4x 2y 12 4x 8y 24
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
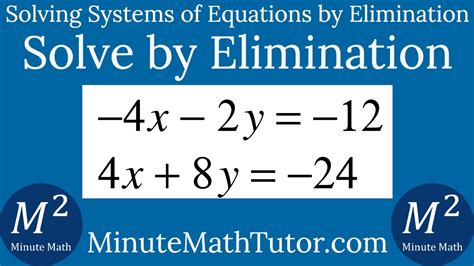
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Exploring the Relationship Between 4x + 2y = 12 and 4x + 8y = 24
The seemingly simple equations, 4x + 2y = 12 and 4x + 8y = 24, present a fascinating opportunity to delve into the world of simultaneous equations, linear algebra, and their practical applications. While at first glance they might appear isolated, these equations reveal a rich interplay of mathematical concepts that can be explored through various methods, from graphical representation to sophisticated algebraic manipulation. This article will dissect these equations, revealing their underlying relationships and demonstrating how to solve them using different techniques. We’ll also touch upon real-world scenarios where such equation systems find application.
Understanding Simultaneous Equations
Before we jump into the specifics of 4x + 2y = 12 and 4x + 8y = 24, let's establish a firm understanding of simultaneous equations. These are a set of two or more equations that contain two or more variables, where the goal is to find values for the variables that satisfy all equations simultaneously. In our case, we have two equations with two variables, x and y. The solution represents the point (or points) where the lines represented by these equations intersect on a graph.
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Solution
One of the most intuitive ways to understand simultaneous equations is through graphical representation. Each equation represents a straight line. Plotting these lines on a Cartesian coordinate system allows us to visualize their intersection point, which represents the solution to the system.
To plot each line, we can find two points that satisfy each equation and then draw a line through them. For 4x + 2y = 12:
- If x = 0, then 2y = 12, so y = 6. One point is (0, 6).
- If y = 0, then 4x = 12, so x = 3. Another point is (3, 0).
For 4x + 8y = 24:
- If x = 0, then 8y = 24, so y = 3. One point is (0, 3).
- If y = 0, then 4x = 24, so x = 6. Another point is (6, 0).
Plotting these points and drawing the lines reveals that the lines intersect. The coordinates of this intersection point represent the solution to the simultaneous equations. This graphical method provides a clear visual representation of the solution, but it can be imprecise for determining exact values, especially if the intersection point doesn't fall on easily identifiable grid points.
Solving using Elimination Method: A Step-by-Step Approach
The elimination method is an algebraic technique for solving simultaneous equations. The goal is to eliminate one of the variables by manipulating the equations to create opposite coefficients for that variable. Subtracting the modified equations then eliminates that variable, allowing us to solve for the remaining variable. Let's apply this to our equations:
-
Notice the common term: Both equations have 4x.
-
Subtract the equations: Subtracting (4x + 2y = 12) from (4x + 8y = 24) eliminates the x term:
(4x + 8y) - (4x + 2y) = 24 - 12
This simplifies to:
6y = 12
-
Solve for y: Dividing both sides by 6 gives:
y = 2
-
Substitute y back into either equation: Let's use the first equation (4x + 2y = 12):
4x + 2(2) = 12
4x + 4 = 12
4x = 8
x = 2
Therefore, the solution to the simultaneous equations is x = 2 and y = 2.
Solving using Substitution Method: An Alternative Approach
The substitution method involves solving one equation for one variable in terms of the other and then substituting this expression into the second equation. This reduces the system to a single equation with one variable, which can then be solved.
-
Solve one equation for one variable: Let's solve the first equation (4x + 2y = 12) for x:
4x = 12 - 2y
x = 3 - 0.5y
-
Substitute into the second equation: Substitute this expression for x into the second equation (4x + 8y = 24):
4(3 - 0.5y) + 8y = 24
12 - 2y + 8y = 24
6y = 12
y = 2
-
Substitute y back to find x: Substitute y = 2 back into the expression for x:
x = 3 - 0.5(2) = 3 - 1 = 2
Again, the solution is x = 2 and y = 2.
Analyzing the Relationship Between the Equations
A closer examination reveals a significant relationship between the two equations. If we divide the second equation (4x + 8y = 24) by 2, we get:
2x + 4y = 12
This is essentially a simplified version of the second equation. This highlights that the second equation is simply a multiple of the first equation. This means that the two lines are parallel and therefore will never intersect at any other point than the solution we found. In a case where one equation is a multiple of the other, this creates linear dependence between the equations, giving us only one unique solution.
Real-World Applications of Simultaneous Equations
Simultaneous equations are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have numerous real-world applications across various fields:
-
Economics: Analyzing supply and demand, determining market equilibrium points, and modeling economic growth.
-
Engineering: Solving structural problems, circuit analysis, and fluid dynamics calculations.
-
Physics: Analyzing forces and motion, determining projectile trajectories, and understanding electrical circuits.
-
Computer Science: Solving optimization problems, analyzing algorithms' efficiency and creating computer graphics.
-
Chemistry: Determining the concentrations of chemical solutions and understanding chemical reactions.
Further Exploration and Extensions
The simple system presented here serves as a foundation for exploring more complex systems of equations. These can involve more variables and more complex relationships. Techniques like matrix algebra and Gaussian elimination provide powerful tools for solving larger systems of equations. These advanced methods are essential in areas like data analysis, machine learning, and scientific modeling.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
Understanding and solving simultaneous equations like 4x + 2y = 12 and 4x + 8y = 24 is crucial for building a solid foundation in mathematics. The graphical, elimination, and substitution methods provide different perspectives and approaches to solving these problems. Recognizing the relationships between equations and understanding the implications of linear dependence are essential for interpreting the results accurately. Moreover, the applications of these concepts extend far beyond the classroom, demonstrating the practical relevance of mathematics in various real-world fields. Mastering these fundamental concepts unlocks the door to solving more complex mathematical challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Do Protists Make Their Own Food
May 09, 2025
-
38 Out Of 60 As A Percentage
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Are In 1 05 Qt
May 09, 2025
-
How To Determine Most Stable Chair Conformation
May 09, 2025
-
A Pair Of Pants With A Marked Price Of 35 00
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4x 2y 12 4x 8y 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.