How Many Light Years Is The Moon From The Earth
listenit
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
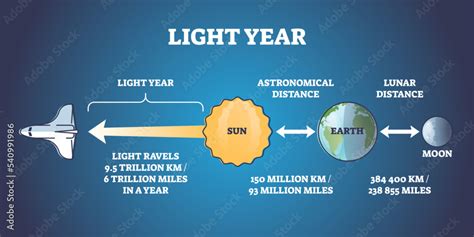
Table of Contents
How Many Light Years is the Moon from the Earth? A Deep Dive into Distance and Scale
The question, "How many light-years is the moon from the Earth?" might seem straightforward, but it reveals a fascinating misunderstanding about the vast scales we use to measure cosmic distances. The answer isn't a simple number; it highlights the difference between astronomical units (AU), kilometers, and the truly immense light-year. Understanding this difference provides a valuable lesson in astronomical scaling and the sheer size of the universe.
Understanding the Units: Kilometers, AU, and Light-Years
Before we tackle the moon's distance, let's clarify our units of measurement:
-
Kilometers (km): A familiar unit, perfectly suitable for measuring terrestrial distances. The moon's average distance is approximately 384,400 kilometers from Earth.
-
Astronomical Units (AU): One AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun—about 149.6 million kilometers. This unit is more practical for measuring distances within our solar system. The moon's distance in AU is a tiny fraction of an AU, approximately 0.00257 AU.
-
Light-Years (ly): A light-year is the distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> kilometers (9.46 trillion kilometers). This unit is used for measuring the vast distances between stars and galaxies.
The Moon's Distance in Light-Years: A Miniscule Fraction
Given the moon's average distance of 384,400 kilometers, converting this to light-years requires a simple calculation:
384,400 km / (9.461 × 10<sup>12</sup> km/ly) ≈ 0.00000004067 light-years
This is an incredibly small fraction. To put it in perspective, imagine a light-year as the entire length of a marathon race. The moon's distance in this analogy would be roughly the length of a single grain of sand. The vastness of a light-year dwarfs the relatively short distance to the moon.
Why the Confusion? Understanding Scale in Astronomy
The confusion often arises because we use different scales for different distances. Using light-years to describe the Earth-Moon distance is like using miles to measure the length of an ant. It's not wrong, but it's incredibly impractical and doesn't convey a clear sense of scale.
Light-years are essential when discussing interstellar or intergalactic distances. For example, the nearest star system to us, Alpha Centauri, is about 4.37 light-years away. This means it takes light 4.37 years to travel from Alpha Centauri to Earth. Imagine the scale: the distance to the moon is a tiny fraction of the distance to the nearest star system!
Exploring the Lunar Distance Further: Variations and Implications
The moon's distance isn't constant. Its orbit is elliptical, meaning the distance varies throughout its orbit. The moon's distance ranges from about 363,104 kilometers at its perigee (closest point) to 405,696 kilometers at its apogee (farthest point). These variations, while significant in kilometer terms, are still negligible when considering light-years.
This variation in distance affects Earth’s tides. A closer moon produces stronger tidal forces. Understanding the lunar distance is therefore crucial for predicting tides and other Earth-based phenomena influenced by lunar gravity.
The Moon's Influence: Tides, Eclipses, and More
The relatively close proximity of the moon significantly impacts life on Earth. The moon's gravitational pull is the primary driver of Earth's tides, creating rhythmic rises and falls in sea levels. These tides have profoundly shaped coastal ecosystems and influenced human civilization for millennia.
Furthermore, the moon plays a pivotal role in solar and lunar eclipses. The moon's position relative to the Sun and Earth determines whether a solar or lunar eclipse occurs. The precise distance and orbital mechanics govern the duration and visibility of these celestial events.
The Moon: A Vital Part of Our Solar System
The moon isn't just a celestial body; it’s a crucial component of our solar system and a key factor influencing life on Earth. Its relatively close proximity and gravitational influence have shaped our planet's geology, oceans, and even the timing of our days.
Understanding the distance to the moon, regardless of the units used, allows us to appreciate its impact on Earth and our place within the much larger cosmos. While it's a tiny fraction of a light-year away, its importance to us is immeasurable.
Comparing the Moon's Distance to Other Celestial Distances
Let's now compare the Moon's distance to other distances within our solar system and beyond:
- Sun to Earth: Approximately 1 AU (149.6 million km) – significantly larger than the Earth-Moon distance.
- Earth to Mars (at closest approach): About 0.37 AU – several times the Earth-Moon distance.
- Earth to Jupiter (at closest approach): About 4.2 AU – considerably larger than the Earth-Moon distance.
- Earth to Pluto (at closest approach): About 26 AU – many orders of magnitude larger.
- Earth to the nearest star (Alpha Centauri): 4.37 light-years. This immense distance highlights the vast scale of interstellar space compared to the Earth-Moon system.
- Earth to the Andromeda Galaxy: Approximately 2.54 million light-years – an almost incomprehensible distance.
These comparisons emphasize the relatively small distance between the Earth and the Moon in the grand scheme of the universe.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Scale for Astronomical Distances
The key takeaway is that choosing the appropriate unit of measurement is crucial when discussing astronomical distances. While it's technically correct to say the moon is approximately 0.00000004067 light-years away, it’s far more meaningful and practical to use kilometers or AU. Using light-years for such a relatively short distance obscures the true scale and significance of the Earth-Moon relationship. Understanding the differences in these units allows us to appreciate the vastness of space while simultaneously appreciating the intimate connection between Earth and its closest celestial neighbor. The moon's influence, though from a seemingly small distance, is profoundly impactful on our planet and our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Double Derivative Of Natural Log Function
Apr 06, 2025
-
How To Find The Domain Of Fog
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Can You Measure The Wavelength Of A Longitudinal Wave
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Are In 40 Miles
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Value Of 3 4
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Light Years Is The Moon From The Earth . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
