Is 2/3 The Same As 3/4
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 4 min read
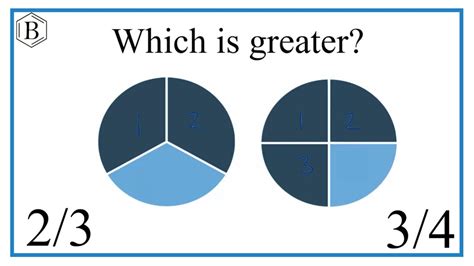
Table of Contents
Is 2/3 the Same as 3/4? A Deep Dive into Fraction Comparison
The question, "Is 2/3 the same as 3/4?" might seem simple at first glance. However, a thorough understanding of fractions and their representation unlocks a deeper appreciation for mathematical reasoning. This article will delve into various methods for comparing fractions, demonstrating why 2/3 and 3/4 are not equivalent, and exploring related concepts to solidify your understanding of fractional arithmetic.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Refresher
Before comparing 2/3 and 3/4, let's revisit the fundamental concept of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two key components:
- Numerator: The top number indicates how many parts we have.
- Denominator: The bottom number represents the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
For example, in the fraction 2/3, the numerator (2) signifies that we possess two parts, while the denominator (3) indicates that the whole is divided into three equal parts.
Method 1: Finding a Common Denominator
One of the most straightforward methods for comparing fractions is to find a common denominator. This involves converting both fractions so they share the same denominator. The common denominator is a multiple of both original denominators.
Let's apply this to 2/3 and 3/4:
-
Find the Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of 3 and 4 is 12. This means we will convert both fractions to have a denominator of 12.
-
Convert 2/3: To get a denominator of 12, we multiply both the numerator and denominator of 2/3 by 4: (2 x 4) / (3 x 4) = 8/12
-
Convert 3/4: To get a denominator of 12, we multiply both the numerator and denominator of 3/4 by 3: (3 x 3) / (4 x 3) = 9/12
-
Compare: Now we can easily compare 8/12 and 9/12. Since 9 > 8, we conclude that 3/4 > 2/3.
Method 2: Converting to Decimals
Another effective way to compare fractions is to convert them into decimals. This involves dividing the numerator by the denominator.
-
Convert 2/3 to a decimal: 2 ÷ 3 ≈ 0.6667 (repeating decimal)
-
Convert 3/4 to a decimal: 3 ÷ 4 = 0.75
-
Compare: Comparing 0.6667 and 0.75, we see that 0.75 > 0.6667, confirming that 3/4 > 2/3.
Method 3: Visual Representation
Visual aids can be incredibly helpful in understanding fraction comparisons, especially for beginners. Imagine two identical circles:
-
Representing 2/3: Divide the first circle into three equal parts and shade two of them.
-
Representing 3/4: Divide the second circle into four equal parts and shade three of them.
By visually comparing the shaded areas, it's evident that the shaded portion in the 3/4 circle is larger than the shaded portion in the 2/3 circle. This visual representation reinforces the conclusion that 3/4 > 2/3.
Understanding the Difference: Why it Matters
The difference between 2/3 and 3/4, while seemingly small, can have significant implications in various contexts:
-
Baking: Precise measurements are crucial in baking. Using 2/3 of a cup instead of 3/4 could result in a noticeably different outcome.
-
Construction: In construction, even minor discrepancies in measurements can lead to structural problems.
-
Finance: In financial calculations, accurate fraction representation is essential for precise interest calculations and investment analysis.
-
Science: Scientific experiments often require precise measurements and calculations, making a clear understanding of fractions indispensable.
Further Exploration: Working with Fractions
Beyond comparing 2/3 and 3/4, understanding various fraction operations is vital:
Adding and Subtracting Fractions:
To add or subtract fractions, you must have a common denominator. Once you have a common denominator, add or subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same.
Example: 1/2 + 1/4 = (2/4) + (1/4) = 3/4
Multiplying Fractions:
Multiplying fractions is straightforward: multiply the numerators together and multiply the denominators together.
Example: (1/2) x (1/4) = 1/8
Dividing Fractions:
To divide fractions, invert the second fraction (reciprocal) and then multiply.
Example: (1/2) ÷ (1/4) = (1/2) x (4/1) = 4/2 = 2
Conclusion: Mastering Fractions for Everyday Life
The seemingly simple question of whether 2/3 is the same as 3/4 leads us to a deeper understanding of fractions and their significance in various aspects of life. Whether you're baking a cake, building a house, or analyzing financial data, a solid grasp of fraction operations is essential. By mastering the techniques outlined above – finding common denominators, converting to decimals, and using visual aids – you'll confidently navigate the world of fractions and their practical applications. Remember that precision in dealing with fractions is not just a mathematical concept; it's a skill that translates to accuracy and success in many real-world scenarios. So, next time you encounter fractions, remember the methods discussed, and confidently compare and manipulate these important mathematical building blocks.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Graph Absolute Value On A Ti 84
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Cups In 1 2 Liters
May 09, 2025
-
How To Find Square Root Of 12
May 09, 2025
-
What Is A 14 Out Of 30
May 09, 2025
-
Graph The Equation Y 3x 1
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 2/3 The Same As 3/4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.