Is 10 A Prime Or Composite
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
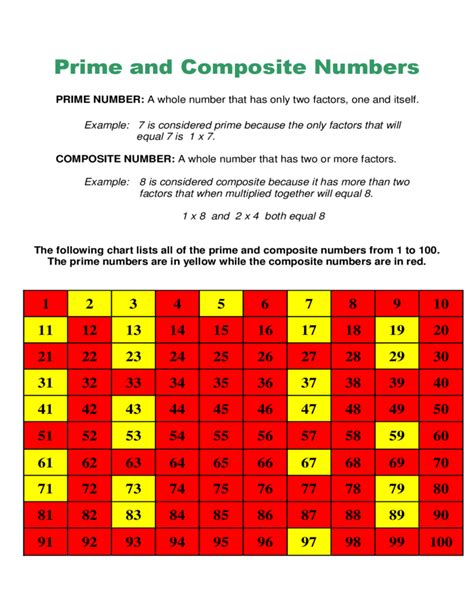
Table of Contents
Is 10 a Prime or Composite Number? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Determining whether a number is prime or composite is a fundamental concept in number theory. This seemingly simple question – is 10 a prime or composite number? – opens the door to understanding the building blocks of mathematics and the fascinating world of prime factorization. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question definitively but will also explore the underlying principles, providing you with a solid grasp of prime and composite numbers.
Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
Before we delve into the specifics of the number 10, let's establish a clear understanding of the definitions:
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This means it's only divisible by 1 and the number itself without leaving a remainder. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other natural numbers through a process called prime factorization.
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not prime. In other words, it has at least one positive divisor other than 1 and itself. Composite numbers can be expressed as a product of two or more prime numbers. Examples include 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 9 (3 x 3), and 10 (2 x 5).
The Number 1: The number 1 is neither prime nor composite. This is a special case that's crucial to understand. While it's a divisor of all other natural numbers, it doesn't fit the definition of a prime number (it doesn't have two distinct divisors) nor a composite number (it can't be expressed as a product of primes).
Is 10 a Prime or Composite Number? The Answer
Now, let's address the main question: Is 10 a prime or composite number?
The answer is unequivocally composite.
Here's why:
-
Divisibility: 10 is divisible by 1, 2, 5, and 10. Since it has divisors other than 1 and itself (specifically, 2 and 5), it fails the definition of a prime number.
-
Prime Factorization: 10 can be expressed as a product of prime numbers: 2 x 5. This prime factorization confirms its composite nature. It's built from smaller, indivisible prime numbers.
Exploring the Properties of Composite Numbers: The Case of 10
The number 10 serves as a great example to illustrate several properties of composite numbers:
1. Multiple Divisors:
As mentioned earlier, 10 has multiple divisors beyond 1 and itself (2 and 5). This abundance of divisors is a hallmark of composite numbers. The more divisors a number possesses, the more "composite" it is considered to be.
2. Prime Factorization:
The prime factorization of 10 (2 x 5) is unique. Every composite number can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic). This factorization is a powerful tool in various mathematical applications, from cryptography to number theory.
3. Abundant Numbers (A Special Case):
While not directly related to the prime/composite classification, the number of divisors of 10 can be used to illustrate the concept of abundant numbers. An abundant number is a number where the sum of its proper divisors (excluding itself) is greater than the number itself. The proper divisors of 10 are 1, 2, and 5, which sum to 8 (less than 10). Therefore, 10 is not an abundant number, but this exemplifies a further property that can be explored in relation to divisors.
Practical Applications and Significance
Understanding the difference between prime and composite numbers is not just an academic exercise. It has significant practical implications in various fields:
1. Cryptography:
Prime numbers play a crucial role in modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms, such as RSA, rely on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime components. The security of these systems hinges on the fact that factoring very large numbers is computationally very intensive.
2. Computer Science:
Prime numbers and their properties are used in various computer science algorithms and data structures, such as hash tables and random number generators. Efficient algorithms for prime factorization and primality testing are crucial for optimization.
3. Number Theory:
The study of prime numbers is a core area of number theory, a branch of mathematics with deep theoretical implications and connections to other fields. Many unsolved problems in mathematics are related to prime numbers, such as the Riemann Hypothesis.
Further Exploration: Beyond the Basics
Once we've established the fundamental understanding of prime and composite numbers, we can delve deeper into related concepts:
1. Sieve of Eratosthenes:
This is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit. It's a fascinating example of how algorithmic thinking can be applied to number theory.
2. Twin Primes:
These are pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2 (e.g., 3 and 5, 11 and 13). The distribution of twin primes is a subject of ongoing research in number theory.
3. Goldbach's Conjecture:
This famous unsolved conjecture states that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two primes. It remains unproven despite extensive research.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
The simple question, "Is 10 a prime or composite number?" serves as a gateway to a much broader understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. By understanding prime and composite numbers, we gain insight into the building blocks of numbers, their properties, and their significant applications in various fields. The composite nature of 10, its prime factorization (2 x 5), and the implications of its divisors illustrate the richness and depth of number theory. The exploration doesn't end here; the journey into the world of primes and composites is a continuous adventure filled with fascinating discoveries and unsolved mysteries.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2 1 4 As A Fraction
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 4 Percent Of 100
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Percentage Is 7 Of 20
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Do Insulators Have A Low Heat Capacity
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Distinguishes One Element From Another
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 10 A Prime Or Composite . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
