Human Body Temperature In Kelvin Scale
listenit
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
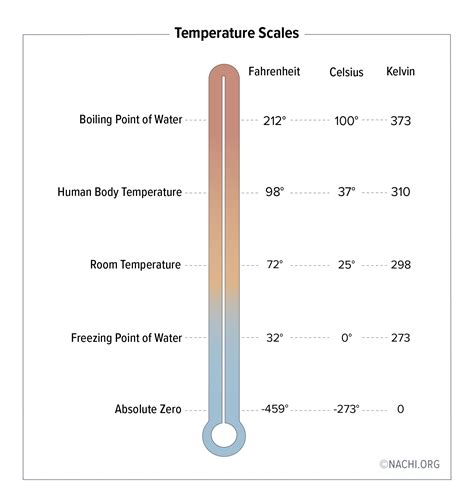
Table of Contents
Human Body Temperature in the Kelvin Scale: A Comprehensive Guide
Human body temperature is a fundamental aspect of our physiology, reflecting the intricate balance of metabolic processes and heat exchange with the environment. While commonly expressed in Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F), understanding body temperature in the Kelvin scale (K) provides a deeper insight into its thermodynamic significance. This article delves into the intricacies of human body temperature, exploring its measurement, regulation, variations, and implications within the Kelvin scale.
Understanding the Kelvin Scale
Before diving into human body temperature, let's briefly revisit the Kelvin scale. Unlike Celsius and Fahrenheit, which are relative scales with arbitrary zero points, the Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. Its zero point, 0 K (absolute zero), represents the theoretical absence of all thermal energy. This makes it particularly useful in scientific contexts where absolute temperature values are crucial. The relationship between Kelvin and Celsius is straightforward: K = °C + 273.15.
Normal Human Body Temperature in Kelvin
The average human body temperature is often cited as 37°C (98.6°F). Converting this to Kelvin, we get:
37°C + 273.15 = 310.15 K
This value, 310.15 K, represents the average human body temperature in the Kelvin scale. It's important to note that this is an average, and individual body temperatures can fluctuate slightly throughout the day and between individuals.
Factors Affecting Body Temperature
Several factors can influence an individual's body temperature, leading to variations from the average 310.15 K. Understanding these factors is crucial for proper interpretation of temperature readings and for diagnosing potential health issues.
1. Diurnal Variation: The Body's Internal Clock
The body's internal clock, or circadian rhythm, plays a significant role in daily temperature fluctuations. Body temperature typically exhibits a diurnal rhythm, with the lowest temperature occurring in the early morning hours and the highest in the late afternoon or early evening. This variation can range from 0.5°C to 1°C (approximately 0.9 K to 1.8 K), a seemingly small difference with significant physiological implications.
2. Age: Developmental Changes in Thermoregulation
Body temperature regulation changes throughout life. Infants and young children have less efficient thermoregulation, making them more susceptible to hypothermia and hyperthermia. Elderly individuals also experience altered thermoregulation, often exhibiting lower average body temperatures than younger adults. These variations translate directly to differences in Kelvin values, with lower temperatures in Kelvin reflecting reduced metabolic activity and heat production.
3. Physical Activity: Metabolic Heat Production
Physical activity significantly increases metabolic rate, resulting in greater heat production. Intense exercise can elevate body temperature by several degrees Celsius, which translates to a noticeable increase in Kelvin. The body's thermoregulatory mechanisms, such as sweating and increased blood flow to the skin, work to dissipate this excess heat, maintaining a relatively stable core temperature.
4. Environmental Factors: External Temperature and Humidity
Environmental conditions such as ambient temperature and humidity play a crucial role in heat exchange between the body and its surroundings. In hot and humid environments, the body's ability to dissipate heat through sweating is reduced, potentially leading to hyperthermia. Conversely, exposure to cold environments can lead to hypothermia, a dangerous drop in body temperature. These environmental effects directly impact the body's temperature in Kelvin, reflecting the dynamic interplay between internal heat production and external heat loss.
5. Hormonal Influences: The Role of Hormones in Thermoregulation
Hormones, particularly those involved in metabolism and stress response, can influence body temperature. For instance, women experience fluctuating body temperatures throughout their menstrual cycle, with slightly elevated temperatures during the luteal phase. Furthermore, certain illnesses and medications can alter hormonal balance, indirectly affecting body temperature.
6. Illness and Disease: Fever as a Defense Mechanism
Fever, a temporary increase in body temperature, is a common physiological response to infection or inflammation. While often viewed as a symptom, fever is actually a crucial part of the body's immune response, enhancing the effectiveness of immune cells in fighting pathogens. The increase in body temperature, measured in Kelvin, reflects the body's attempt to create an unfavorable environment for pathogens.
Measuring Body Temperature in Kelvin
While body temperature is commonly measured using Celsius or Fahrenheit scales, conversion to Kelvin is straightforward. Various methods exist for measuring body temperature, each with its own advantages and limitations.
- Oral Temperature: This method is convenient and widely used, but can be affected by recent food or beverage intake.
- Rectal Temperature: This method provides a more accurate core body temperature, particularly useful in infants and young children.
- Axillary Temperature: This method is less accurate than oral or rectal measurements but is often preferred for its non-invasive nature.
- Tympanic Temperature: This method utilizes an infrared thermometer to measure temperature in the ear canal, providing a relatively quick and convenient measurement.
Regardless of the method used, the temperature obtained in Celsius or Fahrenheit can be easily converted to Kelvin using the formula K = °C + 273.15.
Clinical Significance of Body Temperature in Kelvin
Understanding body temperature in the Kelvin scale, though not routinely used in clinical practice, offers a valuable perspective for researchers and clinicians. The absolute nature of the Kelvin scale allows for a more precise representation of thermodynamic changes within the body. This is particularly important in studies focusing on metabolic processes, heat exchange, and the effects of environmental factors on thermoregulation. Deviations from the typical 310.15 K, whether due to illness, environmental stress, or other factors, can provide crucial diagnostic information.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Human Thermophysiology
Understanding human body temperature in the Kelvin scale adds a layer of precision and scientific rigor to our understanding of thermophysiology. While clinical practice predominantly uses Celsius or Fahrenheit, the absolute nature of Kelvin provides a valuable perspective for research and advanced understanding. By considering the various factors influencing body temperature and its measurement methods, we gain a deeper appreciation of the intricate mechanisms that maintain our internal thermal homeostasis, a fundamental aspect of life itself. Further research using the Kelvin scale will continue to refine our understanding of human thermoregulation and its implications for health and disease. This improved understanding is crucial for the development of more effective diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions. The dynamic interplay between internal metabolic processes and external environmental conditions, clearly visible in the context of the Kelvin scale, continues to be a fertile area for scientific investigation and innovation. This detailed exploration not only enhances our scientific understanding but also underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy body temperature, measured however, to ensure optimal physiological function and overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Is Water Liquid At Room Temperature
Apr 01, 2025
-
How To Determine The Density Of A Solid
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Long Does It Take To Drive 1500 Miles
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is 1 6 As A Percent
Apr 01, 2025
-
11 Is What Percent Of 97
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Human Body Temperature In Kelvin Scale . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
