How Many Protons Are In Magnesium 24
listenit
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
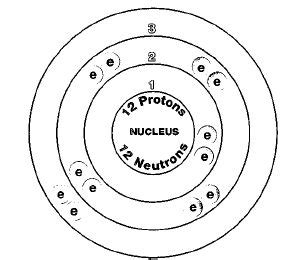
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Are in Magnesium-24? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Magnesium is a vital element for life, playing crucial roles in various biological processes. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of protons it contains, is fundamental to comprehending its chemical behavior and biological significance. This article will delve into the specifics of magnesium-24, explaining not just the number of protons but also the broader context of isotopes, atomic number, and mass number.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we pinpoint the number of protons in magnesium-24, let's refresh our understanding of basic atomic structure. An atom is the fundamental building block of matter, composed of three primary subatomic particles:
-
Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's identity. Changing the number of protons fundamentally alters the element itself.
-
Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also found in the nucleus. Neutrons contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge. Variations in the number of neutrons within the same element lead to isotopes.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in shells or energy levels. Electrons determine an atom's chemical properties and its ability to form bonds with other atoms. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
What is Magnesium (Mg)?
Magnesium (Mg), atomic number 12, is an alkaline earth metal. This means it's relatively reactive, readily losing two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Its reactivity contributes to its crucial role in numerous biological processes, including:
-
Muscle contraction: Magnesium ions are essential for muscle function, facilitating the interaction between actin and myosin filaments.
-
Enzyme activity: Magnesium acts as a cofactor for many enzymes, influencing their catalytic activity.
-
Nerve transmission: Magnesium plays a role in regulating nerve impulse transmission.
-
Protein synthesis: Magnesium is involved in the synthesis of proteins, crucial building blocks of life.
-
DNA and RNA replication: Magnesium facilitates the processes of DNA and RNA replication.
These crucial biological roles highlight the importance of understanding magnesium's atomic structure at a fundamental level.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Number
The term "magnesium-24" refers to a specific isotope of magnesium. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons. This difference in neutron count affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly. Magnesium has several naturally occurring isotopes, including magnesium-24, magnesium-25, and magnesium-26.
The mass number, denoted by the superscript number (e.g., the "24" in magnesium-24), represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus.
Determining the Number of Protons in Magnesium-24
Now, let's answer the central question: how many protons are in magnesium-24?
Since the atomic number of magnesium is 12, this means magnesium-24 contains 12 protons. This is true for all isotopes of magnesium; the defining characteristic of magnesium is its 12 protons. The "24" in magnesium-24 indicates the total number of protons and neutrons (12 protons + 12 neutrons in this case).
The Significance of Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number and mass number are crucial identifiers for any element and its isotopes.
-
Atomic Number: Uniquely identifies an element. It represents the number of protons in the nucleus. All atoms of a given element have the same atomic number.
-
Mass Number: Represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. Isotopes of the same element have different mass numbers due to variations in their neutron counts.
Understanding these two numbers is fundamental to grasping the behavior of elements and their isotopes in chemical reactions and biological systems.
Magnesium Isotopes: A Closer Look
Magnesium's three main isotopes – magnesium-24, magnesium-25, and magnesium-26 – exist in varying natural abundances. Magnesium-24 is the most abundant isotope, comprising approximately 79% of naturally occurring magnesium. Magnesium-25 accounts for roughly 10%, and magnesium-26 makes up about 11%. These isotopic abundances are important in various applications, including geological dating and tracing geochemical processes.
While the number of protons remains constant at 12 for all magnesium isotopes, the differing neutron numbers influence the atomic mass and, to a smaller extent, the physical properties. These slight variations in mass and properties do not significantly affect the chemical behavior of the element.
Applications of Magnesium and its Isotopes
The unique properties of magnesium and its isotopes lend themselves to a variety of applications:
-
Lightweight alloys: Magnesium's low density and relatively high strength make it ideal for lightweight alloys used in automotive and aerospace industries.
-
Medical applications: Magnesium's biological importance makes it essential in various medical applications, such as dietary supplements and treatments for magnesium deficiency.
-
Pyrotechnics: Magnesium's tendency to burn brightly and intensely makes it a key component in flares and fireworks.
-
Chemical industry: Magnesium is used in various chemical reactions and processes as a reducing agent.
-
Geological studies: The isotopic ratios of magnesium can provide insights into geological processes and the age of geological formations.
These applications underscore the importance of understanding the fundamental properties of magnesium, including the number of protons in its various isotopes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Atomic Structure
Understanding the atomic structure of an element, especially the number of protons, is crucial for comprehending its chemical and physical properties and its role in various applications. In the case of magnesium-24, the presence of 12 protons defines its identity as magnesium, while the mass number of 24 indicates the total number of protons and neutrons. This knowledge is vital in various scientific fields, from biology and chemistry to geology and materials science. The abundance of magnesium-24 in nature further highlights its importance in geological and biological processes. Therefore, grasping the concept of atomic structure, including the significance of the atomic number and mass number, is key to understanding the world around us at its most fundamental level. The 12 protons in magnesium-24, then, are not just a number; they represent the very essence of this essential element.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Finding The Angle Between Two Planes
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Are The Common Multiples Of 2 And 7
Apr 02, 2025
-
Ratio Of Each 90 If Ratio Is 7 3
Apr 02, 2025
-
Density Of Water At 4 C
Apr 02, 2025
-
Select The Graphs That Have An Equation With A 0
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Are In Magnesium 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
