How Do You Factor X 3 8
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 4 min read
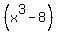
Table of Contents
How Do You Factor x³ + 8?
Factoring cubic expressions can seem daunting, but with the right approach, it becomes manageable. This article will delve into the process of factoring the cubic expression x³ + 8, exploring various methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. We'll cover the sum of cubes formula, demonstrate its application, and even explore alternative strategies for factoring similar expressions. By the end, you'll be able to confidently tackle similar cubic factoring problems.
Understanding the Sum of Cubes Formula
The expression x³ + 8 is a special case of a sum of cubes. The general form of a sum of cubes is:
a³ + b³ = (a + b)(a² - ab + b²)
In our case, x³ + 8 can be rewritten as:
x³ + 2³
Here, 'a' represents x and 'b' represents 2 (since 2³ = 8). Applying the sum of cubes formula, we get:
x³ + 2³ = (x + 2)(x² - 2x + 4)
This is the factored form of x³ + 8. Let's break down why this formula works and how we can derive it.
Deriving the Sum of Cubes Formula
While you can directly use the formula, understanding its derivation provides deeper insight. We can derive the sum of cubes formula through polynomial long division or by expanding the factored form:
(x + 2)(x² - 2x + 4)
Expanding this expression using the distributive property (FOIL method):
- x(x²) = x³
- x(-2x) = -2x²
- x(4) = 4x
- 2(x²) = 2x²
- 2(-2x) = -4x
- 2(4) = 8
Combining like terms:
x³ - 2x² + 4x + 2x² - 4x + 8 = x³ + 8
This confirms that (x + 2)(x² - 2x + 4) is indeed the factored form of x³ + 8.
Applying the Sum of Cubes Formula to Other Expressions
The sum of cubes formula is incredibly versatile and can be applied to a wide range of cubic expressions. Let's look at some examples:
Example 1: 8y³ + 64
First, rewrite the expression as a sum of cubes:
(2y)³ + 4³
Now, apply the formula with a = 2y and b = 4:
(2y + 4)((2y)² - (2y)(4) + 4²) = (2y + 4)(4y² - 8y + 16)
Notice that we can further factor out a 4 from the second parenthesis:
4(2y + 4)(y² - 2y + 4) = 8(y+2)(y²-2y+4)
Example 2: 27z³ + 1
Rewrite as a sum of cubes:
(3z)³ + 1³
Applying the formula with a = 3z and b = 1:
(3z + 1)((3z)² - (3z)(1) + 1²) = (3z + 1)(9z² - 3z + 1)
What if it's a Difference of Cubes?
While we've focused on the sum of cubes, it's important to also understand the difference of cubes. The formula for the difference of cubes is:
a³ - b³ = (a - b)(a² + ab + b²)
Notice the subtle but crucial difference: the middle term in the second parenthesis is positive, unlike in the sum of cubes formula.
Example: x³ - 27
Rewrite as a difference of cubes:
x³ - 3³
Applying the formula with a = x and b = 3:
(x - 3)(x² + 3x + 9)
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While the sum and difference of cubes formulas are powerful tools, some cubic expressions may require more advanced factoring techniques, especially those involving more complex coefficients or additional terms. These might include:
- Grouping: Used when expressions can be grouped into pairs that share common factors.
- Rational Root Theorem: A method used to identify potential rational roots of a polynomial. Once a root is found, synthetic division can be used to reduce the polynomial to a quadratic, which is usually easier to factor.
- Cubic Formula: This complex formula provides the exact roots of a cubic equation. However, it is generally cumbersome and not often practical for simple factoring problems.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Many students encounter minor errors while applying the sum or difference of cubes formulas. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Incorrect identification of 'a' and 'b': Ensure you correctly identify the cube roots of the terms in your expression.
- Errors in expanding: Double-check your expansion of the factored form to ensure it simplifies to the original expression.
- Forgetting the middle term's sign: The sign in the middle term of the quadratic factor is crucial and depends on whether it is a sum or difference of cubes.
- Not factoring completely: Always check if the resulting quadratic factor can be further factored.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Factoring cubic expressions, including the sum of cubes, has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Calculus: Finding roots of cubic equations is essential in optimization problems and curve sketching.
- Physics: Cubic equations appear in physics problems related to motion, energy, and oscillations.
- Engineering: Design and analysis of structures often involve solving cubic equations.
- Computer Graphics: Cubic curves are commonly used to create smooth and realistic shapes in computer graphics.
Conclusion
Factoring x³ + 8, and other similar cubic expressions, is a valuable skill with widespread applications. Mastering the sum and difference of cubes formulas is the foundation for efficiently solving these types of problems. Remember to practice regularly, understand the underlying concepts, and watch out for common errors to build your confidence and proficiency in algebraic manipulation. With consistent effort, factoring cubic expressions will become second nature.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Calories Are In One Gram Of Lipids
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of These Is The Quadratic Parent Function
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Molar Mass Of Calcium Chloride
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 3 10 In A Decimal
Mar 28, 2025
-
Whats The Sum Of 2 5 And 2 4
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Factor X 3 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
