How Many Protons Are In Phosphorus
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
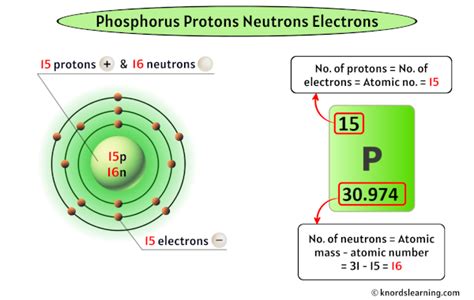
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Are in Phosphorus? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
The seemingly simple question, "How many protons are in phosphorus?" opens a fascinating door into the world of atomic structure, chemistry, and the periodic table. Understanding the answer requires a grasp of fundamental concepts, and this article will explore these concepts in detail, going beyond a simple numerical answer to provide a comprehensive understanding of phosphorus and its place in the universe.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Building Blocks of Matter
Before diving into phosphorus specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. All matter is composed of atoms, and atoms are made up of three fundamental subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons determines the element's atomic number and its identity.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also residing in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. They determine an atom's chemical properties and its ability to form bonds with other atoms.
The nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, forms the dense, central core of the atom, while the electrons occupy a much larger volume surrounding the nucleus. The positive charge of the protons is balanced by the negative charge of the electrons, resulting in a neutral atom.
Phosphorus: Its Position and Properties on the Periodic Table
Phosphorus (symbol: P), atomic number 15, is a nonmetal found in Group 15 (also known as the pnictogens) of the periodic table. This group is characterized by elements with five valence electrons—electrons in the outermost shell that participate in chemical bonding. Phosphorus's position on the periodic table directly dictates its properties and behavior.
The periodic table's arrangement is not arbitrary; it reflects the systematic organization of elements based on their atomic number and electronic configuration. Elements within the same group share similar chemical properties due to their identical number of valence electrons. This similarity in valence electrons leads to similar reactivity patterns.
Key Properties of Phosphorus
Phosphorus exists in several allotropic forms, meaning it can exist in different structural modifications with varying physical and chemical properties. The most common allotropes are white phosphorus (highly reactive and toxic), red phosphorus (less reactive), and black phosphorus (the least reactive).
Some key characteristics of phosphorus include:
- Reactivity: Phosphorus is a reactive element, readily forming compounds with other elements, particularly oxygen.
- Abundance: It's a relatively abundant element in the Earth's crust, primarily found in phosphate rocks.
- Biological Importance: Phosphorus is crucial for life, forming a vital component of DNA, RNA, and ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells. It's also a crucial element in bones and teeth.
- Industrial Uses: Phosphorus is widely used in fertilizers, detergents, and various industrial applications.
Answering the Question: How Many Protons in Phosphorus?
Now, we can directly address the central question: Phosphorus has 15 protons. This is a fundamental characteristic of phosphorus. Its atomic number, 15, is defined by the number of protons in its nucleus. No other element has 15 protons; this number uniquely identifies phosphorus.
Any atom with 15 protons is, by definition, a phosphorus atom, regardless of the number of neutrons or electrons it possesses. Variations in the number of neutrons lead to different isotopes of phosphorus, such as phosphorus-31 (the most common isotope) and phosphorus-32 (a radioactive isotope used in medical and scientific applications). However, the number of protons remains constant for all isotopes of phosphorus.
Isotopes of Phosphorus: Variations in Neutron Number
While the number of protons defines the element, the number of neutrons can vary. This variation gives rise to isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. This means they have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (the sum of protons and neutrons).
For example, the most common isotope of phosphorus is phosphorus-31, with 15 protons and 16 neutrons (15 + 16 = 31). Phosphorus-32, on the other hand, has 15 protons and 17 neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the stability of the atom; phosphorus-32 is radioactive, undergoing decay over time.
Understanding isotopes is crucial in various fields, including nuclear medicine (where radioactive isotopes like phosphorus-32 are used for diagnosis and treatment), geochemistry (where isotope ratios are used to trace the origin of materials), and archaeology (where radioactive carbon dating utilizes isotope analysis).
Beyond the Number: The Significance of Phosphorus in the Wider Context
The seemingly simple answer—15 protons—opens the door to a much broader understanding of the element's role in the world. Phosphorus's unique atomic structure dictates its chemical properties, which in turn determine its biological significance and industrial applications.
The abundance of phosphorus in the Earth's crust is a testament to its importance. Its incorporation into DNA and RNA highlights its crucial role in the genetic blueprint of life. Its presence in ATP underscores its fundamental role in energy transfer, powering biological processes. Finally, its widespread use in fertilizers and detergents reflects its contribution to modern agriculture and industry.
The study of phosphorus, therefore, transcends a simple counting of protons. It invites us to explore the intricate connections between atomic structure, chemical properties, biological functions, and industrial applications, showcasing the profound impact of a single element on the world around us. From its fundamental place on the periodic table to its vital role in life itself, phosphorus embodies the fascinating interconnections within the natural world.
Further Exploration: Connecting Protons to Chemical Bonding and Reactivity
The number of protons, specifically the number of valence electrons (those in the outermost shell), directly influences an atom's chemical behavior. Phosphorus, with five valence electrons, tends to form covalent bonds, sharing electrons with other atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration. This tendency is reflected in its diverse range of compounds, from simple phosphates to complex organophosphorus molecules.
Understanding the interplay between protons, valence electrons, and chemical bonding allows us to predict the reactivity of phosphorus and its tendency to form specific types of chemical compounds. This is a critical aspect in various fields, including materials science, pharmaceutical chemistry, and environmental science.
The study of phosphorus and its chemistry provides a powerful example of how the seemingly simple understanding of the number of protons in an atom can unlock a deeper appreciation for the complexity and interconnectedness of the natural world. This understanding is fundamental to advances in various scientific and technological disciplines.
Conclusion: A Simple Number with Profound Implications
The answer to "How many protons are in phosphorus?" is 15. However, this simple numerical answer serves as a gateway to understanding the fascinating world of atomic structure, chemical bonding, and the vital role this element plays in our world. From the fundamental principles of the periodic table to the intricacies of biological processes and industrial applications, phosphorus's story is one of intricate connections and profound implications. Its 15 protons are not just a number; they are the foundation of an element essential for life and indispensable to modern society.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write 1 8 As A Decimal Number
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 8 And 18
May 09, 2025
-
Actively Dividing Cells Can Be Found In
May 09, 2025
-
Write 35 As A Fraction In Simplest Form
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Atoms Is The Largest
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Are In Phosphorus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.