How Many Neutrons Does Strontium Have
listenit
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
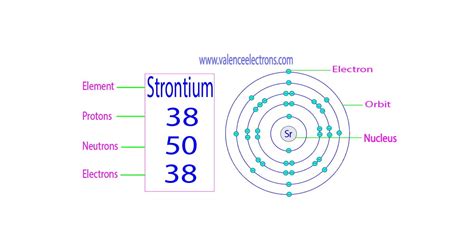
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Does Strontium Have? A Deep Dive into Isotopes and Nuclear Physics
Strontium, a fascinating alkaline earth metal, isn't defined by a single number of neutrons. Unlike the atomic number (number of protons), which defines an element, the number of neutrons in strontium can vary, leading to the existence of multiple isotopes. Understanding this variation requires a journey into the heart of nuclear physics and isotopic abundance. This comprehensive guide will explore the nuances of strontium's neutron count, delving into its isotopes, their properties, and their significance in various fields.
Understanding Isotopes and Atomic Structure
Before we delve into the specifics of strontium, let's establish a foundational understanding of isotopes. An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that differs in neutron number. All isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons (and therefore the same atomic number), but they differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atomic mass of the isotope.
The atomic number of an element, denoted by Z, represents the number of protons in the nucleus. For strontium (Sr), Z = 38. The mass number, denoted by A, represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus (A = Z + N, where N is the number of neutrons).
Therefore, to determine the number of neutrons in a strontium atom, we need to know its specific isotope, identified by its mass number. Different isotopes of strontium will have different numbers of neutrons.
The Isotopes of Strontium: A Diverse Family
Strontium has a total of 38 known isotopes, ranging from Strontium-70 (⁷⁰Sr) to Strontium-108 (¹⁰⁸Sr). However, only four of these isotopes are found in significant amounts in nature: ⁸⁴Sr, ⁸⁶Sr, ⁸⁷Sr, and ⁸⁸Sr. The abundance of these isotopes varies, impacting the average atomic weight of strontium found on Earth.
Let's break down the neutron count for these naturally occurring isotopes:
-
⁸⁴Sr (Strontium-84): Mass number (A) = 84, Atomic number (Z) = 38. Therefore, the number of neutrons (N) = A - Z = 84 - 38 = 46 neutrons.
-
⁸⁶Sr (Strontium-86): Mass number (A) = 86, Atomic number (Z) = 38. Therefore, the number of neutrons (N) = A - Z = 86 - 38 = 48 neutrons.
-
⁸⁷Sr (Strontium-87): Mass number (A) = 87, Atomic number (Z) = 38. Therefore, the number of neutrons (N) = A - Z = 87 - 38 = 49 neutrons.
-
⁸⁸Sr (Strontium-88): Mass number (A) = 88, Atomic number (Z) = 38. Therefore, the number of neutrons (N) = A - Z = 88 - 38 = 50 neutrons.
Isotopic Abundance and Average Atomic Weight
The abundance of each strontium isotope in nature influences the average atomic weight reported on the periodic table. The average atomic weight is a weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes, taking their relative abundances into account. Strontium's average atomic weight is approximately 87.62 atomic mass units (amu). This value reflects the higher abundance of ⁸⁸Sr compared to the other isotopes.
The significant difference in neutron numbers between isotopes does not drastically alter the chemical properties of strontium. Chemical properties are primarily determined by the number of electrons and the arrangement of electrons in the electron shells, which are directly related to the number of protons (atomic number). However, the difference in neutron numbers does significantly affect the nuclear properties of the isotopes, particularly their stability and radioactivity.
Radioactive Isotopes of Strontium
While ⁸⁴Sr, ⁸⁶Sr, ⁸⁷Sr, and ⁸⁸Sr are stable isotopes, many other strontium isotopes are radioactive. Radioactive isotopes decay over time, emitting radiation as they transform into more stable isotopes or elements. This decay process follows specific patterns and rates, characterized by their half-life.
One notable radioactive isotope is ⁹⁰Sr (Strontium-90). ⁹⁰Sr has 52 neutrons (90 - 38 = 52) and is a byproduct of nuclear fission. It's a significant environmental concern due to its relatively long half-life (approximately 28.8 years) and its tendency to accumulate in the food chain. Because of its chemical similarity to calcium, ⁹⁰Sr can be absorbed by bones, causing health problems.
Other radioactive isotopes of strontium, while potentially less environmentally significant than ⁹⁰Sr, are also studied in various scientific applications.
Applications of Strontium Isotopes
The different isotopes of strontium find applications in diverse fields:
-
Geochronology: The different ratios of strontium isotopes (particularly ⁸⁷Sr/⁸⁶Sr) are used in geochronology to date rocks and minerals. This technique provides valuable insights into the age and formation of geological formations.
-
Environmental Studies: The presence and ratio of strontium isotopes in environmental samples (like water and soil) can help track pollution sources and environmental processes.
-
Biomedical Research: Certain strontium isotopes are used in biomedical research, including bone metabolism studies and cancer treatment.
-
Nuclear Medicine: Some radioactive isotopes are utilized in nuclear medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
-
Material Science: The properties of strontium isotopes can influence the characteristics of materials, making them useful in materials science.
Conclusion: The Neutron Count in Strontium's Nuances
There isn't one definitive answer to "how many neutrons does strontium have?". The number of neutrons varies depending on the specific isotope of strontium being considered. While several stable isotopes exist, with neutron numbers ranging from 46 to 50 for the most common isotopes, many radioactive isotopes also exist, exhibiting a wider range of neutron counts. Understanding strontium's isotopic diversity is crucial in diverse scientific disciplines, from geochronology and environmental science to nuclear medicine and materials science. The study of strontium isotopes highlights the complexity and fascinating diversity within the world of nuclear physics and its impact on our understanding of the natural world. Further research into the specific isotopic composition of strontium in various samples is often necessary for accurate analyses in many fields. This exploration into strontium's neutron count underscores the intricate relationship between atomic structure and the properties of matter, reminding us of the richness and complexity found within seemingly simple elements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
4 5 To The Power Of 2
Mar 31, 2025
-
Can You Determine The Activation Energy Of The Reverse Reaction
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is 3 4 Of A Mile
Mar 31, 2025
-
Find The Limit Of A Sequence
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Atoms In One Mole
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Does Strontium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
