How To Find The Radian Measure Of A Central Angle
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
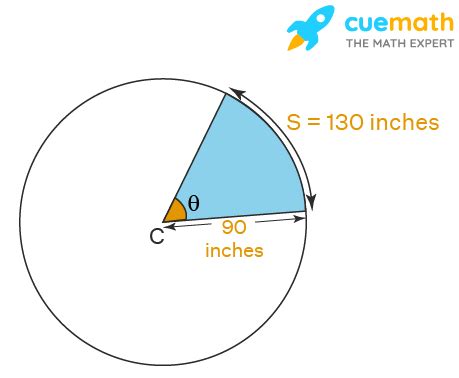
Table of Contents
How to Find the Radian Measure of a Central Angle
Understanding how to find the radian measure of a central angle is fundamental to mastering trigonometry and various applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, exploring different methods, offering practical examples, and clarifying common misconceptions. By the end, you'll be confident in calculating radian measures and applying this knowledge to solve real-world problems.
What is a Radian?
Before diving into the methods, let's establish a clear understanding of what a radian actually represents. A radian is a unit of measurement for angles, just like degrees. However, instead of relying on an arbitrary division of a circle into 360 parts (degrees), a radian is defined using the circle's radius.
One radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc that is equal in length to the radius of the circle. This definition is crucial. Imagine a circle with radius 'r'. If you trace an arc along the circumference that's also of length 'r', the angle formed at the circle's center by that arc is one radian.
The Relationship Between Radians and Degrees
The circumference of a circle is given by the formula: C = 2πr. Since one radian corresponds to an arc length equal to the radius, there are 2π radians in a full circle (360 degrees). This gives us the essential conversion factors:
- Radians to Degrees: Multiply the radian measure by
180/π - Degrees to Radians: Multiply the degree measure by
π/180
This relationship is the cornerstone of converting between these two angle measurement systems.
Methods for Finding the Radian Measure of a Central Angle
There are several ways to determine the radian measure of a central angle, depending on the information provided.
Method 1: Using the Arc Length and Radius
This is the most direct method, stemming directly from the definition of a radian. The formula is:
θ (in radians) = arc length / radius
Where:
- θ represents the central angle in radians.
- Arc length is the length of the arc subtended by the central angle.
- Radius is the radius of the circle.
Example:
A circle has a radius of 5 cm. An arc subtends a central angle. If the arc length is 10 cm, what is the radian measure of the central angle?
θ = 10 cm / 5 cm = 2 radians
This method is straightforward when you know both the arc length and the radius.
Method 2: Using the Proportion Method
This method leverages the relationship between the circumference of a circle (2πr) and the total angle (2π radians or 360 degrees). We can set up a proportion:
(Central Angle in Radians) / (2π radians) = (Arc Length) / (2πr)
This proportion allows us to find the radian measure when we know the arc length and the radius. Note that this method is essentially the same as Method 1, just expressed differently.
Method 3: Converting from Degrees
If the central angle is given in degrees, the conversion factor is applied directly:
Radians = Degrees × (π/180)
Example:
Convert 60 degrees to radians:
Radians = 60° × (π/180) = π/3 radians
Method 4: Using Trigonometric Functions (Advanced)
In more complex scenarios involving triangles within a circle, trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) can be used in conjunction with the radius and other known side lengths to determine the central angle. This often involves employing inverse trigonometric functions (arcsin, arccos, arctan) to find the angle.
Example: Imagine a right-angled triangle inscribed within a circle. You know the length of the opposite side and the hypotenuse (which is the radius). You can use the arcsin function to find the angle, which is also the central angle subtended by the arc. The formula would be:
θ = arcsin (opposite/hypotenuse)
Remember to check your calculator's settings to ensure it's in radian mode.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Mixing Degrees and Radians: The most frequent error is performing calculations without converting angles to a consistent unit (either degrees or radians). Always make sure your units are consistent throughout your calculations.
-
Incorrect Use of the Formula: Ensure you use the correct formula (θ = arc length / radius) and understand the units involved.
-
Calculator Mode: Double-check your calculator's mode setting. It must be set to "radians" for calculations involving radians and "degrees" for calculations involving degrees. Performing operations in the incorrect mode will lead to inaccurate results.
Practical Applications of Radian Measure
Radian measure is not just a theoretical concept; it has significant practical applications in various fields:
-
Physics: In rotational motion, angular velocity and angular acceleration are naturally expressed in radians per second and radians per second squared, respectively.
-
Engineering: Radian measure is crucial in designing circular gears, rotating machinery, and other mechanical systems.
-
Calculus: Many calculus concepts, such as derivatives and integrals of trigonometric functions, are much simpler and more elegant when using radian measure.
-
Computer Graphics: Radian measure plays a vital role in computer graphics and animation, particularly when dealing with rotations and transformations.
-
Navigation and Surveying: Calculating distances and bearings using spherical trigonometry relies heavily on understanding and applying radian measure.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
As you delve deeper into mathematics, you'll encounter more advanced concepts related to radian measure, such as:
-
Taylor Series Expansions: The Taylor series expansions of trigonometric functions are based on radian measure.
-
Complex Numbers: Euler's formula (e^(ix) = cos(x) + i sin(x)) connects exponential functions with trigonometric functions through the use of radian measure.
-
Differential Geometry: Radian measure is fundamental in differential geometry, which deals with the properties of curves and surfaces.
Conclusion
Mastering the ability to find the radian measure of a central angle is a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. By using the methods outlined in this guide, practicing diligently, and avoiding common pitfalls, you'll develop a strong foundation in this critical concept. Remember to understand the relationship between radians and degrees, apply the appropriate formulas accurately, and be mindful of your calculator's mode settings. With consistent practice and a clear understanding of the underlying principles, you can confidently tackle any problem involving radian measure. The more you work with radians, the more intuitive and valuable they'll become in your mathematical journey.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In Eukaryotic Cells Where Does Dna Replication Occur
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Happens To Water Molecules In The Light Reactions
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Are In 1 4 Of A Pound
Mar 29, 2025
-
Does Blue Litmus Turns Red In Acid
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 6 And 14
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find The Radian Measure Of A Central Angle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
