1/2 Divided By Root 3 Over 2
listenit
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
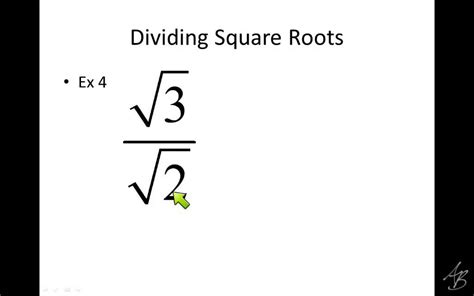
Table of Contents
Decoding 1/2 Divided by √3/2: A Deep Dive into Mathematical Operations
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the mathematical expression "1/2 divided by √3/2," covering its simplification, practical applications, and connections to broader mathematical concepts. We'll delve into the step-by-step process, addressing potential areas of confusion and highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying principles. The goal is not just to solve the problem, but to build a solid foundation for tackling similar fractional and radical expressions.
Understanding the Problem: Fractional Division and Radicals
Before diving into the solution, let's clarify the components of the expression: 1/2 ÷ √3/2. This involves two key mathematical elements:
-
Fractions: These represent parts of a whole, expressed as a numerator (top number) divided by a denominator (bottom number). In our expression, we have two fractions: 1/2 and √3/2.
-
Radicals (specifically, square roots): A square root (√) finds a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number under the radical sign (radicand). Here, we have √3, which represents the square root of 3. It's an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
The problem asks us to divide one fraction (1/2) by another (√3/2). This necessitates an understanding of fractional division.
Step-by-Step Solution: Simplifying the Expression
The division of fractions can be simplified by multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. The reciprocal is simply the fraction flipped upside down. Let's break this down:
1. Find the reciprocal of the second fraction:
The reciprocal of √3/2 is 2/√3.
2. Rewrite the division as multiplication:
1/2 ÷ √3/2 becomes 1/2 × 2/√3
3. Simplify the multiplication:
Notice that the '2' in the numerator of the second fraction cancels out with the '2' in the denominator of the first fraction. This leaves us with:
1/√3
4. Rationalize the denominator:
In mathematics, it's generally preferred to have a rational number (a number that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers) in the denominator. To achieve this, we need to rationalize the denominator. We multiply both the numerator and the denominator by √3:
(1 × √3) / (√3 × √3) = √3 / 3
Therefore, the simplified answer is √3/3.
Alternative Methods: Exploring Different Approaches
While the above method is straightforward, alternative approaches can provide valuable insight and enhance mathematical understanding. Let's explore a couple of them:
Method 1: Converting to Decimals (Approximate Solution):
We can approximate the solution by converting the fractions and radical to decimal values. Keep in mind this provides an approximate answer, not the exact value:
1/2 ≈ 0.5
√3/2 ≈ 0.866
0.5 ÷ 0.866 ≈ 0.577
Now, let's compare this to the decimal approximation of our simplified answer (√3/3):
√3/3 ≈ 0.577
This confirms the accuracy of our earlier simplification. However, it's crucial to remember that using decimal approximations introduces a degree of error and should be avoided when precision is paramount.
Method 2: Working with Radicals Directly:
Another approach involves manipulating the radicals directly. Let's revisit step 3 of our initial solution:
1/2 × 2/√3
We could have also simplified this by canceling out the 2's before rationalizing:
1/√3
Then rationalize:
√3/3
Connecting to Broader Mathematical Concepts
This seemingly simple problem touches upon several crucial areas of mathematics:
-
Rational and Irrational Numbers: The problem highlights the distinction between rational numbers (like 1/2 and √3/3 after rationalization) and irrational numbers (like √3).
-
Real Numbers: All the numbers involved in this problem (including the irrational √3) belong to the set of real numbers.
-
Field Axioms: The operations performed (division and multiplication) are governed by the field axioms, which define the fundamental properties of arithmetic operations on real numbers. For instance, the commutative property of multiplication allows us to change the order of multiplication without changing the outcome.
-
Trigonometry: This simplified expression, √3/3, is frequently encountered in trigonometry, often representing trigonometric ratios for specific angles. For instance, it’s closely related to the tangent of 30 degrees (π/6 radians).
Practical Applications: Where This Matters
Understanding the simplification of fractional and radical expressions, such as the one we've analyzed, is essential in numerous fields:
-
Physics: Many physics formulas involve fractions and radicals, representing quantities like velocity, acceleration, or forces. Simplifying such expressions is crucial for accurate calculations and problem-solving.
-
Engineering: Similar to physics, engineering applications often rely on precise calculations involving fractions and radicals in design, construction, and analysis.
-
Computer Science: While seemingly abstract, these mathematical concepts are fundamental to algorithms and computations in computer science.
-
Finance: Calculations involving interest rates, compound growth, and other financial concepts often require manipulating fractional and radical expressions.
Conclusion: Mastering Fractional and Radical Operations
Solving "1/2 divided by √3/2" is not merely about arriving at the answer √3/3. It's about mastering the underlying principles of fractional division, radical simplification, and rationalization. Understanding these concepts is foundational for success in various academic and professional fields. The techniques discussed—using reciprocals, rationalizing denominators, and exploring alternative approaches—are valuable tools for tackling more complex mathematical problems involving fractions and radicals. By mastering these skills, you significantly enhance your mathematical prowess and ability to solve real-world problems across diverse disciplines. The emphasis should always be on understanding why a particular step is taken, not just how it is done. This deeper understanding allows for flexibility and adaptability when faced with similar but potentially more challenging expressions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Range Of Function Algebraically
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is 1 2 3 4
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Type Of Rock Are Fossils Mostly Found In
Mar 30, 2025
-
During Which Phase Of Meiosis Do Homologous Chromosomes Separate
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes Do Daughter Cells Have After Mitosis
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1/2 Divided By Root 3 Over 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
