How Much Of The World Is Desert
listenit
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
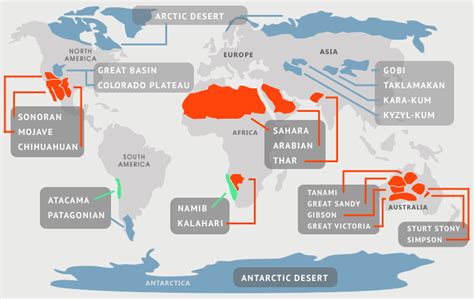
Table of Contents
How Much of the World is Desert? Unveiling the Expansive Arid Landscapes
The vastness of deserts often captures our imagination, conjuring images of endless sand dunes, scorching sun, and hardy, uniquely adapted life. But how much of our planet is actually covered by these arid regions? Understanding the extent of deserts is crucial not only for geographical knowledge but also for addressing crucial environmental concerns like desertification, water scarcity, and biodiversity conservation. This comprehensive exploration delves into the definition of deserts, their global distribution, the impact of climate change, and the importance of understanding these often-misunderstood ecosystems.
Defining Deserts: More Than Just Sand
Before we quantify the world's deserts, it's essential to understand what constitutes a desert. The common misconception of deserts as solely sand-covered expanses is inaccurate. A desert is primarily defined by its low precipitation, typically less than 250 millimeters (10 inches) of rainfall annually. This low rainfall directly impacts the landscape, resulting in sparse vegetation and unique soil characteristics.
However, precipitation is only one component. Other factors contribute to desert formation, including:
- High temperatures: Many deserts experience extremely high temperatures, leading to high rates of evaporation. However, some deserts, like the Gobi Desert, can experience frigid winters.
- Soil type: Desert soils are often poorly developed, rocky, or sandy, hindering water retention.
- Wind erosion: Strong winds play a crucial role in shaping desert landscapes, creating features like sand dunes and exposed bedrock.
This multifaceted definition highlights the diversity within desert environments. We have hot and dry deserts, cold deserts, coastal deserts, and even polar deserts. Each possesses its own unique characteristics, flora, and fauna.
Types of Deserts: A Diverse Landscape
The diverse nature of deserts demands a classification system. Several types exist, based on factors like temperature, precipitation, and location:
- Hot and Dry Deserts: These are the quintessential image of a desert, characterized by high temperatures and minimal rainfall. Examples include the Sahara Desert in Africa and the Arabian Desert in the Middle East.
- Semi-arid Deserts (Steppe): These regions receive slightly more rainfall than true deserts, typically between 250 and 500 millimeters (10-20 inches) annually. They often transition between deserts and other biomes.
- Coastal Deserts: These deserts form along coastlines, influenced by cold ocean currents that suppress rainfall. The Atacama Desert in Chile is a prime example.
- Cold Deserts: These deserts, like the Gobi Desert in Mongolia and the Patagonian Desert in South America, experience cold temperatures, sometimes even freezing winters, despite low precipitation.
- Polar Deserts: These extremely cold and dry regions exist in polar areas like Antarctica and the Arctic. Although covered in ice and snow, they receive minimal precipitation, fulfilling the definition of a desert.
Quantifying the World's Deserts: A Global Perspective
Determining the precise percentage of the Earth's land surface covered by deserts is challenging due to the various definitions and the difficulty in accurately mapping transitional zones. However, estimates suggest that deserts and semi-deserts cover around one-third to one-fifth of the Earth's landmass. This translates to roughly 30-20%, a substantial portion of our planet.
This figure isn't static. The extent of desert regions can fluctuate due to several factors, most notably climate change. Also, the definition of a desert is subjective, leading to differing calculations. Some studies may include semi-arid regions while others might not. Therefore, it's crucial to understand the methodology used when encountering different percentages in research literature.
Major Desert Regions: A Geographic Overview
Deserts are distributed across the globe, often located in specific latitudes known as subtropical high-pressure zones. However, their occurrence also depends on other factors, including proximity to mountains and ocean currents. Some of the world's most prominent desert regions include:
- Sahara Desert (Africa): The largest hot desert in the world, encompassing parts of North Africa.
- Arabian Desert (Middle East): A vast desert spanning several countries in the Middle East.
- Gobi Desert (Asia): A cold desert covering parts of Mongolia and China.
- Patagonian Desert (South America): A cold desert in southern South America.
- Australian Desert (Australia): A large desert region covering much of central Australia.
- Sonoran Desert (North America): A major desert in southwestern North America.
- Atacama Desert (South America): One of the driest deserts in the world, located in Chile.
- Arctic and Antarctic Deserts: Encompassing vast polar regions.
Each of these deserts supports unique ecosystems, adapted to the harsh conditions.
The Impact of Climate Change on Deserts: An Expanding Threat
Climate change significantly impacts desert environments. Rising global temperatures contribute to increased evaporation rates, leading to further aridity and desertification. Changes in precipitation patterns, including increased frequency of droughts and extreme rainfall events, further destabilize fragile desert ecosystems. These changes have far-reaching consequences:
- Desertification: The process by which fertile land becomes desert. This is a major threat to agricultural lands bordering deserts.
- Water scarcity: Decreased rainfall and increased evaporation exacerbate water scarcity, impacting both human populations and desert ecosystems.
- Biodiversity loss: Changes in climate and water availability threaten the unique flora and fauna adapted to desert environments.
- Dust storms: More frequent and intense dust storms can impact air quality regionally and globally.
The Importance of Understanding Deserts: Conservation and Sustainability
Understanding the extent and characteristics of deserts is paramount for several reasons:
- Conservation efforts: Protecting desert ecosystems requires knowledge of their unique biodiversity and the threats they face.
- Sustainable resource management: Managing scarce water resources and minimizing human impact requires a deep understanding of desert environments.
- Combating desertification: Efforts to prevent and reverse desertification require an understanding of the underlying causes and effective strategies.
- Climate change mitigation and adaptation: Understanding the role of deserts in the global climate system is crucial for developing effective strategies for mitigating and adapting to climate change.
Conclusion: A Deeper Appreciation of Arid Landscapes
Deserts, covering a significant portion of the Earth's landmass, represent a vital component of our planet's biodiversity and climate system. While often perceived as barren wastelands, these environments harbor a surprising wealth of unique life and play a crucial role in global climate patterns. Accurate estimates of desert coverage, though challenging to pin down precisely, consistently point towards a substantial portion of the globe classified as desert or semi-desert. However, the dynamic nature of these ecosystems, compounded by the pressures of climate change, necessitates continued research and effective conservation strategies. Only through a deeper understanding and appreciation of these environments can we hope to protect them for future generations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Are Electromagnetic Waves Different From Other Waves
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Part Of The Cow Does T Bone Come From
Apr 01, 2025
-
Can Baking Soda Dissolve In Water
Apr 01, 2025
-
Which Quadrilaterals Always Have Opposite Angles That Are Congruent
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Organelle Carries Out Cellular Respiration
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Much Of The World Is Desert . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
