Cos X + Sin X Tan X
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
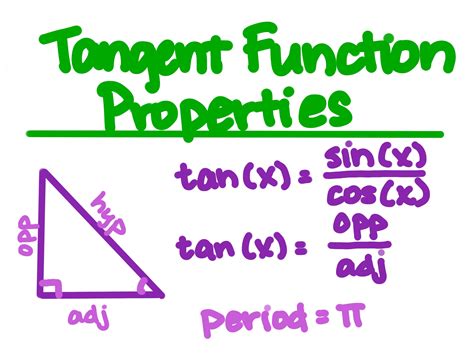
Table of Contents
Exploring the Trigonometric Expression: cos x + sin x tan x
The trigonometric expression cos x + sin x tan x, while seemingly simple, offers a rich landscape for exploration, revealing deeper connections within trigonometry and providing opportunities for simplification and insightful analysis. This article will delve into this expression, examining its properties, simplifications, and applications, ultimately aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of its behavior and significance.
Understanding the Components
Before embarking on a detailed analysis of cos x + sin x tan x, let's refresh our understanding of the individual components:
-
cos x: The cosine of x represents the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle with angle x. It's a fundamental trigonometric function, oscillating between -1 and 1.
-
sin x: The sine of x represents the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle with angle x. Similar to cosine, it's a fundamental function oscillating between -1 and 1.
-
tan x: The tangent of x is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side in a right-angled triangle with angle x. It can be defined as sin x / cos x, highlighting its relationship to the other two functions. Unlike sine and cosine, tangent has a range of (-∞, ∞), exhibiting asymptotes where cos x = 0.
Simplifying the Expression
The key to unlocking the insights within cos x + sin x tan x lies in simplification. By leveraging the fundamental trigonometric identity tan x = sin x / cos x, we can rewrite the expression:
cos x + sin x tan x = cos x + sin x (sin x / cos x)
Combining the terms, we obtain:
cos x + sin x tan x = cos x + sin²x / cos x
To further simplify, we can find a common denominator:
cos x + sin²x / cos x = (cos²x + sin²x) / cos x
Now, we recall the Pythagorean identity: cos²x + sin²x = 1. Substituting this into our simplified expression, we arrive at a remarkably concise form:
cos x + sin x tan x = 1 / cos x = sec x
This simplification reveals that the seemingly complex expression is, in fact, equivalent to the secant function, sec x. This equivalence significantly simplifies further analysis and applications.
Graphical Representation and Analysis
Visualizing the expression's behavior through a graph provides valuable insights. Since we've established the equivalence to sec x, we can directly analyze the graph of the secant function. The graph of y = sec x exhibits:
- Periodicity: The function is periodic with a period of 2π. This means its values repeat every 2π units along the x-axis.
- Asymptotes: Vertical asymptotes occur at x = π/2 + nπ, where n is an integer. These asymptotes represent points where cos x = 0, and the function is undefined.
- Range: The range of sec x is (-∞, -1] ∪ [1, ∞). The function never takes values between -1 and 1.
- Symmetry: The function exhibits symmetry about the y-axis, reflecting its even nature (sec(-x) = sec x).
Understanding these graphical properties provides a visual representation of the behavior of cos x + sin x tan x across different values of x.
Applications and Implications
The simplification to sec x opens up several avenues for application and further exploration:
-
Solving Trigonometric Equations: If you encounter an equation involving cos x + sin x tan x, you can substitute sec x, potentially simplifying the solution process.
-
Calculus: The derivative and integral of sec x are well-established, allowing for easier computation of derivatives and integrals involving the original expression. The derivative of sec x is sec x tan x, and its integral involves natural logarithms and inverse trigonometric functions.
-
Physics and Engineering: The secant function appears frequently in various physical phenomena involving oscillations and waves. Therefore, understanding cos x + sin x tan x can be instrumental in analyzing systems governed by such phenomena.
-
Geometry: In certain geometric contexts, the secant function might provide a more convenient representation than the original expression.
Further Exploration: Considering Special Angles
Analyzing the expression's behavior at special angles, like 0, π/4, π/2, etc., provides further insights.
-
x = 0: cos 0 + sin 0 tan 0 = 1 + 0 = 1. This corresponds to sec 0 = 1.
-
x = π/4: cos(π/4) + sin(π/4)tan(π/4) = (√2/2) + (√2/2)(1) = √2. This corresponds to sec(π/4) = √2.
-
x = π/2: The expression is undefined at x = π/2 because tan(π/2) is undefined. Similarly, sec(π/2) is also undefined.
These examples highlight the consistency between the original expression and its simplified form.
Error Handling and Domain Restrictions
It's crucial to acknowledge the domain restrictions of the original expression. Since tan x is undefined when cos x = 0, the expression cos x + sin x tan x is undefined at x = π/2 + nπ, where n is an integer. This limitation underscores the importance of considering the domain when working with trigonometric expressions.
Advanced Applications and Connections
The expression's connection to the secant function opens doors to more advanced applications in:
-
Complex Analysis: The secant function has a complex extension, allowing for analysis in the complex plane.
-
Differential Equations: The secant function and its derivatives frequently appear in the solutions of certain types of differential equations.
-
Fourier Analysis: The secant function, through its relationship with other trigonometric functions, can play a role in Fourier series and transforms.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple trigonometric expression, cos x + sin x tan x, upon simplification, reveals a profound connection to the secant function, sec x. This equivalence unlocks a wealth of applications, simplifying calculations, enhancing problem-solving, and offering deeper insights into the interconnectedness of trigonometric functions. Understanding its graphical behavior, domain restrictions, and its role in various mathematical and scientific fields provides a comprehensive understanding of its significance. From basic trigonometric equation solving to advanced applications in calculus and beyond, the expression's simplification to sec x unveils a richer understanding of this fascinating aspect of mathematics. Further exploration into its properties and applications will continue to reveal its importance across various mathematical and scientific disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Of 40 Is 80
Mar 15, 2025
-
70 Of What Number Is 35
Mar 15, 2025
-
Words That Start With Same Letter
Mar 15, 2025
-
60 Miles Per Hour Is How Many Feet Per Second
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Meters Is A Lightyear
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cos X + Sin X Tan X . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
