringent safety precautions, including the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
Chemical Reactions of NaOH
NaOH's strong basicity underlies its extensive reactivity. It participates in a variety of chemical reactions, including:
Neutralization Reactions
The most characteristic reaction of a base is its neutralization reaction with an acid. When NaOH reacts with an acid, it produces salt and water. For example, the reaction with hydrochloric acid (HCl) is:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
This reaction is an example of a strong acid-strong base neutralization. The resulting solution, containing sodium chloride (NaCl), is neutral (pH 7) if stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base are used.
Reactions with Metal Oxides and Hydroxides
NaOH reacts with amphoteric metal oxides and hydroxides (those that can act as both acids and bases). For instance, its reaction with aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) is:
2NaOH(aq) + Al₂O₃(s) → 2NaAlO₂(aq) + H₂O(l)
Saponification
NaOH plays a crucial role in saponification, the process of making soap. It reacts with fats and oils (triglycerides) to produce glycerol and soap (fatty acid salts). This process has been used for centuries in soap-making.
Ester Hydrolysis
NaOH can also catalyze the hydrolysis of esters. Esters are organic compounds formed by the reaction of an acid and an alcohol. NaOH cleaves the ester bond, producing the corresponding carboxylic acid and alcohol.
Applications of NaOH
The strong basicity and reactivity of NaOH make it an invaluable chemical in a vast array of applications across numerous industries. Some key applications include:
Industrial Applications
- Pulp and Paper Industry: NaOH is extensively used in the kraft process for pulping wood, breaking down lignin and cellulose fibers to create paper pulp.
- Soap and Detergent Production: As mentioned earlier, saponification using NaOH is crucial for soap manufacturing. It's also a component in many detergents.
- Chemical Synthesis: NaOH is a vital reagent in numerous chemical syntheses, acting as a base, a nucleophile, and a catalyst.
- Textile Industry: NaOH is used in processes such as mercerization (treating cotton fibers to improve their luster and strength) and dyeing.
- Water Treatment: NaOH is employed to adjust the pH of water and remove heavy metals.
Domestic Applications
- Drain Cleaners: Many commercial drain cleaners contain NaOH to dissolve clogs of grease and organic matter. Caution: These cleaners are extremely corrosive and should be used with extreme care.
- Food Processing: In small quantities, NaOH is used in the processing of certain foods, such as pretzels and olives.
Safety Precautions When Handling NaOH
Due to its corrosive nature, it's crucial to exercise extreme caution when handling NaOH. Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat. Avoid skin contact and inhalation of dust. In case of contact, immediately flush the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention if necessary. Proper ventilation is essential when working with NaOH, particularly in large quantities. Always store NaOH in tightly sealed containers to prevent moisture absorption and degradation.
Conclusion
In summary, NaOH is unequivocally a strong base. Its ability to dissociate completely in water to yield a high concentration of hydroxide ions, its reactions with acids to form salts and water, and its wide range of industrial and domestic applications clearly demonstrate its basic nature. Understanding its properties and handling it safely is essential for anyone working with this important chemical compound. Remember, always prioritize safety when working with NaOH due to its highly corrosive nature. Proper handling and safety procedures are paramount to prevent accidents and ensure responsible usage. The information provided here should enhance your understanding and safe handling of this powerful chemical.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Common Multiples Of 9 And 15
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Sides Does A Dodecagon Has
Mar 18, 2025
-
Are The Kidneys Inferior To The Lungs
Mar 18, 2025
-
Distance From Atlanta Ga To Nashville Tennessee
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is 80 Percent Of 12
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Naoh A Acid Or Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
