How Many Valence Electrons Are In Ar
listenit
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
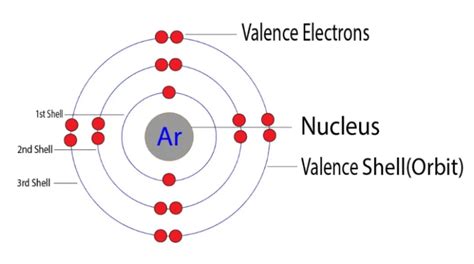
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons are in Argon? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Chemical Behavior
Argon (Ar), a noble gas residing in Group 18 of the periodic table, holds a unique position in chemistry due to its complete valence shell. Understanding the number of valence electrons in argon is crucial to comprehending its inert nature and its role in various applications. This article will delve into the intricacies of argon's atomic structure, explaining why it possesses the number of valence electrons it does and the implications of this for its chemical properties and applications.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Reactivity
Before diving into the specifics of argon, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell (also known as the valence shell) of an atom. These electrons are the primary participants in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. Atoms strive for stability, often achieved by having a full valence shell, typically containing eight electrons (the octet rule, with some exceptions).
The number of valence electrons an atom possesses is directly related to its position on the periodic table. Elements within the same group (vertical column) share the same number of valence electrons, accounting for their similar chemical behavior.
Argon's Electronic Configuration: A Stable Octet
Argon's atomic number is 18, meaning it has 18 protons and 18 electrons in a neutral atom. Its electronic configuration, depicting the arrangement of electrons in different energy levels or shells, is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶.
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: Two electrons in the first energy level (shell).
- 2s²2p⁶: Eight electrons in the second energy level (shell).
- 3s²3p⁶: Eight electrons in the third energy level (shell).
Notice that argon's outermost shell, the third energy level, is completely filled with eight electrons (2 in the 3s subshell and 6 in the 3p subshell). This full valence shell is the key to understanding argon's chemical behavior.
The Significance of a Complete Valence Shell
A complete valence shell signifies exceptional stability. Atoms with full valence shells are less likely to participate in chemical reactions because they have no tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a more stable configuration. This is why argon, and other noble gases, are incredibly unreactive.
How Many Valence Electrons Does Argon Have? The Answer and its Implications
Based on argon's electronic configuration, the definitive answer is: Argon has eight valence electrons. These eight electrons in the outermost shell (3s²3p⁶) contribute to its exceptional stability and inertness.
This characteristic has profound implications:
- Inertness: Argon's reluctance to form chemical bonds means it rarely participates in chemical reactions. This makes it incredibly useful in applications where reactivity is undesirable.
- Noble Gas Properties: Argon exhibits the typical characteristics of noble gases: it is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas under standard conditions.
- Applications: The inertness of argon makes it invaluable in numerous industrial and scientific applications, including:
- Welding: Argon is used as a shielding gas in welding processes to prevent oxidation and contamination.
- Lighting: Argon is used in incandescent and fluorescent lighting to prevent filament oxidation and enhance lamp lifetime.
- Electronics: Argon is employed in electronics manufacturing to provide an inert atmosphere during processes like semiconductor fabrication.
- Medicine: Argon is used in certain medical procedures, particularly in laser surgery.
- Food Preservation: Argon's inertness makes it suitable for preserving food products.
Beyond the Octet Rule: Exceptions and Nuances
While the octet rule provides a useful framework for understanding chemical bonding, it's important to acknowledge exceptions. While argon perfectly adheres to the octet rule, some elements may have fewer or more than eight valence electrons, particularly those in higher periods of the periodic table. These exceptions are often explained by considering factors such as atomic size, orbital hybridization, and the relative energies of different orbitals.
Argon's Isotopes and Valence Electrons
All naturally occurring isotopes of argon (³⁶Ar, ³⁸Ar, and ⁴⁰Ar) have the same number of protons and electrons, and consequently, the same number of valence electrons – eight. The variations in mass number (the sum of protons and neutrons) do not affect the electronic configuration or the number of valence electrons.
Argon's Position in the Periodic Table and its Relationship to Other Elements
Argon's placement in Group 18 (Group VIIIA), the noble gases, highlights its unique chemical behavior. All elements in this group share the common characteristic of having a complete valence shell, resulting in their exceptional inertness. This group's position at the far right of the periodic table reflects their stability and low reactivity.
Understanding argon's position within the periodic table provides crucial context to its properties and behavior. Its location highlights its relationship with other noble gases (helium, neon, krypton, xenon, radon, and oganesson), which also possess a full valence shell and share similar inert characteristics.
Argon's Role in Atmospheric Chemistry and the Environment
Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, making up approximately 0.93% of its volume. Its inert nature means it plays a relatively passive role in atmospheric chemistry, unlike reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen. However, its presence is important for maintaining atmospheric pressure and understanding the overall composition of the atmosphere. Human activities have negligible impact on argon's atmospheric concentration.
Conclusion: Argon's Eight Valence Electrons and their Significance
In summary, argon possesses eight valence electrons, a feature that decisively influences its chemical behavior and diverse applications. Its complete valence shell renders it incredibly unreactive, making it an essential component in various industrial processes, medical techniques, and scientific endeavors. Understanding the link between electronic configuration, valence electrons, and chemical properties is fundamental to appreciating argon's unique role in our world. The stability inherent in its eight valence electrons is a cornerstone of its exceptional inertness, setting it apart from many other elements and defining its crucial contributions to numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Boron Is Solid Liquid Or Gas
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 36 And 60
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do You Graph Y 3x 4
Apr 04, 2025
-
Is Ch3oh An Acid Or Base
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Isotopes Does Argon Have
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Are In Ar . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
