Give The Formula For Plumbous Nitrate.
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
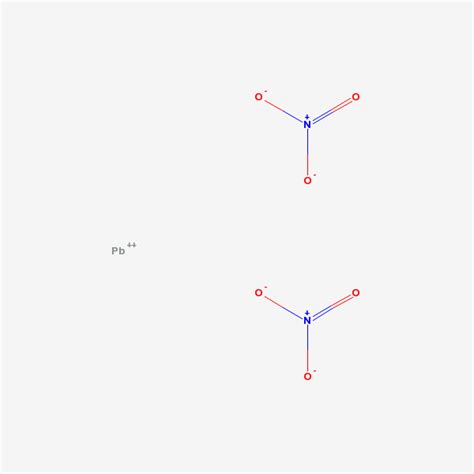
Table of Contents
The Formula for Plumbous Nitrate: Unveiling the Chemistry of Lead(II) Nitrate
Lead(II) nitrate, historically and sometimes still colloquially referred to as plumbous nitrate, is an inorganic compound with a fascinating history and a range of applications. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and uses is crucial for anyone working with this substance in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and even history. This comprehensive guide will delve into the formula for plumbous nitrate, exploring its composition, properties, preparation methods, safety precautions, and diverse applications.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: Pb(NO₃)₂
The chemical formula for plumbous nitrate, or lead(II) nitrate, is Pb(NO₃)₂. This formula succinctly communicates the composition of the compound:
-
Pb: Represents one lead (II) ion (Pb²⁺). The Roman numeral II indicates the oxidation state of lead, meaning it has lost two electrons. This is crucial, as lead can exist in other oxidation states (like +4), leading to different compounds with drastically different properties.
-
(NO₃): Represents one nitrate ion (NO₃⁻). The nitrate ion is a polyatomic anion composed of one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms, carrying a -1 charge.
-
₂: Indicates that there are two nitrate ions for every one lead(II) ion. This ensures that the overall charge of the compound is neutral (2+ from Pb²⁺ balanced by 2- from two NO₃⁻ ions).
Understanding the formula is fundamental to understanding the stoichiometry and reactivity of plumbous nitrate. It dictates the molar ratios in reactions, allowing accurate calculations and predictions of reaction outcomes.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Lead(II) Nitrate
Lead(II) nitrate presents distinct physical and chemical characteristics that define its behavior and applications:
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: It exists as a colorless crystalline solid at room temperature. Its crystals are typically cubic or octahedral.
- Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, a property frequently exploited in its applications. The solubility increases with temperature. It is also soluble in some organic solvents.
- Melting Point: It melts at a relatively low temperature of around 217°C (423 °F), demonstrating its relative thermal instability compared to many other inorganic salts.
- Density: Lead(II) nitrate exhibits a higher density than water, making it heavier for its volume.
- Toxicity: Crucially, lead(II) nitrate is highly toxic. Contact with skin, inhalation of dust, or ingestion can lead to serious health consequences. This necessitates stringent safety precautions during handling and disposal.
Chemical Properties:
- Thermal Decomposition: Upon heating to higher temperatures than its melting point, lead(II) nitrate decomposes, yielding lead(II) oxide (PbO), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), and oxygen (O₂). This decomposition reaction is often used in laboratory settings to prepare lead(II) oxide.
- Reactions with Iodides and Sulfides: Lead(II) nitrate readily reacts with soluble iodides and sulfides to produce insoluble lead(II) iodide (PbI₂) and lead(II) sulfide (PbS), respectively. These reactions are often used in qualitative analysis to identify the presence of lead(II) ions.
- Reactions with Alkalis: Reaction with alkalis like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) leads to the precipitation of lead(II) hydroxide, Pb(OH)₂.
- Oxidizing Agent: In certain reactions, lead(II) nitrate can act as a mild oxidizing agent.
Preparation of Lead(II) Nitrate: Methods and Considerations
The synthesis of lead(II) nitrate can be achieved through various methods; one common approach involves reacting metallic lead with dilute nitric acid:
Pb(s) + 4HNO₃(aq) → Pb(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2NO₂(g) + 2H₂O(l)
This reaction is relatively straightforward, producing lead(II) nitrate in an aqueous solution. The solution can then be evaporated carefully to obtain the crystalline solid. It's important to note that this reaction releases toxic nitrogen dioxide gas, requiring careful handling in a well-ventilated area or fume hood.
Another method involves dissolving lead(II) oxide or lead(II) carbonate in nitric acid:
PbO(s) + 2HNO₃(aq) → Pb(NO₃)₂(aq) + H₂O(l)
PbCO₃(s) + 2HNO₃(aq) → Pb(NO₃)₂(aq) + H₂O(l) + CO₂(g)
These methods offer alternative routes to producing lead(II) nitrate, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of yield, purity, and safety. The choice of method often depends on the available starting materials and desired purity of the final product.
Applications of Lead(II) Nitrate: A Diverse Range of Uses
Lead(II) nitrate finds applications in several industrial and laboratory settings, though its use is increasingly restricted due to its toxicity:
Historical and Traditional Applications:
- Pyrotechnics: Historically, lead(II) nitrate was used in fireworks and other pyrotechnic displays to produce colorful effects. However, its toxicity has led to its largely being replaced with less hazardous alternatives.
- Dyeing and Printing: It has been used in specific dyeing processes and in the production of certain pigments for printing. Again, concerns about toxicity have driven the search for safer alternatives.
Modern Applications (with caveats due to toxicity):
- Laboratory Reagent: Despite its toxicity, it remains relevant in certain laboratory settings. It is sometimes used as a source of lead ions in controlled experiments. Strict safety precautions are paramount.
- Electroplating: Lead(II) nitrate may be employed in certain electroplating processes to deposit a lead coating onto other metals. Alternatives are increasingly preferred due to environmental concerns and health risks.
- Manufacturing of Lead-Based Compounds: It serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of other lead-containing compounds, although this application is diminishing owing to the growing awareness of lead toxicity.
Safety Precautions: Handling Lead(II) Nitrate Responsibly
The toxicity of lead(II) nitrate demands rigorous adherence to safety protocols during handling, storage, and disposal:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, eye protection, and a lab coat, when handling lead(II) nitrate.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area or a fume hood to minimize inhalation of dust or fumes.
- Skin Contact: Avoid skin contact. Wash thoroughly with soap and water if contact occurs.
- Ingestion: Avoid ingestion. If ingested, immediately seek medical attention.
- Disposal: Dispose of lead(II) nitrate and its waste products according to local regulations. This often involves special hazardous waste disposal procedures.
Conclusion: Balancing Utility and Safety
Lead(II) nitrate, while possessing useful properties that have historically driven its applications, demands careful consideration due to its inherent toxicity. The transition to less hazardous alternatives is ongoing in many applications. However, understanding its chemical formula, properties, and safe handling procedures remains crucial for anyone working with or encountering this compound. Strict adherence to safety protocols is non-negotiable to mitigate the risks associated with this potentially harmful substance. The information provided here should empower users to make informed decisions and prioritize safety when working with lead(II) nitrate or its related compounds. Always consult with relevant safety data sheets (SDS) and follow local regulations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Length Of Ab
Mar 15, 2025
-
Two Airplanes Leave An Airport At The Same Time
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is One Sixth Of 24
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Do Solids And Liquids Have In Common
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 8 Percent Of 40
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Give The Formula For Plumbous Nitrate. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
