Is Chlorine A Gas At Room Temperature
listenit
Apr 08, 2025 · 5 min read
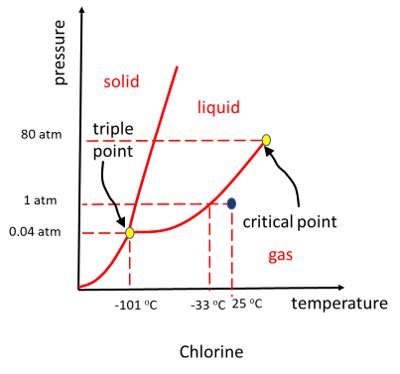
Table of Contents
Is Chlorine a Gas at Room Temperature? A Deep Dive into Chlorine's Properties
Chlorine. The very name conjures images of swimming pools, clean water, and perhaps even a touch of apprehension. But beyond its common applications, chlorine's fascinating properties, particularly its state at room temperature, warrant a closer look. This article delves into the intricacies of chlorine, explaining why it exists as a gas under standard conditions and exploring its diverse roles in our world.
Understanding Chlorine's Basic Properties
Before we dive into the specifics of its state at room temperature, let's establish a foundational understanding of chlorine's properties. Chlorine (Cl) is a chemical element, a halogen residing in Group 17 of the periodic table. This group, also known as the halogens, is characterized by highly reactive nonmetals.
Key Characteristics of Chlorine:
- Atomic Number: 17
- Atomic Mass: Approximately 35.45 u
- Electron Configuration: [Ne]3s²3p⁵
- Appearance: Yellow-green gas (at room temperature)
- Reactivity: Highly reactive, readily forming compounds with many other elements.
- Oxidation States: Variable, ranging from -1 to +7, contributing to its diverse chemistry.
- Toxicity: Highly toxic in its gaseous form, causing respiratory irritation and other health problems.
Why is Chlorine a Gas at Room Temperature?
The fact that chlorine exists as a gas at room temperature (around 25°C or 77°F) is directly related to its molecular structure and intermolecular forces.
Intermolecular Forces: The Key to State of Matter
The state of a substance—solid, liquid, or gas—is determined by the strength of the intermolecular forces (IMFs) between its molecules. These forces are weaker than the intramolecular forces (bonds within molecules) but still play a crucial role in determining physical properties.
In chlorine's case, the molecules are diatomic, meaning they exist as Cl₂ (two chlorine atoms bonded together). The primary IMF acting between Cl₂ molecules is the London dispersion force. London dispersion forces are weak, temporary attractions that arise due to fluctuations in electron distribution around the molecules. While present in all molecules, they are particularly significant in nonpolar molecules like Cl₂ which lack permanent dipoles.
Because the London dispersion forces between Cl₂ molecules are relatively weak, they are easily overcome by the kinetic energy of the molecules at room temperature. This means the molecules are free to move around independently, resulting in the gaseous state.
Comparing Chlorine's Behavior to Other Halogens
It's helpful to compare chlorine's behavior to other halogens to better understand its gaseous nature. Bromine (Br₂) is a liquid at room temperature, while iodine (I₂) is a solid. This progression reflects the increasing strength of London dispersion forces as the size and mass of the halogen atoms increase. Larger atoms have more electrons, leading to stronger temporary dipoles and stronger London dispersion forces, thus requiring more energy to overcome these forces and transition to the gaseous phase.
Chlorine's Applications: From Water Purification to Industrial Processes
Chlorine's reactivity and properties make it incredibly versatile, contributing to its widespread use in numerous applications.
Water Treatment: A Crucial Role in Public Health
Perhaps the most widely known application of chlorine is in water purification. Its strong oxidizing properties effectively kill harmful bacteria and viruses, making water safe for consumption. This is critical in preventing waterborne diseases and ensuring public health.
Industrial Uses: Diverse and Essential
Beyond water treatment, chlorine is a key component in various industrial processes:
- Production of PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Chlorine is a crucial ingredient in the production of PVC, a widely used plastic in pipes, flooring, and many other products.
- Production of Solvents: Chlorine is used in the synthesis of various solvents, essential in various industrial applications.
- Bleaching Agent: Chlorine-based compounds are utilized as bleaching agents in the paper and textile industries.
- Disinfectants and Antiseptics: Chlorine compounds find application as disinfectants and antiseptics in various settings.
Other Applications
Chlorine also plays a role in:
- Pharmaceutical Production: Chlorine is incorporated into the synthesis of certain pharmaceuticals.
- Pesticide Production: While the environmental impact is a concern, chlorine-based compounds are used in some pesticides.
Safety Precautions: Handling Chlorine Responsibly
Because chlorine is a highly toxic gas, handling it requires strict safety precautions.
Health Risks: Understanding the Dangers
Inhalation of chlorine gas can cause severe respiratory problems, including coughing, shortness of breath, and even lung damage. Skin contact can lead to irritation and burns. Therefore, appropriate safety equipment, such as respirators and protective clothing, is essential when working with chlorine.
Environmental Concerns: Minimizing Impact
The release of chlorine into the environment can have detrimental consequences for both human health and ecosystems. Responsible handling and disposal practices are crucial to minimize its environmental impact. The proper management of chlorine-containing waste is a significant area of concern.
Conclusion: A Powerful Element with Crucial Applications
Chlorine, a yellow-green gas at room temperature due to its weak intermolecular forces, is a powerful and versatile element with numerous applications. Its crucial role in water purification underscores its significance in public health, while its industrial uses span various sectors. However, its toxicity demands careful handling and responsible use to ensure both human and environmental safety. Understanding chlorine's properties, both its benefits and risks, is essential for its safe and effective utilization. Further research continues to explore its applications and potential, while simultaneously focusing on responsible handling and minimizing environmental impact. This detailed understanding of chlorine, from its atomic structure to its vast applications and inherent safety concerns, highlights its vital yet challenging position within our modern world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Number Of Valence Electrons For Boron
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Holds Two Strands Of Dna Together
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Happens To Atoms After A Chemical Change
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Decimal Is Equivalent To 1 3
Apr 08, 2025
-
Vertical Angles Are Supplements Of Each Other
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Chlorine A Gas At Room Temperature . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.