14v 6 2 5 7v 4
listenit
May 25, 2025 · 5 min read
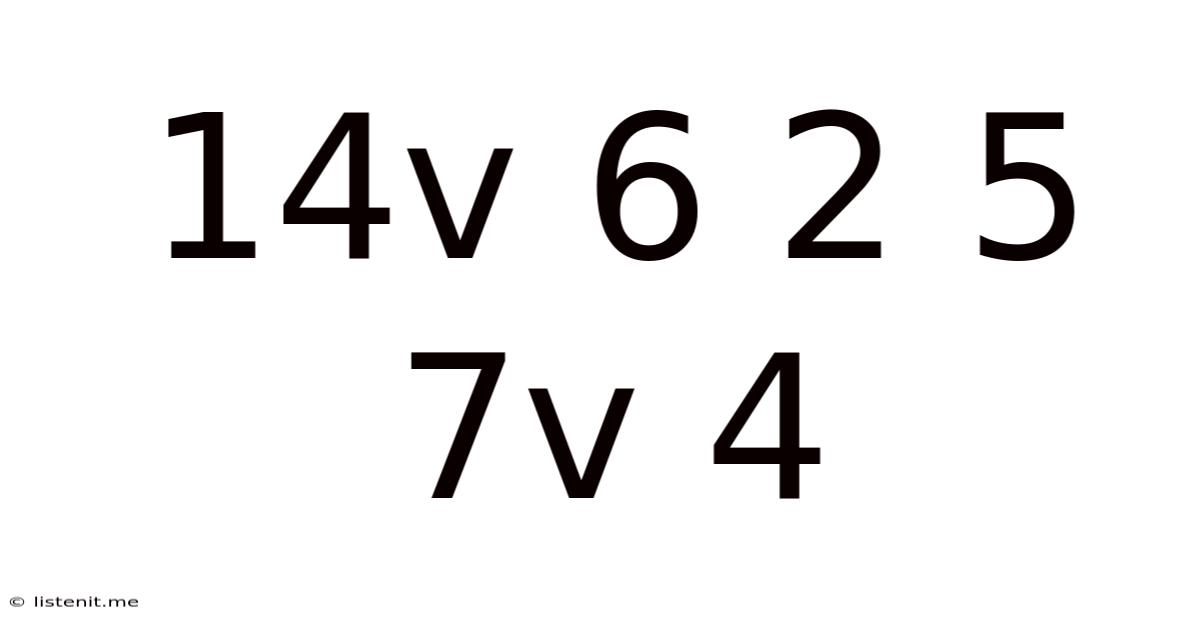
Table of Contents
Decoding 14V, 6, 2, 5, 7V, 4: A Deep Dive into Power, Voltage, and Potential Applications
The seemingly random sequence "14V, 6, 2, 5, 7V, 4" hints at a discussion surrounding voltage, current, and potentially other electrical parameters. While lacking immediate context, this sequence likely represents specifications related to power systems, batteries, or electronic components. Let's explore the possible meanings behind each number and the potential applications they suggest.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Voltage and Current
Before delving into the specifics of the sequence, it's crucial to understand the fundamental concepts of voltage and current. In simple terms:
-
Voltage (V): This is the electrical potential difference between two points. It's the "push" that drives electrons through a circuit. Think of it as the water pressure in a pipe. A higher voltage means a stronger push. The numbers 14V and 7V in our sequence clearly represent voltage values.
-
Current (A): This refers to the rate of flow of electric charge. It's the actual movement of electrons through a circuit. Using the water analogy again, current is the amount of water flowing through the pipe. The units for current are Amperes (A). While not explicitly stated as "A", the numbers 6, 2, 4, and 5 likely represent current ratings, component quantities, or other related parameters.
-
Power (W): Power is the rate at which energy is transferred or converted. It's calculated as the product of voltage and current: Power (W) = Voltage (V) * Current (A). Understanding power is essential for determining the capacity and capabilities of a system.
Interpreting the Sequence: 14V, 6, 2, 5, 7V, 4
Now let's analyze the sequence, considering the possibilities based on electrical engineering principles and common applications:
1. 14V: This voltage is commonly associated with:
- Automotive Systems: Many vehicles operate on a 12V or 14V system. 14V is often the charging voltage of a lead-acid battery while the engine is running.
- Power Tools: Some high-power tools, such as drills and saws, use 14V batteries for increased performance.
- Specialized Electronics: Certain industrial or specialized electronic devices might require 14V for their operation.
2. 6: This number could represent various parameters:
- Number of Components: Perhaps six specific components, such as resistors, capacitors, or transistors, are involved in a circuit.
- Current Rating (Amperes): It could signify a 6-Ampere current limit for a particular component or the maximum current draw of a system.
- Battery Cells: Six battery cells might be connected in series or parallel to achieve a desired voltage and capacity.
3. 2: Similarly to 6, the number 2 could represent:
- Number of Components: Two specific components in a circuit design.
- Current Rating (Amperes): A 2-Ampere current limit for a specific circuit branch.
- Number of Batteries: Two batteries may be used in parallel to increase the overall capacity.
4. 5: Potential interpretations for 5 include:
- Number of Components: Five components in a circuit.
- Current Rating (Amperes): A 5-Ampere current limit.
- Phase Count (AC systems): In AC systems, the number 5 might (though less likely without further information) refer to a five-phase system.
5. 7V: This voltage is lower than 14V and suggests:
- Low-Voltage Systems: Suitable for smaller electronic devices, sensors, or integrated circuits.
- Battery Cells: A battery pack comprising cells that deliver 7V collectively.
- Voltage Regulators: A system might use a voltage regulator to step down from 14V to 7V for particular components needing lower voltage.
6. 4: Similar interpretations as with 2, 5, and 6 exist for the number 4:
- Number of Components: Four components in a circuit.
- Current Rating (Amperes): A 4-Ampere current limit.
- Number of Batteries: Four batteries in a system.
Possible Scenarios and Applications
Combining these interpretations, several plausible scenarios emerge:
Scenario 1: Automotive Battery System
Imagine a vehicle system where:
- 14V: The charging voltage of the main battery.
- 6: Six 2-ampere fuses in the system protecting different circuits.
- 2: Two smaller 12V batteries used for auxiliary systems.
- 5: Five sensors monitoring various parameters.
- 7V: A regulated 7V supply derived from the main battery for a particular component.
- 4: Four power transistors in the main ignition system.
Scenario 2: Power Tool Battery Pack
Consider a power tool's battery pack:
- 14V: The nominal voltage of the battery pack.
- 6: Six battery cells connected in series to achieve 14V.
- 2: Two identical battery packs used in a parallel configuration for longer run time.
- 5: Five LEDs indicating battery charge level.
- 7V: A regulated 7V supply for the control electronics of the tool.
- 4: Four amp-hour battery capacity per cell.
Scenario 3: Industrial Control System
Imagine an industrial control system:
- 14V: The main power supply voltage.
- 6: Six relays controlling different actuators.
- 2: Two separate control units.
- 5: Five sensors feeding data to the control units.
- 7V: A regulated 7V supply for microcontrollers.
- 4: Four input/output modules in the system.
Expanding the Analysis: Considering Additional Parameters
The sequence alone doesn't provide complete information. To fully understand the system, additional parameters would be necessary, including:
- Current ratings (A): Precise current limits for each component.
- Power ratings (W): The maximum power each component can handle.
- Component types: Precise identification of the components (resistors, capacitors, etc.).
- Circuit diagram: A visual representation of how the components are connected.
- Application context: Understanding the intended use of the system.
Without this additional information, it remains challenging to definitively determine the exact meaning of the sequence.
Conclusion: The Importance of Context and Complete Specifications
The "14V, 6, 2, 5, 7V, 4" sequence highlights the importance of comprehensive specifications when discussing electrical systems. While each number might represent different parameters, their true meaning becomes clear only when placed within the proper context. To accurately interpret and design such systems, always refer to complete datasheets, specifications, and diagrams provided by the manufacturer or designer. This detailed information ensures safe and effective implementation, minimizing the risk of errors and malfunctions. The absence of sufficient information often leads to inaccurate interpretation and the potential for safety hazards. Always prioritize complete and precise documentation in all electrical projects.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Born July 1982 How Old Am I
May 25, 2025
-
Solve For X In A Triangle Geometry
May 25, 2025
-
2 To The Power Of 55
May 25, 2025
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 15 And 24
May 25, 2025
-
1 Hour And 42 Minutes From Now
May 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 14v 6 2 5 7v 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.