How Many Valence Electrons Are In Beryllium
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
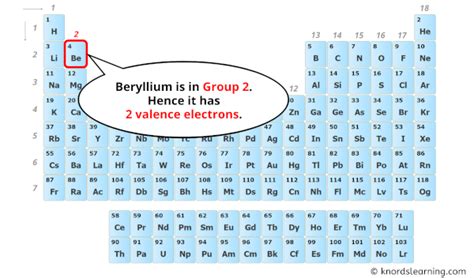
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Are in Beryllium? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Beryllium, a fascinating element with a unique set of properties, often sparks curiosity among students and enthusiasts alike. One of the key aspects of understanding beryllium's behavior and reactivity lies in determining its number of valence electrons. This article delves deep into the concept of valence electrons, explains how to determine them for beryllium, and explores the implications of its valence electron configuration on its chemical properties. We’ll cover everything from basic atomic structure to more advanced concepts, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this essential element.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Reactivity
Before focusing specifically on beryllium, let's establish a solid foundation in the concept of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom. They are the electrons that are involved in chemical bonding and determine an element's chemical reactivity. These electrons reside in the highest energy level, also known as the valence shell. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses directly impacts its ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms.
Atoms strive for stability, often achieving this by filling their valence shell. This is often described using the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons (similar to the noble gases). However, the octet rule is not a rigid law and has exceptions, particularly for elements in the first few rows of the periodic table, such as beryllium.
Beryllium's Position on the Periodic Table: A Clue to its Valence Electrons
Beryllium (Be) is an alkaline earth metal located in Group 2 (or IIA) of the periodic table. Its atomic number is 4, meaning it possesses four protons and, in a neutral atom, four electrons. The periodic table's organization provides a valuable shortcut for determining the number of valence electrons for main group elements (elements not in the transition metal or lanthanide/actinide series).
Group number (for main group elements) directly indicates the number of valence electrons. Since beryllium is in Group 2, it has two valence electrons.
Electron Configuration: A Detailed Look at Beryllium's Electron Arrangement
To fully understand the location of beryllium's valence electrons, we need to examine its electron configuration. The electron configuration describes how electrons are distributed among different energy levels and sublevels within an atom. Beryllium's electron configuration is:
1s² 2s²
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: This indicates that the first energy level (n=1) has a single sublevel (s) containing two electrons.
- 2s²: This shows that the second energy level (n=2) has a single sublevel (s) also containing two electrons.
The outermost electrons, those in the highest energy level (n=2), are the 2s electrons. These two electrons are beryllium's valence electrons. Therefore, we can definitively say beryllium has two valence electrons.
Implications of Beryllium's Two Valence Electrons on its Chemical Properties
The presence of only two valence electrons significantly influences beryllium's chemical behavior:
-
Reactivity: Beryllium is relatively reactive, although less so than other alkaline earth metals. Its two valence electrons can be readily involved in chemical bonding, typically by losing them to form a +2 cation (Be²⁺). This is a common method for beryllium to achieve a stable electron configuration.
-
Bonding: Beryllium primarily forms ionic bonds, where it donates its two valence electrons to a more electronegative atom. It can also participate in covalent bonding, although this is less common. In covalent bonds, it shares its electrons.
-
Oxidation State: The most common oxidation state for beryllium is +2, reflecting its tendency to lose its two valence electrons.
-
Compounds: Beryllium forms various compounds, exhibiting different properties depending on the other elements involved. These compounds, while important in various applications, often display toxicity which needs careful handling.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Aspects of Beryllium's Electronic Structure
While the core concept of beryllium having two valence electrons is straightforward, exploring further aspects enhances a deeper understanding:
-
Effective Nuclear Charge: The effective nuclear charge experienced by the valence electrons influences their reactivity. In beryllium, the relatively small size of the atom and the relatively high nuclear charge lead to stronger attraction to the valence electrons. This contributes to beryllium's slightly lower reactivity compared to other alkaline earth metals.
-
Orbital Hybridization: In some beryllium compounds, the valence orbitals undergo hybridization, a process of mixing atomic orbitals to create new hybrid orbitals with different shapes and energies. This phenomenon leads to the formation of specific molecular geometries in beryllium compounds.
-
Quantum Mechanical Description: A full understanding of beryllium's electronic structure requires employing quantum mechanics principles. These concepts go beyond the simple electron configuration and describe the probability distribution of electrons within the atom.
Beryllium's Role in Science and Technology: Applications Leveraging its Unique Properties
Beryllium's unique properties stemming from its electronic structure make it vital in several technological applications:
-
Aerospace: Beryllium's high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness make it suitable for aerospace components, such as aircraft and spacecraft structures.
-
Nuclear Reactors: Beryllium's low neutron absorption cross-section makes it useful as a neutron reflector in nuclear reactors.
-
X-ray Windows: Beryllium's low atomic number and high transparency to X-rays make it ideal for X-ray windows in various scientific instruments.
-
Electronics: Beryllium compounds find uses in certain electronic applications, although toxicity is a major concern.
Safety Precautions: Handling Beryllium Requires Careful Consideration
It's crucial to emphasize the importance of safety when dealing with beryllium and its compounds. Beryllium is toxic, and inhalation of beryllium dust can lead to a serious lung disease called berylliosis. Proper safety precautions, including appropriate respiratory protection and handling procedures, are essential when working with beryllium.
Conclusion: Understanding Beryllium's Valence Electrons – A Foundation for Further Exploration
In conclusion, beryllium possesses two valence electrons, a characteristic directly derived from its position in Group 2 of the periodic table and its electron configuration. This seemingly simple fact has profound implications on beryllium's chemical properties, influencing its reactivity, bonding behavior, and ultimately, its diverse applications in various fields. Understanding its valence electrons provides a crucial foundation for further exploration into the complexities of beryllium's atomic structure, chemical behavior, and its role in modern science and technology. While it's important to remember the toxicity and associated safety precautions when working with beryllium, its unique properties, directly linked to its two valence electrons, ensure its continued importance in diverse technological applications. This comprehensive analysis highlights how seemingly fundamental aspects of atomic structure can significantly impact the macroscopic properties of an element, underscoring the power and beauty of chemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percentage Is 7 Of 20
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Do Insulators Have A Low Heat Capacity
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Distinguishes One Element From Another
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 12 And 36
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Nahco3
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Are In Beryllium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
