33 And 1 3 As A Fraction
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
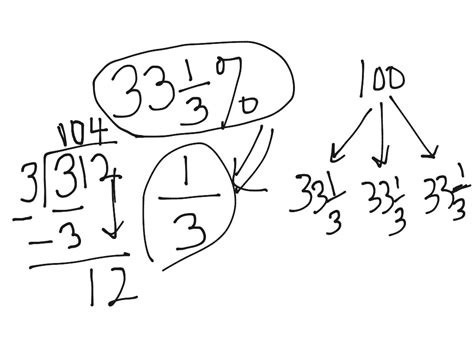
Table of Contents
33 and 1/3 as a Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions is fundamental to mathematics, and converting mixed numbers like "33 and 1/3" into improper fractions is a crucial skill. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process, explore different approaches, and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also touch upon the importance of fractions in various applications.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before we dive into the conversion, let's define our terms. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, like 33 and 1/3. An improper fraction, on the other hand, has a numerator (top number) that is greater than or equal to its denominator (bottom number). For example, 100/3 is an improper fraction. Converting between these forms is essential for various mathematical operations.
Converting 33 and 1/3 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Method
The conversion process is straightforward and involves two simple steps:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
In our example, the whole number is 33 and the denominator of the fraction is 3. Therefore, we multiply 33 by 3:
33 * 3 = 99
Step 2: Add the numerator to the result from Step 1.
The numerator of our fraction is 1. We add this to the result from Step 1:
99 + 1 = 100
Step 3: Write the result as the numerator over the original denominator.
The result from Step 2 (100) becomes the numerator, and the original denominator (3) remains unchanged. This gives us our improper fraction:
100/3
Therefore, 33 and 1/3 is equivalent to 100/3.
Alternative Methods and Visual Representations
While the above method is the most common and efficient, let's explore alternative approaches to solidify understanding and cater to different learning styles.
Visual Representation using Circles
Imagine 33 complete circles, each representing a whole unit, and a third of another circle. To represent this as a single fraction, imagine dividing all 33 circles into thirds. Each circle would then contribute 3 thirds. Therefore, 33 circles would yield 33 * 3 = 99 thirds. Adding the extra 1/3 gives a total of 100 thirds, hence 100/3.
Using Repeated Addition
We can express 33 and 1/3 as repeated addition: 1/3 + 1/3 + 1/3 + ... (33 times) + 1/3. This simplifies to (33 * 1)/3 + 1/3 = 33/3 + 1/3 = (33 + 1)/3 = 100/3. This approach helps visualize the accumulation of fractions to reach the mixed number equivalent.
Importance and Applications of Fractions
Fractions are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they are integral to numerous real-world applications across various fields:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often require precise measurements, frequently expressed as fractions (e.g., 1/2 cup of sugar, 2/3 cup of flour). Understanding fractions ensures accurate recipe execution.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements and calculations are critical in construction and engineering. Fractions are used extensively in blueprints, calculations involving dimensions, and material estimations.
-
Finance and Economics: Fractions are used in calculating interest rates, stock prices, and other financial metrics. Understanding fractional components is essential for accurate financial analysis.
-
Science and Medicine: Scientific experiments and medical dosages often involve precise measurements, where fractions are crucial for ensuring accuracy and preventing errors. For instance, administering medicine in fractional doses is vital.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: Fractions and proportions are fundamental to representing data, calculating probabilities, and interpreting statistical results. Understanding these concepts enables effective data analysis.
Further Exploration of Improper Fractions
Improper fractions, while seemingly more complex than mixed numbers, offer advantages in certain mathematical operations. They simplify calculations involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of fractions. Understanding their conversion to mixed numbers and vice versa allows for flexibility in problem-solving.
Converting Improper Fractions back to Mixed Numbers
Let's reverse the process and convert the improper fraction 100/3 back into a mixed number. This involves:
Step 1: Perform the division.
Divide the numerator (100) by the denominator (3): 100 ÷ 3 = 33 with a remainder of 1.
Step 2: Write the whole number and the remainder as a fraction.
The quotient (33) becomes the whole number. The remainder (1) becomes the numerator of the fraction, and the denominator remains the same (3).
This gives us 33 and 1/3.
Solving Problems with 33 and 1/3
Let's explore some practical applications using 33 and 1/3 (or its equivalent improper fraction, 100/3):
Example 1: Sharing Resources
Imagine you have 100 cookies to share equally among 3 friends. Each friend receives 100/3 cookies, which is equivalent to 33 and 1/3 cookies.
Example 2: Calculating Costs
If a certain item costs $100 and you need to purchase 3 of them, the total cost would be 3 * $100 = $300. If the same item is sold in packages of 3, where each package costs $100/3, the total cost for one package remains the same. This highlights the equivalency between the mixed number and the improper fraction.
Example 3: Measurement Conversions
In construction, you might have a measurement of 100 inches and need to convert it to feet. Since 1 foot equals 12 inches, you divide 100 by 12: 100/12 = 8 and 4/12 = 8 and 1/3 feet. This illustrates how fractions simplify the conversion of units.
Conclusion
Mastering the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics. The ability to seamlessly convert 33 and 1/3 to 100/3, and vice-versa, opens doors to more advanced mathematical operations and problem-solving. By understanding the underlying principles and applying the methods described above, you'll build a strong foundation for tackling complex mathematical challenges in various fields. Remember the visual representations and practical examples to reinforce your comprehension and make the concept more relatable to everyday situations. This understanding will significantly enhance your mathematical proficiency and problem-solving capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Make A 10 Solution
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 14 And 6
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is 36 A Prime Number Or Composite
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Organisms Can Perform Photosynthesis
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Do You Find A Perpendicular Slope
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 33 And 1 3 As A Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
