4 13 20 As A Decimal
listenit
May 25, 2025 · 5 min read
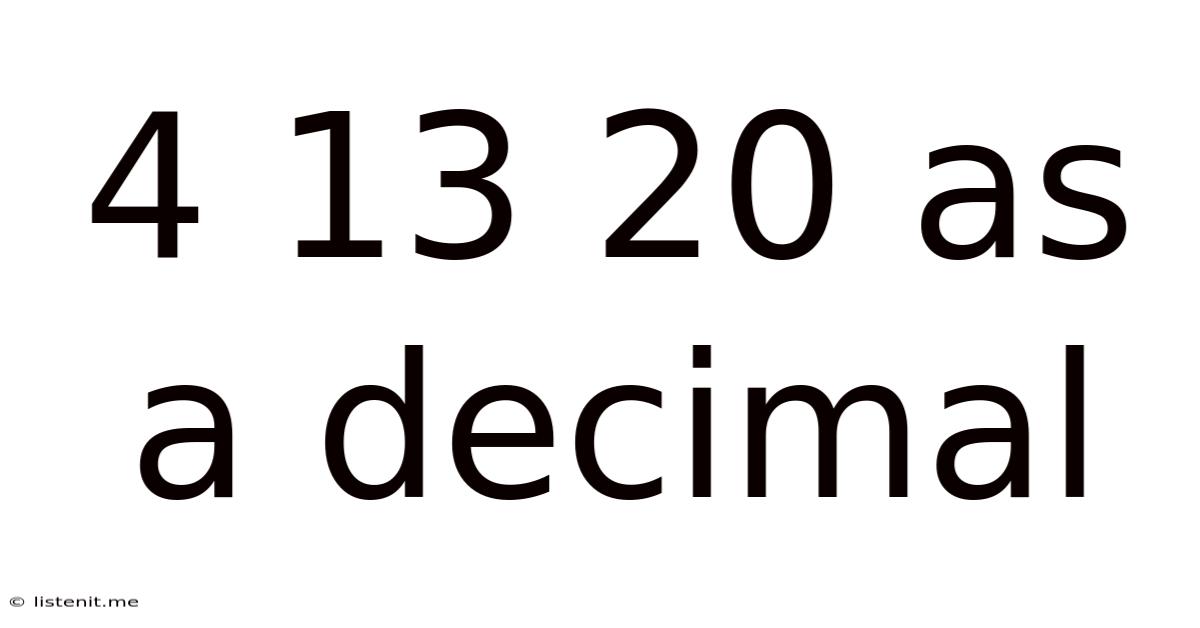
Table of Contents
4 13 20 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide to Mixed Number Conversion
The seemingly simple question of converting the mixed number 4 13/20 into a decimal form unveils a fascinating exploration of mathematical concepts. While the conversion itself is straightforward, understanding the underlying principles and exploring related concepts enhances our grasp of numerical representation. This comprehensive guide will delve into the conversion process, discuss the significance of decimal representation, and explore related mathematical ideas, ensuring a thorough understanding for both beginners and those seeking a deeper understanding.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Decimals
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the terms. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, like 4 13/20. This signifies four whole units plus thirteen twentieths of another unit. A decimal, on the other hand, expresses a number using base-ten notation, where digits to the right of the decimal point represent fractions with denominators of powers of ten (tenths, hundredths, thousandths, etc.).
Converting 4 13/20 to a Decimal: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion of 4 13/20 to a decimal involves two key steps:
Step 1: Convert the Fraction to a Decimal
The fraction 13/20 represents 13 divided by 20. We perform this division:
13 ÷ 20 = 0.65
Therefore, 13/20 is equivalent to 0.65.
Step 2: Combine the Whole Number and the Decimal
Now, we simply combine the whole number part (4) with the decimal equivalent of the fraction (0.65):
4 + 0.65 = 4.65
Therefore, the mixed number 4 13/20 is equal to 4.65 in decimal form.
The Significance of Decimal Representation
The decimal system is fundamental to various aspects of our lives, making the conversion of mixed numbers to decimals a crucial skill. Here are some key reasons why decimal representation holds such significance:
-
Universality and Ease of Use: Decimals provide a standardized and universally understood way to represent fractional values. They are easier to compare and perform calculations with than fractions with diverse denominators.
-
Scientific and Engineering Applications: Decimals are essential in scientific notation, measurements, and calculations across various scientific disciplines and engineering fields. Precision and consistency are vital, and decimals provide the necessary accuracy.
-
Financial Transactions: From calculating the price of goods to managing bank accounts and investments, decimals are integral to all aspects of finance. Interest rates, tax calculations, and currency conversions all rely heavily on decimal representation.
-
Computer Programming: Computers fundamentally operate using binary code, but they handle decimal input and output, making the conversion between decimal and other number systems a cornerstone of computer programming.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: Data analysis and statistical calculations often involve large datasets with fractional values. Decimals make comparisons, analysis, and interpretation of data easier and more efficient.
Expanding on Fractional Concepts: Types of Fractions
To gain a deeper understanding of the conversion process, it's beneficial to explore different types of fractions:
-
Proper Fractions: These fractions have a numerator smaller than the denominator (e.g., 13/20). Their decimal equivalents are always less than 1.
-
Improper Fractions: In these fractions, the numerator is equal to or larger than the denominator (e.g., 20/20 or 25/20). Improper fractions can be converted to mixed numbers or whole numbers.
-
Mixed Numbers: As discussed earlier, mixed numbers combine a whole number and a proper fraction (e.g., 4 13/20).
-
Equivalent Fractions: Different fractions can represent the same value (e.g., 1/2, 2/4, 5/10 are all equivalent to 0.5). Understanding equivalent fractions helps simplify calculations and conversions.
Alternative Methods for Decimal Conversion
While the direct division method is most straightforward for 4 13/20, let's explore alternative approaches:
-
Converting to an Improper Fraction: We can convert 4 13/20 to an improper fraction first: (4 * 20) + 13 = 93, giving us 93/20. Then, dividing 93 by 20 directly yields 4.65.
-
Using a Calculator: Most calculators handle mixed number conversions effortlessly. Simply input the mixed number (4 13/20) and the calculator will display the equivalent decimal (4.65).
-
Long Division: For a deeper understanding of the underlying process, performing long division of 13 by 20 offers a valuable step-by-step visualization of the decimal conversion.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The ability to convert mixed numbers to decimals is crucial in a multitude of real-world scenarios:
-
Measurement Conversions: Converting inches to centimeters, pounds to kilograms, or other unit conversions often involve mixed numbers and require decimal conversion for accuracy.
-
Baking and Cooking: Recipes frequently employ fractional measurements, requiring conversions to decimal forms for easier use with measuring tools.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are paramount, and converting mixed numbers to decimals ensures accuracy in construction projects and engineering designs.
-
Financial Calculations: Interest rates, stock prices, and other financial data often employ decimals, requiring a thorough understanding of conversions from other numerical representations.
-
Data Analysis and Visualization: Many data analysis and visualization tools prefer decimal inputs for smoother processing and more accurate graphical representations.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further Mathematical Concepts
The conversion of 4 13/20 to a decimal lays the foundation for exploring more advanced mathematical topics:
-
Number Systems: This conversion highlights the relationship between different number systems, showing how fractions and decimals represent the same values but use different notations.
-
Approximations and Rounding: When dealing with infinite decimals (like 1/3 = 0.333...), understanding approximation and rounding is essential for practical applications.
-
Algebraic Manipulation: Decimals simplify algebraic manipulation involving fractions, making solving equations and performing calculations more efficient.
-
Calculus and Analysis: Decimals are fundamentally involved in calculus and other advanced mathematical fields, where precision in numerical representation is critical.
-
Computer Science and Algorithms: Efficient algorithms for handling decimal numbers are vital in various computing applications, emphasizing the importance of understanding their underlying structure and operations.
Conclusion: Mastering Decimal Conversions
The seemingly simple conversion of 4 13/20 to 4.65 opens a window into the wider world of mathematics. Understanding the underlying principles, exploring related concepts, and recognizing the significance of decimal representation empowers us to tackle complex calculations and apply these skills in various real-world situations. From baking to engineering, finance to computer science, the ability to convert between fractions and decimals is an invaluable skill for anyone seeking to excel in mathematics and related fields. By mastering this fundamental concept, you build a stronger mathematical foundation and enhance your problem-solving abilities across various disciplines. So, next time you encounter a mixed number, remember the straightforward process and the wider context it represents within the world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 21 And 49
May 26, 2025
-
Tangent Of A Circle Formula Calculator
May 26, 2025
-
Find The Prime Factorization Of 35
May 26, 2025
-
1 In 450 As A Percentage
May 26, 2025
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 32 And 56
May 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4 13 20 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.