How Do You Find The Radius Of A Diameter
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
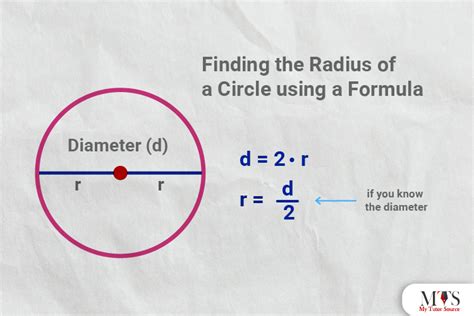
Table of Contents
How Do You Find the Radius of a Diameter? A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the radius of a diameter is a fundamental concept in geometry and a crucial skill for various applications, from basic math problems to advanced engineering calculations. This comprehensive guide will explore different methods to determine the radius, catering to various levels of understanding. We'll cover the basics, delve into practical examples, and even touch on real-world applications where this simple yet powerful calculation proves invaluable.
Understanding the Relationship Between Radius and Diameter
Before we delve into the methods, let's establish the fundamental relationship: the radius of a circle is exactly half its diameter. This seemingly simple fact underpins all the calculations we'll explore.
- Diameter: The diameter is a straight line passing from one side of a circle to the other, through the center.
- Radius: The radius is a straight line from the center of a circle to any point on its circumference.
Therefore, the formula connecting radius (r) and diameter (d) is:
r = d/2 or d = 2r
Methods for Finding the Radius Given the Diameter
Now, let's explore various approaches to calculating the radius when the diameter is known.
Method 1: Direct Application of the Formula
This is the most straightforward method. If you're given the diameter, simply divide it by 2 to find the radius.
Example:
A circle has a diameter of 10 cm. What is its radius?
Solution:
r = d/2 = 10 cm / 2 = 5 cm
The radius of the circle is 5 cm.
Method 2: Using a Ruler or Measuring Tool (For Physical Circles)
If you're dealing with a physical circle (like a plate or a coin), you can directly measure the diameter using a ruler or caliper. Then, apply the formula r = d/2 to calculate the radius.
Important Considerations:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of your radius calculation depends entirely on the accuracy of your diameter measurement. Using a precise measuring tool is crucial for accurate results.
- Practical Limitations: This method is only applicable to physical circles where direct measurement is possible.
Method 3: Deriving the Diameter from Other Given Information (More Advanced Scenarios)
Sometimes, the diameter isn't explicitly given. You might need to use other information about the circle to find the diameter first, then calculate the radius.
Examples:
-
Circumference: If you know the circumference (C) of the circle, you can use the formula C = πd to find the diameter, and then calculate the radius using r = d/2. Remember that π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
-
Area: If you know the area (A) of the circle, you can use the formula A = πr² to find the radius. While this doesn't directly use the diameter, it's an alternative method that leads to the same result. You can then calculate the diameter using d = 2r.
-
Equation of a Circle: In coordinate geometry, the equation of a circle can provide information to find the diameter. The general equation is (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r², where (h, k) is the center and r is the radius. The diameter can be derived from the radius.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The ability to calculate the radius from the diameter is vital in numerous fields. Here are some examples:
- Engineering: Designing circular components like pipes, gears, or wheels requires precise radius calculations.
- Architecture: Creating circular structures or spaces, such as domes or roundabouts, relies heavily on accurate radius measurements.
- Construction: Laying out circular foundations or features often involves determining the radius.
- Mapping and Surveying: Determining the radius of a circular area on a map is crucial for various applications.
- Astronomy: Calculating the radius of celestial bodies (like planets or stars) involves intricate mathematical models, but the fundamental concept of radius and diameter remains central.
- Graphic Design: Creating perfectly circular logos or images in software often requires precise radius input.
Solving More Complex Problems Involving Radius and Diameter
Let's look at more challenging problems to solidify your understanding:
Problem 1:
A circular garden has a circumference of 30 meters. What is the radius of the garden?
Solution:
- Find the diameter: Use the formula C = πd. Rearranging, we get d = C/π = 30 meters / π ≈ 9.55 meters.
- Find the radius: Use the formula r = d/2. Therefore, r ≈ 9.55 meters / 2 ≈ 4.77 meters.
Problem 2:
A circular swimming pool has an area of 78.5 square meters. What is its diameter?
Solution:
- Find the radius: Use the formula A = πr². Rearranging, we get r² = A/π = 78.5 square meters / π ≈ 25 square meters. Taking the square root, we get r ≈ 5 meters.
- Find the diameter: Use the formula d = 2r. Therefore, d = 2 * 5 meters = 10 meters.
Problem 3:
A circle is defined by the equation (x - 3)² + (y + 2)² = 25. What is its diameter?
Solution:
The equation is in the standard form (x - h)² + (y - k)² = r², where r is the radius. In this case, r² = 25, so r = 5. The diameter is d = 2r = 2 * 5 = 10.
Conclusion
Finding the radius of a diameter is a fundamental skill in geometry with far-reaching applications. By understanding the basic relationship between radius and diameter and applying the appropriate formulas, you can solve various problems involving circles, from simple calculations to more complex scenarios in diverse fields. Remember the core formula: r = d/2. Master this, and you'll unlock a crucial aspect of geometric understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Gcf Of 54 And 72
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is Fungi A Eukaryote Or Prokaryote
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is A Half Of A Half
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Structures Inside Plant And Animal Cells Look Like Bacteria
Mar 23, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 7
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Find The Radius Of A Diameter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
