Does Vapor Pressure Depend On Atmospheric Pressure
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
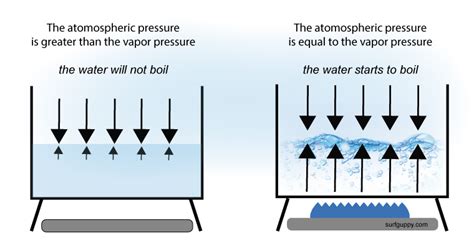
Table of Contents
Does Vapor Pressure Depend on Atmospheric Pressure?
Vapor pressure, a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, describes the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. Understanding its behavior, particularly its relationship with atmospheric pressure, is crucial in various applications, from meteorology and distillation to chemical engineering and materials science. This article delves deep into the question: Does vapor pressure depend on atmospheric pressure? The short answer is a nuanced "no," but understanding the nuances is key.
Understanding Vapor Pressure
Before tackling the main question, let's solidify our understanding of vapor pressure. Imagine a sealed container containing a liquid. Liquid molecules are constantly in motion; some possess enough kinetic energy to overcome the intermolecular forces holding them in the liquid phase and escape into the gaseous phase above the liquid. This process is called vaporization or evaporation. Simultaneously, some gas molecules collide with the liquid surface and condense back into the liquid phase.
When the rates of vaporization and condensation become equal, a dynamic equilibrium is established. The pressure exerted by the vapor molecules in this equilibrium state is the vapor pressure. This vapor pressure is solely dependent on the temperature of the liquid and the identity of the substance. A higher temperature translates to a higher vapor pressure, as more molecules possess the energy to escape the liquid. The identity of the substance matters because different intermolecular forces require different amounts of energy to overcome.
Factors Affecting Vapor Pressure (Besides Atmospheric Pressure):
-
Temperature: As mentioned, temperature is the most significant factor influencing vapor pressure. An increase in temperature leads to a significant increase in vapor pressure. This relationship is often described by the Clausius-Clapeyron equation.
-
Intermolecular Forces: Stronger intermolecular forces (like hydrogen bonding) require more energy to overcome, resulting in lower vapor pressure at a given temperature compared to substances with weaker forces.
-
Molecular Weight: Generally, substances with higher molecular weights tend to have lower vapor pressures because stronger London dispersion forces are present.
-
Purity: The presence of impurities can affect vapor pressure. Non-volatile solutes in a liquid solution will typically lower its vapor pressure (Raoult's Law).
The (Mostly) Independent Nature of Vapor Pressure
Now, we can directly address the central question: Does atmospheric pressure affect vapor pressure? The answer is largely no, under most circumstances. Vapor pressure is an intrinsic property of a substance at a given temperature, determined by the equilibrium between the liquid and its vapor within a closed system. Atmospheric pressure acts on the total pressure within a container but does not directly influence the equilibrium between the liquid and its vapor.
Consider a closed container filled with a liquid. The liquid establishes its vapor pressure irrespective of the external atmospheric pressure. The total pressure inside the container is the sum of the vapor pressure and the pressure of any other gases present. Increasing the atmospheric pressure might compress the vapor slightly, but this change would be negligible in the context of the vapor-liquid equilibrium.
Boiling Point and the Relationship with Atmospheric Pressure
While vapor pressure itself isn't directly affected by atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of a liquid is. Boiling occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the external pressure (typically atmospheric pressure). Therefore, at higher altitudes where atmospheric pressure is lower, the boiling point decreases because the liquid reaches its vapor pressure at a lower temperature. Conversely, at higher pressures (e.g., in a pressure cooker), the boiling point increases because the liquid needs to achieve a higher vapor pressure to equal the external pressure.
Understanding the Difference:
It's critical to distinguish between vapor pressure and boiling point. Vapor pressure is a property of the liquid-vapor equilibrium at a given temperature. The boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals the external pressure. While they're related, they're not interchangeable concepts. Vapor pressure exists even below the boiling point; it simply hasn't reached the level to overcome the external pressure to create bubbles within the liquid.
Special Cases and Exceptions
Although the statement that atmospheric pressure doesn't directly affect vapor pressure holds true in most situations, some nuanced exceptions and considerations exist:
-
Very high pressures: At extremely high pressures, the compressibility of the vapor becomes significant enough that the external pressure might slightly alter the equilibrium, leading to a minor impact on the vapor pressure. This effect, however, is usually negligible under normal conditions.
-
Open systems: In an open system, where the vapor can escape into the atmosphere, atmospheric pressure could indirectly influence the rate of evaporation but not the equilibrium vapor pressure itself. The continuous removal of vapor prevents the establishment of a true equilibrium.
-
Dissolved Gases: The presence of dissolved gases within a liquid, which can be influenced by external pressure, could slightly alter the vapor pressure by interfering with the equilibrium process. This is a secondary and often small effect.
Applications and Real-World Examples
The relationship (or lack thereof) between vapor pressure and atmospheric pressure plays a vital role in numerous applications:
-
Distillation: Distillation techniques rely heavily on the concept of vapor pressure and its dependence on temperature. The difference in boiling points, influenced by vapor pressure, allows for the separation of components in a mixture.
-
Meteorology: Understanding vapor pressure is crucial in predicting weather patterns. The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, and its ability to condense (related to vapor pressure), directly impacts cloud formation, precipitation, and humidity levels.
-
Refrigeration: Refrigerants utilize substances with high vapor pressures at low temperatures to absorb heat efficiently and facilitate cooling.
-
Chemical Engineering: Accurate prediction of vapor pressure is essential in designing chemical processes and handling volatile substances. This applies to diverse areas like reaction kinetics, separation processes, and safety protocols.
-
Material Science: Understanding vapor pressure helps in the design of materials with specific properties. The vapor pressure of components within a composite material can impact its durability and stability.
Conclusion: A Subtle but Important Distinction
In summary, while atmospheric pressure does not directly impact the vapor pressure of a substance at a given temperature (in a closed system), it is essential to understand the relationship between vapor pressure and boiling point. Boiling, a process strongly influenced by atmospheric pressure, is intimately linked to vapor pressure. The nuanced interplay between these concepts is vital across diverse scientific and engineering disciplines, highlighting the complexity and practical significance of understanding vapor pressure and its relation to external pressure conditions. Remember, vapor pressure is an intrinsic property under equilibrium conditions, largely independent of the atmospheric pressure except under extreme conditions or when considering open systems or the indirect effects of dissolved gases.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
480 Cm Equals How Many M
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 8 In Fraction Form
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Elbow Is Proximal To The Shoulder
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Radians In A Revolution
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Can Sedimentary Rock Become Metamorphic Rock
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Does Vapor Pressure Depend On Atmospheric Pressure . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
