4 1/2 As An Improper Fraction
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
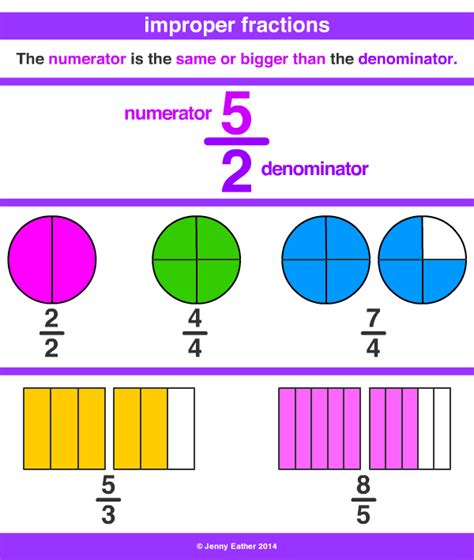
Table of Contents
4 1/2 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, forming the bedrock for more advanced concepts. Mixed numbers, like 4 1/2, and improper fractions are two ways of representing the same quantity. While mixed numbers are easier to visualize (representing a whole number and a fractional part), improper fractions are crucial for various mathematical operations, especially when performing multiplication and division of fractions. This article will delve deep into converting 4 1/2 into an improper fraction, exploring the underlying principles and offering practical examples to solidify your understanding.
What is a Mixed Number?
A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction. For example, 4 1/2 represents four whole units and one-half of another unit. It's a convenient way to represent quantities that aren't whole numbers but are readily understandable in everyday contexts. Think of having four whole pizzas and half of another – that's 4 1/2 pizzas.
What is an Improper Fraction?
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). For instance, 9/2 is an improper fraction because the numerator (9) is larger than the denominator (2). Improper fractions represent values greater than or equal to one. They are essential in simplifying calculations involving fractions.
Converting 4 1/2 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion from a mixed number to an improper fraction is a straightforward process involving two main steps:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, 4 1/2, the whole number is 4, and the denominator is 2. Multiply these together: 4 * 2 = 8
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator in 4 1/2 is 1. Add this to the result from Step 1: 8 + 1 = 9
Step 3: Keep the same denominator.
The denominator remains unchanged throughout the conversion. Therefore, the denominator stays as 2.
Step 4: Combine the results to form the improper fraction.
The result from Step 2 (9) becomes the numerator, and the denominator remains 2. This gives us the improper fraction 9/2.
Therefore, 4 1/2 is equal to 9/2.
Visual Representation of the Conversion
Imagine you have four and a half pizzas. Each pizza is divided into two equal slices. You can represent each whole pizza with 2/2. Therefore, four pizzas are represented by 4 * (2/2) = 8/2. Adding the half pizza (1/2), you get (8/2) + (1/2) = 9/2. This visually demonstrates why 4 1/2 is equivalent to 9/2.
Why is Converting to Improper Fractions Important?
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is crucial for several mathematical operations:
-
Multiplication and Division of Fractions: It's much easier to multiply and divide fractions when they are in improper form. Attempting these operations with mixed numbers can be cumbersome and prone to errors.
-
Simplifying Complex Expressions: In algebraic expressions involving fractions, converting mixed numbers to improper fractions streamlines the simplification process, making it more efficient and less error-prone.
-
Solving Equations: Many equations involving fractions require the use of improper fractions to find solutions accurately and efficiently.
-
Working with Ratios and Proportions: Representing ratios and proportions using improper fractions often leads to simpler and more elegant solutions.
Real-World Applications of Improper Fractions
Improper fractions aren't just confined to the theoretical world of mathematics; they have many practical applications:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes frequently involve fractions, and converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is helpful when scaling recipes up or down. For example, if a recipe calls for 2 1/2 cups of flour and you want to double the recipe, it's much easier to work with the improper fraction 5/2.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are critical in these fields. Improper fractions are frequently used to represent dimensions and quantities for accurate calculations and constructions.
-
Finance and Accounting: Dealing with fractional shares of stocks or percentages often requires using improper fractions for precise calculations.
Further Practice Problems: Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
Here are a few practice problems to solidify your understanding:
-
Convert 3 2/5 to an improper fraction. (Answer: 17/5)
-
Express 1 1/3 as an improper fraction. (Answer: 4/3)
-
Convert 7 3/4 to an improper fraction. (Answer: 31/4)
-
Transform 2 5/8 into an improper fraction. (Answer: 21/8)
-
Express 5 1/6 as an improper fraction. (Answer: 31/6)
Advanced Concepts and Extensions: Working with Negative Mixed Numbers
The principles discussed above also apply to negative mixed numbers. For example, converting -2 1/3 to an improper fraction involves the same steps, but the final result will be a negative improper fraction: -7/3.
Conclusion: Mastering the Conversion
Understanding how to convert mixed numbers to improper fractions is a cornerstone of mathematical proficiency. It simplifies complex calculations, expands your problem-solving abilities, and enhances your understanding of numerical relationships. By mastering this conversion process, you lay a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and real-world applications. Remember the simple steps: multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and keep the same denominator. Practice makes perfect, so keep working through examples and soon you'll find converting mixed numbers to improper fractions second nature. Through consistent practice and understanding of the underlying concepts, you will gain confidence and proficiency in handling fractions, which will benefit you in various aspects of mathematics and beyond. The ability to seamlessly convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions is a skill that will significantly enhance your problem-solving capabilities in numerous mathematical contexts. Remember to always focus on the core steps, and with sufficient practice, you'll be able to master this essential mathematical skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
On The Trip From Detroit To Columbus
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is The Shoulder Distal To The Elbow
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 1 12
Mar 18, 2025
-
Product Of Nacl Hn03 And Na2co3
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is 0 01 As A Fraction
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4 1/2 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
