How To Find The Sum Of Interior Angles
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
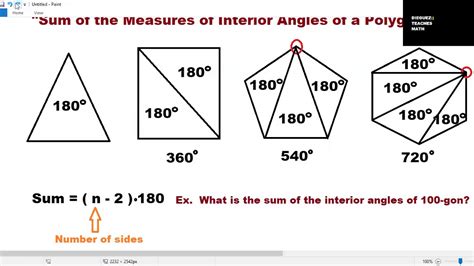
Table of Contents
How to Find the Sum of Interior Angles: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding how to find the sum of interior angles is a fundamental concept in geometry, crucial for solving various problems related to polygons. This comprehensive guide explores different methods, catering to various learning styles and mathematical backgrounds. We'll cover everything from simple triangles to complex polygons, providing you with the tools and knowledge to tackle any angle-sum challenge.
Understanding Polygons and Their Angles
Before diving into the formulas, let's clarify some key terminology:
- Polygon: A closed two-dimensional figure with three or more straight sides. Examples include triangles, squares, pentagons, hexagons, and so on.
- Interior Angle: An angle formed inside a polygon by two adjacent sides.
- Exterior Angle: An angle formed by one side of a polygon and the extension of an adjacent side.
- Regular Polygon: A polygon where all sides are equal in length and all interior angles are equal in measure. An equilateral triangle and a square are examples of regular polygons.
- Irregular Polygon: A polygon where sides and/or angles are not all equal.
Method 1: Using the Formula for Triangles
The foundation of finding the sum of interior angles for any polygon lies in understanding triangles. A triangle, the simplest polygon, always has interior angles that add up to 180 degrees. This is a fundamental postulate in Euclidean geometry.
This seemingly simple fact is the key to unlocking the angle sums of all polygons. Why? Because any polygon can be divided into triangles.
How to apply this method:
-
Divide the polygon into triangles: Choose a single vertex (corner) of the polygon and draw diagonals from this vertex to all other non-adjacent vertices. This will divide the polygon into several triangles.
-
Count the number of triangles: The number of triangles formed will depend on the number of sides of the polygon. A quadrilateral (4 sides) will be divided into 2 triangles. A pentagon (5 sides) will be divided into 3 triangles, and so on.
-
Calculate the total angle sum: Since each triangle has an interior angle sum of 180 degrees, multiply the number of triangles by 180 to find the total sum of interior angles for the polygon.
Example:
Let's find the sum of interior angles of a hexagon (6 sides):
- A hexagon can be divided into 4 triangles.
- Total angle sum = 4 triangles * 180 degrees/triangle = 720 degrees.
Therefore, the sum of interior angles of a hexagon is 720 degrees.
Method 2: Using the Formula Based on the Number of Sides
This method provides a more direct approach, eliminating the need to draw triangles each time. The formula is derived from the triangle method and directly relates the number of sides (n) to the sum of interior angles (S):
S = (n - 2) * 180
Where:
- S represents the sum of interior angles.
- n represents the number of sides of the polygon.
Example:
Let's use this formula to find the sum of interior angles of an octagon (8 sides):
S = (8 - 2) * 180 = 6 * 180 = 1080 degrees.
The sum of interior angles of an octagon is 1080 degrees.
Method 3: Calculating Individual Interior Angles (Regular Polygons)
For regular polygons (where all sides and angles are equal), you can calculate the measure of each individual interior angle using a slightly modified formula derived from the previous methods.
Individual Interior Angle = [(n - 2) * 180] / n
Where:
- n represents the number of sides of the polygon.
Example:
Let's find the measure of each interior angle of a regular pentagon (5 sides):
Individual Interior Angle = [(5 - 2) * 180] / 5 = (3 * 180) / 5 = 108 degrees.
Each interior angle of a regular pentagon measures 108 degrees.
Method 4: Using Exterior Angles
Exterior angles offer an alternative approach. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, regardless of whether it's regular or irregular, is always 360 degrees. This property can be used to indirectly find the sum of interior angles.
How to apply this method:
-
Find the measure of one exterior angle: For regular polygons, this is simply 360/n, where 'n' is the number of sides. For irregular polygons, you'll need to calculate each exterior angle individually and then sum them.
-
Calculate the corresponding interior angle: Remember that an interior angle and its corresponding exterior angle are supplementary (they add up to 180 degrees). Subtract the exterior angle from 180 to find the interior angle.
-
Find the total sum of interior angles: Multiply the individual interior angle by the number of sides (n).
Example (Regular Polygon):
Let's find the sum of interior angles of a regular hexagon (6 sides) using the exterior angle method:
- Each exterior angle = 360 / 6 = 60 degrees.
- Each interior angle = 180 - 60 = 120 degrees.
- Sum of interior angles = 120 degrees/angle * 6 angles = 720 degrees.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
The principles discussed above form the basis for solving more complex geometric problems. Here are some advanced applications:
-
Tessellations: Understanding interior angle sums is crucial for determining which polygons can tessellate (tile a plane without gaps or overlaps). Regular polygons that tessellate have interior angles that are factors of 360 degrees.
-
Calculating Areas of Polygons: Knowing the angles and side lengths of a polygon is often necessary to calculate its area using various trigonometric formulas.
-
Three-Dimensional Geometry: The concept of interior angles extends to three-dimensional shapes, where the focus shifts to dihedral angles (angles between two intersecting planes).
-
Computer Graphics and CAD: These fields heavily rely on precise calculations of angles and polygons for creating and manipulating two and three-dimensional models.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
-
Incorrect Triangle Count: Double-check the number of triangles you've created when dividing a polygon.
-
Confusing Interior and Exterior Angles: Remember the relationship between interior and exterior angles: they are supplementary.
-
Misapplication of Formulas: Carefully review the formulas and ensure you're using the correct values for 'n' (number of sides).
-
Assumptions about Regularity: Don't assume a polygon is regular unless explicitly stated. The formulas for individual interior angles only apply to regular polygons.
Conclusion
Finding the sum of interior angles is a fundamental skill in geometry with applications across various fields. By mastering the methods outlined in this guide, you'll be equipped to confidently solve a wide range of problems involving polygons, enhancing your understanding of geometric principles and their practical applications. Remember to practice regularly and don't hesitate to revisit the different methods to solidify your comprehension. With consistent practice, these concepts will become second nature, and you'll find yourself effortlessly tackling even the most challenging geometric problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 3 Times 8
May 09, 2025
-
1 4 Ton Equals How Many Pounds
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Does An Atom Of Carbon Have
May 09, 2025
-
Number Of Valence Electrons In B
May 09, 2025
-
How To Solve A Polynomial Inequality
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find The Sum Of Interior Angles . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.