Integral Of Square Root Of 4 X 2
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
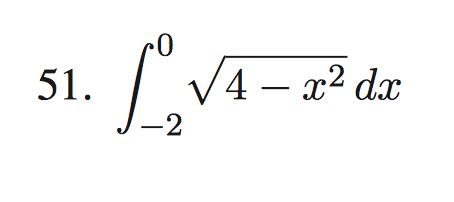
Table of Contents
Decoding the Integral of √(4x²): A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple integral ∫√(4x²) dx might appear daunting at first glance, but with a systematic approach and a solid understanding of integration techniques, it becomes entirely manageable. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of solving this integral, exploring various methods and offering insights into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll cover everything from basic integration rules to more advanced techniques, ensuring a thorough understanding for readers of all levels.
Understanding the Problem: ∫√(4x²) dx
Before diving into the solution, let's break down the problem. The integral ∫√(4x²) dx asks us to find the antiderivative of the function f(x) = √(4x²). This means finding a function F(x) such that F'(x) = f(x). The presence of the square root and the squared term indicates that we'll likely need to employ techniques beyond simple power rule integration.
Simplification and Absolute Values: The Crucial First Step
The first step towards solving this integral is simplification. We can rewrite the expression inside the square root as follows:
√(4x²) = √(4) * √(x²) = 2|x|
Notice the crucial inclusion of the absolute value symbol, |x|. This is essential because the square root of a number is always non-negative. While √(x²) = x might seem correct, it's only true for positive x. For negative x, √(x²) = -x. The absolute value function ensures correctness across the entire domain of x.
Our integral now becomes:
∫2|x| dx
Solving the Integral: Considering Different Cases
Because of the absolute value function, we need to consider two cases: x ≥ 0 and x < 0.
Case 1: x ≥ 0
When x ≥ 0, |x| = x. The integral simplifies to:
∫2x dx
Applying the power rule of integration (∫xⁿ dx = (xⁿ⁺¹)/(n+1) + C, where n ≠ -1 and C is the constant of integration), we get:
∫2x dx = 2 * (x²/2) + C = x² + C
Case 2: x < 0
When x < 0, |x| = -x. The integral becomes:
∫2(-x) dx = ∫-2x dx
Again, applying the power rule of integration:
∫-2x dx = -2 * (x²/2) + C = -x² + C
Combining the Results: The Complete Solution
We now have two solutions, one for x ≥ 0 and one for x < 0. To express the complete solution, we can use a piecewise function:
F(x) = { x² + C₁ if x ≥ 0 { -x² + C₂ if x < 0
where C₁ and C₂ are constants of integration. While C₁ and C₂ can be different, we can simplify this by combining them into a single constant, C. However, it's crucial to understand that this simplification doesn't imply that the function is entirely differentiable at x = 0. The derivative is not continuous at x = 0; it has a jump discontinuity.
A More Concise Solution Using the Absolute Value
While the piecewise function provides a precise representation, a more concise, albeit less explicit, solution utilizes the absolute value:
∫2|x| dx = x|x| + C
This formulation encapsulates both cases within a single expression. It's important to remember that the derivative of x|x| is 2|x|.
Visualizing the Solution: Graphical Representation
A graph of the antiderivative, y = x|x|, helps visualize the solution. Notice the cusp (a sharp point) at x = 0. This cusp reflects the non-differentiability at that point, reinforcing the importance of considering the absolute value and its implications.
Exploring Alternative Approaches: Trigonometric Substitution
While the absolute value method offers the most straightforward solution, alternative approaches exist, such as trigonometric substitution. Although not the most efficient method for this particular integral, exploring it enhances our understanding of different integration techniques. Let's briefly consider this approach:
Let x = (2/2)sinθ (This substitution simplifies the expression under the square root.)
Then dx = (2/2)cosθ dθ
The integral transforms into:
∫√(4((2/2)sinθ)²) * (2/2)cosθ dθ = ∫2|(2/2)sinθ| * (2/2)cosθ dθ = 2∫|sinθ|cosθ dθ
This integral requires careful handling of the absolute value of sinθ, splitting it into cases based on the sign of sinθ within the range of θ. This will lead to a solution equivalent to the previous result after appropriate back-substitution.
Practical Applications and Significance
The integral of √(4x²) and similar integrals find applications in various fields:
- Physics: Calculating areas, volumes, and other physical quantities related to curves and shapes defined by quadratic functions.
- Engineering: Solving problems related to the calculation of distances, areas, and centroids in structural design and mechanics.
- Calculus and Analysis: This integral serves as an important example to illustrate various integration techniques and the significance of the absolute value in handling square roots.
Advanced Considerations and Extensions
The problem can be further generalized to ∫√(ax²) dx, where 'a' is a constant. The solution follows a similar pattern, leading to (√a/3)x|x| + C. This extension showcases the flexibility of the solution method.
Conclusion
Solving the integral ∫√(4x²) dx involves more than just applying the power rule. The critical step lies in correctly handling the absolute value that arises from the square root of x². This emphasizes the importance of careful mathematical rigor when dealing with absolute values and square roots within integrals. Understanding the nuances of this integral provides valuable insight into the versatility of integration techniques and their applications in various scientific and engineering fields. While different approaches exist, such as trigonometric substitution, the method involving absolute values proves to be the most efficient and directly applicable. Remember to always consider the domain and range of the function to ensure accuracy and avoid common pitfalls. By understanding the complete solution and the rationale behind it, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle more complex integration problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Stomach Is Inferior To The Diaphragm
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is Rotting A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which One Warm The Solvent Decrease
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 2 And 12
Mar 18, 2025
-
Simplify 1 X 1 1 X
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of Square Root Of 4 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
