Divides The Body Into Left And Right
listenit
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
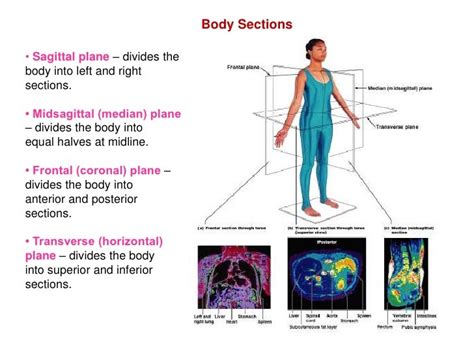
Table of Contents
The Sagittal Plane: Dividing the Body into Left and Right
The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, a complex system of interconnected organs, tissues, and cells working in harmony. Understanding its structure is crucial for anyone studying anatomy, physiology, or related fields. One of the fundamental concepts in understanding body organization is the sagittal plane, which divides the body into left and right halves. This article delves deep into the sagittal plane, exploring its significance in various medical and scientific contexts, examining related anatomical terms, and highlighting its crucial role in understanding human movement and function.
Defining the Sagittal Plane
The sagittal plane, also known as the longitudinal plane, is a vertical plane that runs from the anterior (front) to the posterior (back) of the body, dividing it into left and right portions. It's crucial to note that a perfectly symmetrical division isn't always the case; the sagittal plane can run through the body in multiple positions, creating uneven left and right halves. The specific position of the plane depends on the context and what is being examined.
Different Types of Sagittal Planes:
-
Midsagittal Plane (Median Plane): This is the most commonly discussed sagittal plane. It runs precisely through the midline of the body, creating equal left and right halves. Structures like the nose, navel, and spine typically lie on this plane.
-
Parasagittal Plane: Any plane parallel to the midsagittal plane but not passing through the midline is a parasagittal plane. These planes create unequal left and right portions. Consider a plane that divides the body slightly off-center; this would be a parasagittal plane.
The Importance of the Sagittal Plane in Anatomy and Physiology
The sagittal plane's importance in anatomy and physiology cannot be overstated. It serves as a fundamental reference point for describing the location, orientation, and movement of various body parts. Here are some key applications:
1. Describing Anatomical Location:
Many anatomical terms rely on the sagittal plane for precise descriptions. Terms like medial (closer to the midsagittal plane) and lateral (further from the midsagittal plane) are directly related to this plane. Understanding these terms is essential for accurately communicating the location of structures within the body. For instance, the heart is described as being medial to the lungs, while the arms are lateral to the torso.
2. Understanding Movement and Kinesiology:
The sagittal plane is essential for understanding human movement. Many movements occur primarily within this plane, such as:
-
Flexion and Extension: These movements occur around a joint and reduce or increase the angle between bones. Examples include bending the elbow (flexion) and straightening it (extension). These are sagittal plane movements.
-
Dorsiflexion and Plantarflexion: These movements refer to the upward (dorsiflexion) and downward (plantarflexion) movements of the foot at the ankle joint. These too, occur predominantly in the sagittal plane.
3. Medical Imaging and Diagnosis:
Medical imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, often use sagittal views to visualize internal structures. A sagittal slice provides a clear side profile of the body, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the condition of organs, bones, and tissues. This is particularly useful in diagnosing conditions affecting the spine, brain, or other structures that extend along the body's longitudinal axis.
4. Surgical Planning and Procedures:
Surgeons use the sagittal plane as a critical reference point during surgical planning and execution. Many surgical approaches and incisions are planned along or parallel to the sagittal plane to minimize damage to surrounding tissues and optimize surgical access.
Related Anatomical Terms and Concepts
Several other anatomical terms are inextricably linked to the sagittal plane and contribute to a comprehensive understanding of body organization. These include:
-
Anterior (Ventral): Refers to the front of the body.
-
Posterior (Dorsal): Refers to the back of the body.
-
Superior (Cranial): Refers to a structure located closer to the head.
-
Inferior (Caudal): Refers to a structure located closer to the feet.
-
Proximal: Closer to the point of attachment (e.g., the shoulder is proximal to the hand).
-
Distal: Further away from the point of attachment (e.g., the hand is distal to the shoulder).
These directional terms, used in conjunction with the sagittal plane, allow for precise anatomical descriptions. For example, one might describe a lesion as being "posterior and lateral to the midsagittal plane, at the superior aspect of the right thigh."
Beyond the Sagittal Plane: Other Anatomical Planes
While the sagittal plane is crucial, it's important to understand that it's only one of several anatomical planes used to describe body orientation. These other planes include:
-
Frontal (Coronal) Plane: This vertical plane divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections. It's perpendicular to the sagittal plane. Movements like abduction and adduction (moving a limb away from or towards the midline) occur in the frontal plane.
-
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane: This horizontal plane divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections. Movements like rotation occur in the transverse plane.
Understanding these three planes – sagittal, frontal, and transverse – provides a comprehensive framework for describing the position and movement of body parts.
Clinical Significance of Understanding Sagittal Plane Anatomy
A thorough understanding of the sagittal plane is not merely an academic pursuit; it holds immense clinical significance. Here are some examples:
-
Trauma Assessment: In cases of trauma, assessing the injuries in relation to the sagittal plane is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. For example, a fracture on the lateral aspect of the femur (thigh bone) is vastly different from a fracture on the medial aspect.
-
Neurosurgery: Neurosurgeons use the sagittal plane extensively for planning and executing procedures related to the brain and spine. Precise anatomical knowledge is essential to avoid damaging vital structures.
-
Orthopedic Surgery: Orthopedic surgeons rely on their understanding of the sagittal plane to plan and perform procedures to correct deformities or repair injuries in bones and joints.
Conclusion
The sagittal plane is a fundamental concept in anatomy and physiology, serving as a cornerstone for understanding body organization, describing anatomical locations, and analyzing movement. From its role in medical imaging and diagnosis to its crucial importance in surgical planning and execution, the sagittal plane's significance spans multiple areas of healthcare and scientific research. A solid grasp of this anatomical plane and its related concepts is essential for anyone working in fields related to human biology and medicine. Further exploration of anatomical planes and their interplay will deepen one's understanding of the intricate complexity of the human body. The detailed knowledge of the sagittal plane, coupled with the understanding of other anatomical planes and directional terms, enables precise communication, facilitates accurate medical diagnoses, and enhances the effectiveness of surgical interventions. It's a fundamental concept that underpins a deeper comprehension of human biology and its related disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find All Zeros Of A Polynomial
Apr 06, 2025
-
Domain And Range For X 3
Apr 06, 2025
-
When Water Freezes Ice Floats Why
Apr 06, 2025
-
Write The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Tin
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Possible Combinations Of 6 Numbers
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Divides The Body Into Left And Right . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
