Is 25 A Prime Or Composite Number
listenit
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
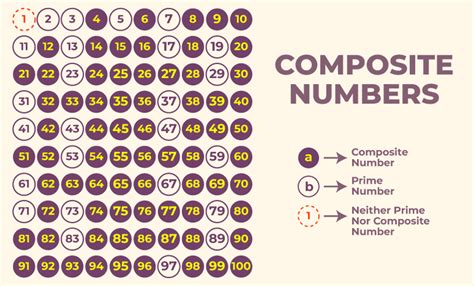
Table of Contents
Is 25 a Prime or Composite Number? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Determining whether a number is prime or composite is a fundamental concept in number theory. This seemingly simple question—is 25 a prime or composite number?—opens the door to understanding the fascinating world of prime numbers, their properties, and their significance in mathematics and computer science. This article will not only answer the question definitively but will also explore the broader concepts surrounding prime and composite numbers, offering a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
Before we tackle the specific case of 25, let's define our key terms:
-
Prime Number: A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on.
-
Composite Number: A composite number is a whole number greater than 1 that is not prime. This means it has more than two positive divisors (including 1 and itself). Examples are 4 (1, 2, 4), 6 (1, 2, 3, 6), 9 (1, 3, 9), and so forth.
-
The Number 1: The number 1 is neither prime nor composite. This is a crucial distinction; it's considered a "unit" in number theory.
Determining if 25 is Prime or Composite
Now, let's address the main question: Is 25 a prime or composite number?
To determine this, we need to find all the positive divisors of 25. These are the numbers that divide 25 without leaving a remainder. Let's list them:
- 1: 25 divided by 1 is 25.
- 5: 25 divided by 5 is 5.
- 25: 25 divided by 25 is 1.
We've found three positive divisors of 25: 1, 5, and 25. Since 25 has more than two divisors, it does not meet the definition of a prime number. Therefore, 25 is a composite number.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers might seem like a niche topic, but they play a surprisingly crucial role in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are the foundation of many modern encryption methods. Algorithms like RSA rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of online transactions, sensitive data protection, and much more depend on this principle. The larger the prime numbers used, the more secure the encryption becomes.
-
Number Theory: Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks within number theory itself. Many theorems and conjectures revolve around their properties and distribution. The distribution of primes, for instance, is a complex and ongoing area of mathematical research, with conjectures like the Riemann Hypothesis still unsolved.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers are used in various algorithms and data structures. Hash functions, which are crucial for data organization and retrieval, often leverage prime numbers for their properties of distribution and collision avoidance.
Methods for Determining Primality
There are several methods to determine whether a number is prime or composite:
-
Trial Division: This is the most basic method. You check for divisibility by all integers from 2 up to the square root of the number. If it's divisible by any of these, it's composite; otherwise, it's prime. This method becomes computationally expensive for very large numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It's more efficient than trial division for finding multiple primes within a range.
-
Probabilistic Primality Tests: For extremely large numbers, probabilistic tests are often used. These tests don't guarantee primality but offer a high probability of correctness. The Miller-Rabin test is a widely used example. These tests are far more efficient than deterministic tests for large numbers.
The Distribution of Prime Numbers
The way prime numbers are distributed among the integers is a fascinating and complex subject. While they appear randomly scattered, there are patterns and regularities that mathematicians have discovered:
-
Prime Number Theorem: This theorem provides an approximation of the number of primes less than a given integer. It states that the number of primes less than x is approximately x/ln(x), where ln(x) is the natural logarithm of x.
-
Prime Gaps: The difference between consecutive prime numbers is known as a prime gap. The study of prime gaps is an active area of research, with questions about the size and distribution of these gaps remaining open problems.
-
Twin Primes: Twin primes are pairs of primes that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13). The twin prime conjecture proposes that there are infinitely many twin prime pairs, but this remains an unsolved problem.
Beyond 25: Exploring Other Composite Numbers
Understanding why 25 is a composite number helps us understand the broader concept and allows us to explore other composite numbers. Let's look at a few examples:
Example 1: 100
100 is a composite number. Its divisors include 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, and 100. The presence of numerous divisors clearly indicates its composite nature.
Example 2: 144
144 is another composite number. It has a large number of divisors, including 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 16, 18, 24, 36, 48, 72, and 144. Note that composite numbers often have many factors.
Example 3: Large Composite Numbers
The concept of composite numbers extends to incredibly large numbers. In cryptography, the security of systems often relies on the difficulty of factoring very large composite numbers into their prime factors. The ability to quickly find the prime factors of a large composite number is crucial for breaking many encryption schemes.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime and Composite Numbers
The seemingly simple question of whether 25 is a prime or composite number opens a vast and intriguing world of mathematical exploration. Understanding the distinction between prime and composite numbers is essential not only for mathematical pursuits but also for comprehending the underpinnings of modern technology, particularly in the realm of cryptography and computer science. The continued study and exploration of prime numbers and their properties promise exciting discoveries and advancements in the future. While 25 is definitively a composite number, its existence within the broader landscape of numbers highlights the rich complexity and enduring significance of number theory. The exploration continues, and the mysteries of prime and composite numbers continue to fascinate and challenge mathematicians and computer scientists alike.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Based On The Ionization Energies Of Element X
Mar 12, 2025
-
Find The Interval Of Convergence Of The Power Series
Mar 12, 2025
-
Go In The Direction Of Your Dreams
Mar 12, 2025
-
How Many Square Inches Are In One Square Foot
Mar 12, 2025
-
How Many Gallons Is 60 Ounces
Mar 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 25 A Prime Or Composite Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
