How To Get Perimeter From Area
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
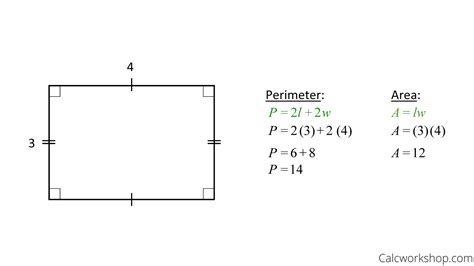
Table of Contents
How to Get Perimeter from Area: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the perimeter of a shape solely from its area is not always possible. This is because area and perimeter are independent geometric properties. Knowing the area only gives you information about the enclosed space, not the length of the boundary. However, for certain shapes, under specific conditions, we can establish a relationship between area and perimeter, allowing us to calculate one from the other. This guide will explore these scenarios and provide you with the necessary formulas and methods.
Understanding Area and Perimeter
Before diving into the methods, let's clarify the definitions:
-
Area: The amount of two-dimensional space within a shape's boundaries. It is measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square feet).
-
Perimeter: The total distance around the shape's exterior boundary. It is measured in linear units (e.g., meters, feet).
The fundamental difference is that area measures the space inside a shape, while perimeter measures the distance around the shape. This distinction is crucial to understanding why we can't always deduce one from the other.
Scenarios Where Perimeter Can Be Determined from Area
There are limited cases where calculating perimeter from area is feasible. These typically involve shapes with constraints or known relationships between their sides. Let's examine the most common scenarios:
1. Squares
A square is a special case because all its sides are equal. Let's denote the side length as 's'.
- Area of a square: A = s²
- Perimeter of a square: P = 4s
To find the perimeter from the area:
- Find the side length: s = √A
- Calculate the perimeter: P = 4√A
Example: If a square has an area of 25 square meters, its side length is √25 = 5 meters. Therefore, its perimeter is 4 * 5 = 20 meters.
2. Circles
For circles, we have a direct relationship between area and radius, and radius is essential to calculating the perimeter (circumference).
- Area of a circle: A = πr²
- Circumference of a circle: C = 2πr
To find the circumference from the area:
- Find the radius: r = √(A/π)
- Calculate the circumference: C = 2π√(A/π) = 2√(Aπ)
Example: If a circle has an area of 16π square centimeters, its radius is √(16π/π) = 4 centimeters. Therefore, its circumference is 2π * 4 = 8π centimeters.
3. Rectangles with a Fixed Ratio of Sides
If we know the ratio between the length and width of a rectangle, we can establish a relationship between area and perimeter. Let's say the length is 'l' and the width is 'w'. If we know that l = kw (where k is a constant), then:
- Area of a rectangle: A = lw = kw²
- Perimeter of a rectangle: P = 2(l + w) = 2(kw + w) = 2w(k+1)
We can solve for 'w' using the area formula and then substitute it into the perimeter formula to find P.
Example: If a rectangle has an area of 24 square inches and the length is twice the width (l = 2w), then:
- Find the width: 2w² = 24 => w² = 12 => w = √12 = 2√3 inches
- Find the length: l = 2w = 4√3 inches
- Calculate the perimeter: P = 2(4√3 + 2√3) = 12√3 inches
4. Regular Polygons
For regular polygons (polygons with all sides and angles equal), a similar approach can be used. However, the formulas become more complex as the number of sides increases. You would need to use trigonometry and the polygon's interior angle to derive a relationship between area and side length, and subsequently the perimeter.
5. Using Calculus (For Irregular Shapes)
For irregular shapes where a simple formula doesn't exist, calculus can be employed. If you have a function describing the shape's boundary, you can integrate to find the area and use techniques like arc length integration to find the perimeter. However, this approach is significantly more advanced and requires a strong understanding of calculus.
Why We Can't Always Find Perimeter from Area
In most cases, knowing the area of a shape doesn't provide enough information to determine its perimeter. Consider these points:
-
Infinite Possibilities: For a given area, an infinite number of shapes can be constructed. For example, you can have rectangles of various dimensions with the same area, each having a different perimeter. Similarly, you can have irregular shapes with the same area but vastly different perimeters.
-
Independent Geometric Properties: Area and perimeter are fundamentally different geometric properties that are not directly related in a universally applicable formula. They quantify different aspects of the shape.
-
Lack of Constraints: Without additional information about the shape (e.g., the type of polygon, ratio of sides, or a specific equation defining the boundary), it's impossible to uniquely determine the perimeter from only the area.
Practical Applications and Considerations
Understanding the relationship between area and perimeter has practical applications in various fields:
-
Land surveying: Determining the perimeter of a land plot from its area, especially when dealing with irregular shapes. While direct calculation is impossible without additional information, approximations can be made using surveying techniques and software.
-
Architecture and engineering: Optimizing the design of buildings and structures to minimize perimeter while maintaining a desired area (e.g., minimizing the length of walls for a specific floor area).
-
Manufacturing and packaging: Designing containers with minimum material usage (perimeter) while ensuring sufficient volume (area) is important for cost efficiency.
Conclusion
While calculating the perimeter from the area is straightforward for specific shapes like squares and circles, it's generally not possible without additional constraints or information about the shape. Understanding the limitations and the scenarios where a relationship exists is crucial for accurately determining perimeter from area. Remember, this relationship is highly dependent on the shape's geometric properties and the available information. This guide provides a solid foundation for understanding this key concept in geometry and its application in various real-world contexts. For irregular shapes, approximate methods or advanced techniques like calculus might be necessary. Always consider the specific shape and its properties before attempting to calculate the perimeter from its area.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm For 12 And 15
Mar 15, 2025
-
6 1 2 In Decimal Form
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Ounces In 5th Of Liquor
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 6 Cm In Mm
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 68 Of 118 Tons
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Get Perimeter From Area . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
