Derivative Of E To The Xy
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
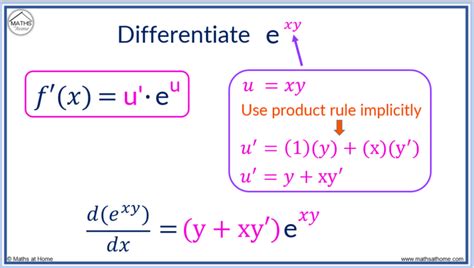
Table of Contents
Delving into the Derivative of e^(xy)
The exponential function, particularly e raised to the power of a function, is a cornerstone of calculus and numerous applications across diverse fields. Understanding its derivative is crucial for solving differential equations, optimizing functions, and interpreting models in physics, engineering, economics, and more. This article dives deep into the derivative of e^(xy), exploring various approaches and highlighting its significance.
Understanding the Chain Rule and Product Rule
Before tackling the derivative of e^(xy), let's refresh our understanding of two fundamental rules of differentiation: the chain rule and the product rule. These are essential for navigating the complexities of composite functions.
The Chain Rule
The chain rule states that the derivative of a composite function is the derivative of the outer function (with the inside function left alone) times the derivative of the inside function. Mathematically:
d/dx[f(g(x))] = f'(g(x)) * g'(x)
For instance, if we have f(x) = e^x and g(x) = x², then the derivative of e^(x²) is:
d/dx[e^(x²)] = e^(x²) * 2x
The Product Rule
The product rule dictates how to differentiate the product of two functions. It states:
d/dx[f(x)g(x)] = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g'(x)
For example, the derivative of x²sin(x) is:
d/dx[x²sin(x)] = 2xsin(x) + x²cos(x)
Differentiating e^(xy) – A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's approach the derivative of e^(xy) with respect to x. This involves a combination of the chain rule and the product rule because we have a composite function (e raised to a power) and a product within the exponent (xy).
1. Identifying the Outer and Inner Functions:
In e^(xy), the outer function is e^u, where u = xy.
2. Applying the Chain Rule:
Using the chain rule, we start by differentiating the outer function with respect to its inner function:
d/du[e^u] = e^u
3. Applying the Product Rule (for the inner function):
Now we need to find the derivative of the inner function, u = xy, with respect to x. This requires the product rule, treating x and y as separate functions of x:
d/dx[xy] = (dx/dx)y + x(dy/dx) = y + x(dy/dx)
4. Combining the Results:
Finally, we combine the results from steps 2 and 3 according to the chain rule:
d/dx[e^(xy)] = e^u * (y + x(dy/dx))
Substituting u = xy back in, we get the final result:
d/dx[e^(xy)] = e^(xy) * [y + x(dy/dx)]
This is the complete derivative of e^(xy) with respect to x. Notice that the result depends on whether y is a constant or a function of x. If y is a constant, dy/dx = 0, simplifying the expression to:
d/dx[e^(xy)] = ye^(xy)
Implications and Applications
The derivative of e^(xy) finds significant applications in various fields:
1. Partial Derivatives and Multivariable Calculus
In multivariable calculus, if we consider x and y as independent variables, we can calculate partial derivatives. The partial derivative with respect to x, holding y constant, is:
∂/∂x [e^(xy)] = ye^(xy)
Similarly, the partial derivative with respect to y, holding x constant, is:
∂/∂y [e^(xy)] = xe^(xy)
2. Solving Differential Equations
Many differential equations involve exponential functions. Understanding the derivative of e^(xy) is crucial for solving these equations, particularly those arising in areas such as:
- Physics: Modeling radioactive decay, heat transfer, and oscillations.
- Engineering: Analyzing circuits, signal processing, and control systems.
- Economics: Describing growth and decay processes.
3. Optimization Problems
In optimization problems, finding critical points often involves setting derivatives to zero. Knowing how to differentiate e^(xy) is vital for identifying potential maxima or minima of functions involving this expression.
4. Probability and Statistics
Exponential functions appear extensively in probability distributions, particularly in the context of exponential and normal distributions. The derivative of e^(xy) is essential in calculating probabilities, expectations, and moments.
5. Machine Learning
In machine learning, particularly in neural networks, exponential functions, along with their derivatives, are used in activation functions. The understanding of e^(xy)'s derivative is crucial for implementing backpropagation algorithms which are the cornerstone of training neural networks.
Advanced Considerations and Extensions
Let's explore some more nuanced aspects of the derivative of e^(xy):
1. Implicit Differentiation
If y is defined implicitly as a function of x (e.g., through an equation like x² + y² = 1), we can use implicit differentiation to find dy/dx and then substitute this into the derivative of e^(xy). Implicit differentiation involves differentiating both sides of the equation with respect to x and then solving for dy/dx.
2. Higher-Order Derivatives
We can further extend our understanding by calculating higher-order derivatives of e^(xy). This involves repeatedly applying the product rule and chain rule. The second derivative, for example, will involve terms with e^(xy), x, y, and their derivatives.
3. Applications in Complex Analysis
The function e^(xy) can also be extended to the complex plane, where x and y are complex numbers. The derivative of e^(xy) in the complex plane relies on concepts from complex analysis such as Cauchy-Riemann equations.
4. Numerical Methods
For complex scenarios where finding an analytical derivative is challenging, numerical methods can be employed to approximate the derivative of e^(xy). Techniques like finite differences can provide reasonable approximations.
Conclusion
The derivative of e^(xy) – whether expressed as a simple partial derivative or a more complex expression involving implicit differentiation – is a significant concept with far-reaching consequences across diverse mathematical and scientific domains. Understanding its derivation, implications, and applications is crucial for anyone pursuing advanced studies in mathematics, science, or engineering. This article has presented a comprehensive exploration of this derivative, providing a foundational understanding for further investigation and application in more complex scenarios. Remember that mastering this concept builds a solid base for tackling more advanced mathematical challenges and opens doors to many exciting possibilities in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Half Of 1 And 1 3
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is 0 4 In A Fraction
Mar 20, 2025
-
Ounces In A Fifth Of Liquor
Mar 20, 2025
-
A Duplicated Chromosome Consists Of Two
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 112
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Derivative Of E To The Xy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
